|
Pasterze Mit Großglockner
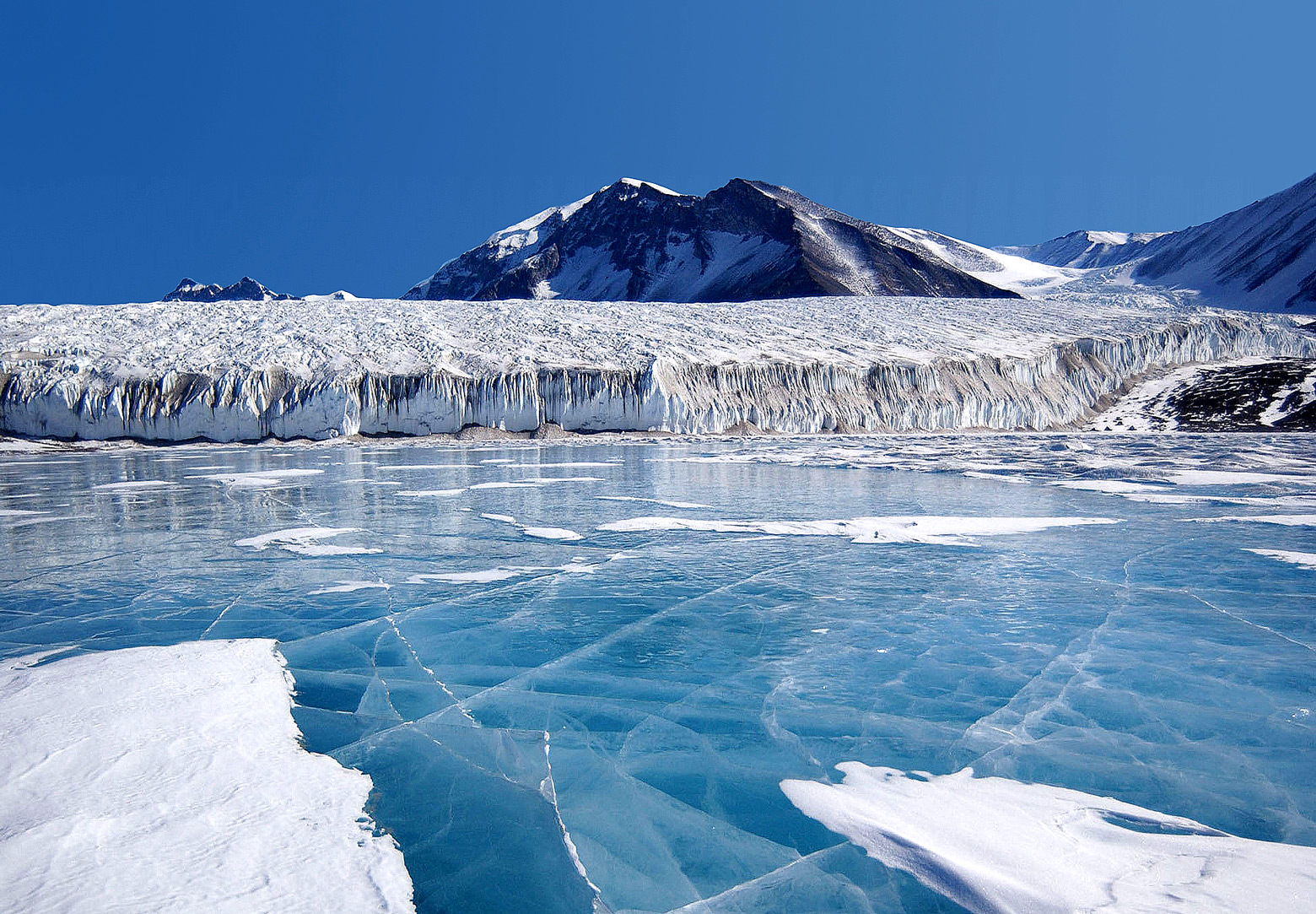
The Pasterze, at approximately 8.4 kilometres (5.2 mi) in length, is the longest glacier in Austria and in the Eastern Alps. It lies within the Glockner Group of the High Tauern mountain range in Carinthia, directly beneath Austria's highest mountain, the Grossglockner. Geography The glacier reaches from its head, the Johannisberg peak at , to above sea level ( m AA). The Pasterze forms the source region of the Möll river, a left tributary of the Drava. Its waters also feed the Margaritze reservoir, used to generate electricity at the Kaprun hydropower plant north of the Alpine crest. The name ''Pasterze'' is possibly derived from , "pasture". Indeed the detection of wood, peat and pollen in the area of the retreating glacier indicate vegetation and also the use as pastureland during the last interglacial period until about 1,500 BC. The surrounding area was purchased by the German and Austrian Alpine Club in 1918; today the glacier is part of the High Tauern Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grossglockner
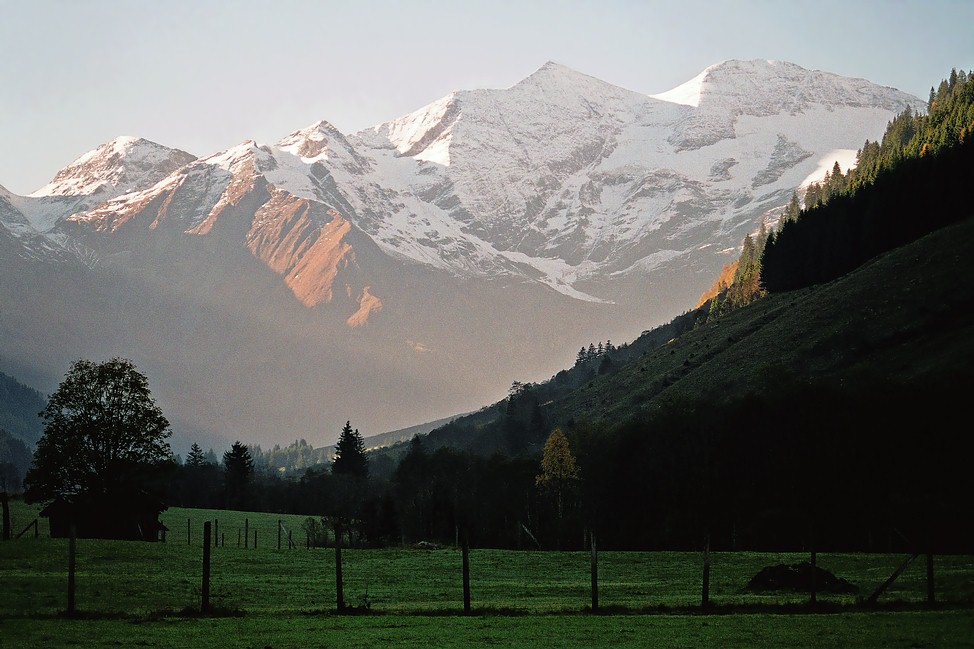
The Großglockner ( ), or just Glockner, is, at 3,798 metres above the Adriatic (12,461 ft), the highest mountain in Austria and highest mountain in the Alps east of the Brenner Pass. It is part of the larger Glockner Group of the Hohe Tauern range, situated along the main ridge of the Central Eastern Alps and the Alpine divide. The Pasterze, Austria's most extended glacier, lies on the Grossglockner's eastern slope. The characteristic pyramid-shaped peak actually consists of two pinnacles, the ''Großglockner'' and the Kleinglockner (, from German: ''groß'' 'big', ''klein'' 'small'), separated by the ''Glocknerscharte'' col. Etymology The name ''Glocknerer'' is first documented in a 1561 map designed by the Viennese cartographer Wolfgang Lazius. The denotation ''Glogger'' is mentioned in a 1583 description of the Tyrolean Kals legal district, then referring to the whole ridge south of the Alpine main chain. In the 1760s, the ''Atlas Tyrolensis'' listed a ''Glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaprun
Kaprun () is a municipality in the Zell am See District in the province of Salzburg (state), Salzburg in Austria. Together with the neighboring city of Zell am See the town presents itself as the tourist destination and skiing area "Zell am See-Kaprun". Kaprun distinguishes itself from its larger neighbor at the lake, by offering all year access to the Kitzsteinhorn with its Top of Salzburg viewing platform at altitude and its glacier ski area that is open October through May. Geography It is located in the Pinzgau region on the northern slopes of the Alpine Glockner Group with Mt. Großes Wiesbachhorn, , part of the Hohe Tauern range, forming the border of Salzburg with Carinthia (state), Carinthia. Located at the foot of the Kitzsteinhorn glacier, Kaprun is a year-round sports center. The Kapruner Ache creek joins the Salzach River south of the settlement. The Mooserboden hydroelectric plant uses water from two reservoirs held back by some of Austria's largest dam walls. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Carinthia
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers Of Austria
A glacier ( ) or () is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight; it forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation (melting and sublimation) over many years, often centuries. Glaciers slowly deform and flow due to stresses induced by their weight, creating crevasses, seracs, and other distinguishing features. Because glacial mass is affected by long-term climate changes, e.g., precipitation, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are considered among the most sensitive indicators of climate change. There are about 198,000 to 200,000 glaciers in the world. Catalogs of glaciers include:World Glacier Inventory* World Glacier Monitoring ServiceGlobal Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) Glacier Database Glaciers by continent ...
|
Effects Of Global Warming
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an overall warming trend, changes to precipitation patterns, and more extreme weather. As the climate changes it impacts the natural environment with effects such as more intense forest fires, thawing permafrost, and desertification. These changes impact ecosystems and societies, and can become irreversible once tipping points are crossed. Climate activists are engaged in a range of activities around the world that seek to ameliorate these issues or prevent them from happening. The effects of climate change vary in timing and location. Up until now the Arctic has warmed faster than most other regions due to climate change feedbacks. Surface air temperatures over land have also increased at about twice the rate they do over the ocean, causing intense heat waves. These temperatures would stabilize if greenhouse gas emissions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retreat Of Glaciers Since 1850
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is a well-documented effects of climate change, effect of climate change. The retreat of Mountain glacier, mountain glaciers provides evidence for the Instrumental temperature record, rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. Examples include mountain glaciers in western North America, Asia, Alps, the Alps in central Europe, and tropical and subtropical regions of South America and Africa. Since glacial mass is affected by long-term climatic changes, e.g. Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, Temperature, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are one of the most sensitive indicators of climate change. The retreat of glaciers is also a major reason for sea level rise. Excluding peripheral glaciers of Ice sheet, ice sheets, the total cumulated global glacial losses over the 26 years from 1993 to 2018 were likely 5500 gigatons, or 210 gigatons per year.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers
A glacier ( ) or () is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight; it forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation (melting and sublimation) over many years, often centuries. Glaciers slowly deform and flow due to stresses induced by their weight, creating crevasses, seracs, and other distinguishing features. Because glacial mass is affected by long-term climate changes, e.g., precipitation, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are considered among the most sensitive indicators of climate change. There are about 198,000 to 200,000 glaciers in the world. Catalogs of glaciers include:World Glacier Inventory* World Glacier Monitoring ServiceGlobal Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) Glacier Database Glaciers by continent
|
Grossglockner High Alpine Road
The Grossglockner High Alpine Road (in German ''Großglockner Hochalpenstraße'') is the highest surfaced mountain pass road in Austria. It connects Bruck in the state of Salzburg with Heiligenblut in Carinthia via Fuscher Törl at 2,428 m (7,966 ft) and Hochtor Pass at . The road is named after the Grossglockner, Austria's highest mountain. Built as a scenic route, a toll is charged. Course The road leads from Bruck in the Salzach Valley via the northern toll booth at Ferleiten (near Fusch) with numbered hairpin curves up to Hochtor Pass, with a branch-off from Fuscher Törl at to the ''Edelweißspitze'' viewpoint at 2,571 m (8,435 ft). The scenic route crosses the Alpine divide in a tunnel and runs southwards passing another branch-off which leads to the ''Glocknerhaus'' mountain hut and the Kaiser-Franz-Josefs-Höhe visitors' centre at . The popular overlook was named after a visit by Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria and his consort Elisabeth i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Parks Of Austria
Austria has six national parks, all of them internationally accepted according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, IUCN standard. The first national park, Hohe Tauern, was established in 1981. They include each of Austria's most important natural landscape types — Alluvium, alluvial forest, Eastern Alps, Alpine massif, Pannonian Basin, Pannonian steppe and rocky valleys. Development First plans for the protection of the Hohe Tauern mountain range were evolved by Austrian Alpine Club, which in 1915-18 acquired large mountainous areas. However, the national park project was abandoned in the late 1930s and not resumed until 1971, when the States of Austria, federal states of Salzburg (state), Salzburg, Tyrol (state), Tyrol and Carinthia signed the Heiligenblut am Großglockner, Heiligenblut Agreement, followed by similar initiatives in Lower Austria, Lower and Upper Austria. The establishment of each national park took several years; as conflicts of use and the q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German And Austrian Alpine Club
The German and Austrian Alpine Club (, DuÖAV) was a merger of the German, Austrian and German Bohemian Alpine Club that existed from 1873 to 1938. History In 1862 the ''Sektion Austria'' was founded in Vienna by the academics Paul Grohmann, Friedrich Simony and Edmund von Mojsisovics. It was the first mountaineering club on the continent, modelled on the London Alpine Club. About seven years later, the Austrian mountaineer Franz Senn founded the '' Bildungsbürgerlicher Bergsteigerverein'' in Munich. Both organisations merged in 1873 to form the German and Austrian Alpine Club. The main organisation consisted of numerous legally independent sections responsible for the upkeep of Alpine club huts and footpaths. In 1918 the DuÖAV purchased about of land at the Pasterze Glacier of the Grossglockner massif, which became the nucleus of the present-day High Tauern National Park. From the mid-1920s the club placed an increased focus on environmental concerns of the high mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
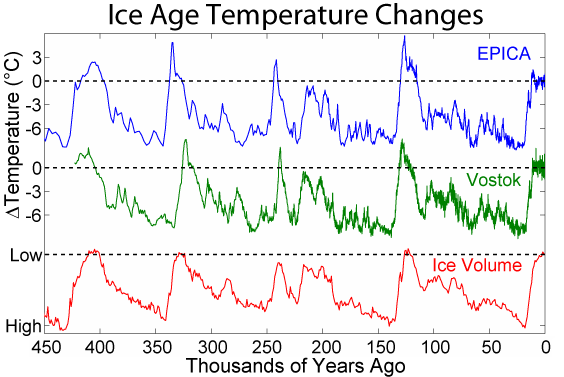
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Chain Of The Alps
The main chain of the Alps, also called the Alpine divide is the central line of mountains that forms the drainage divide of the range. Main chains of mountain ranges are traditionally designated in this way, and generally include the highest pyramidal peak, peaks of a range. The Alps are something of an unusual case in that several significant groups of mountains are separated from the main chain by sizable distances. Among these groups are the Dauphine Alps, the Eastern and Western Graian Alps, Graians, the entire Bernese Alps, the Tödi, Albula Range, Albula and Silvretta groups, the Ortler and Adamello ranges, and the Dolomites of Veneto and South Tyrol, as well as the lower Alps of Vorarlberg, Bavaria, and Salzburg (state), Salzburg. Main features The Alpine Divide is defined for much of its distance by the watershed between the drainage basin of the Po (river), Po in Italy on one side, with the other side of the divide being formed by the Rhone, the Rhine and the Danube. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |