 |
Parsnip
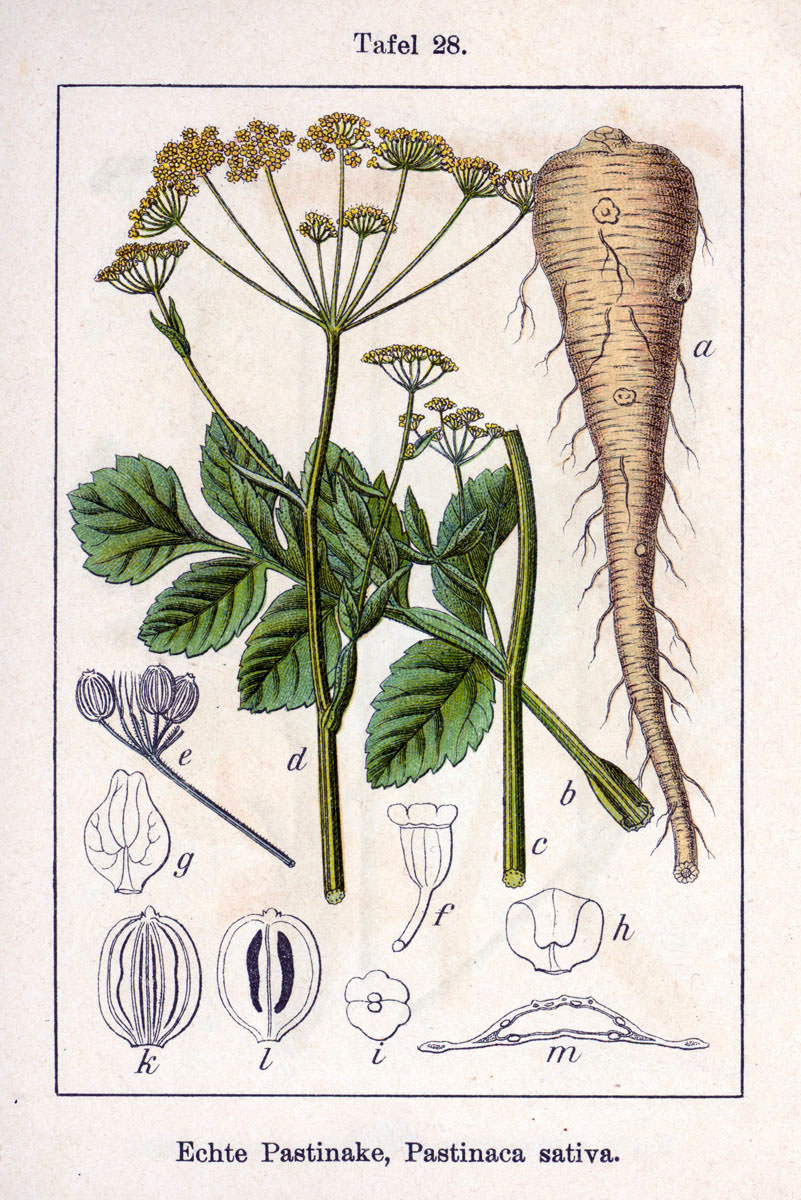
The parsnip (''Pastinaca sativa'') is a root vegetable closely related to carrot and parsley, all belonging to the flowering plant family Apiaceae. It is a biennial plant usually grown as an annual. Its long taproot has cream-colored skin and flesh, and, left in the ground to mature, becomes sweeter in flavor after winter frosts. In its first growing season, the plant has a rosette of pinnate, mid-green leaves. If unharvested, it produces a flowering stem topped by an umbel of small yellow flowers in its second growing season, later producing pale brown, flat, winged seeds. By this time, the stem has become woody, and the taproot inedible. Precautions should be taken when handling the stems and foliage, as parsnip sap can cause a skin rash or even blindness if exposed to sunlight after handling. The parsnip is native to Eurasia; it has been used as a vegetable since antiquity and was cultivated by the Romans, although some confusion exists between parsnips and carrots i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Parsnip Flowering Second Year, June 2016
The parsnip (''Pastinaca sativa'') is a root vegetable closely related to carrot and parsley, all belonging to the flowering plant family Apiaceae. It is a biennial plant usually grown as an Annual plant, annual. Its long taproot has cream-colored skin and flesh, and, left in the ground to mature, becomes sweeter in flavor after winter frosts. In its first growing season, the plant has a rosette (botany), rosette of pinnate, mid-green leaves. If unharvested, it produces a flowering stem topped by an umbel of small yellow flowers in its second growing season, later producing pale brown, flat, winged seeds. By this time, the stem has become woody, and the taproot inedible. Precautions should be taken when handling the stems and foliage, as parsnip sap can cause a skin rash or even blindness if Photosensitivity, exposed to sunlight after handling. The parsnip is native to Eurasia; it has been used as a vegetable since Classical antiquity, antiquity and was cultivated by Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pastinaca Sativa MHNT
''Pastinaca'' (parsnips) is a genus of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, comprising 14 species. Economically, the most important member of the genus is '' Pastinaca sativa'', the parsnip. Etymology The etymology of the generic name ''Pastinaca'' is not known with certainty. The name may be derived from the Latin word ''pastino'' (or ''pastinare''), meaning "to prepare the ground for planting of the vine" (or more simply, "to dig") or the Latin word ''pastus'', meaning "food", liberally translated as "Earth-food". Taxonomy , Plants of the World Online Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online taxonomic database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. History Following the Convention on Biological Diversity, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew launched Plants of the World Online i ... accepted 15 species: *'' Pastinaca argyrophylla'' Delip. *'' Pastinaca armena'' Fisch. & C.A.Mey. *'' Pastinaca aurantiaca'' (Albov) Kolak. *'' Pastinaca clausii'' (Ledeb.) Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Apiaceae
Apiaceae () or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus ''Apium,'' and commonly known as the celery, carrot, or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering plants, with more than 3,800 species in about 446 genus, genera,Stevens, P.F. (2001 onwards).APIACEAE Lindley, nom. cons. ''Angiosperm Phylogeny Website''. Retrieved 16 December 2022. including such well-known, and economically important plants as ajwain, angelica, anise, Ferula assa-foetida, asafoetida, caraway, carrot, celery, chervil, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, lovage, cow parsley, parsley, parsnip and Eryngium maritimum, sea holly, as well as Silphium (antiquity), silphium, a plant whose exact identity is unclear and which may be extinct. The family Apiaceae includes a significant number of phototoxic species, such as giant hogweed, and a smaller number of highly poisonous species, such as Conium maculatum, poison hemlock, Cicuta, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Root Vegetable
Root vegetables are underground plant parts eaten by humans or animals as food. In agricultural and culinary terminology, the term applies to true roots, such as taproots and root tubers, as well as non-roots such as bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and stem tubers. Potatoes are technically not roots, and sweet potatoes are a type of root called tuberous roots. Description Root vegetables are generally storage organs, enlarged to store energy in the form of carbohydrates. They differ in the concentration and balance of starches, sugars, and other carbohydrates. List of root vegetables The following list classifies root vegetables organized by their roots' anatomy. Modified plant stem * Corm **'' Amorphophallus konjac'' (konjac) ** ''Colocasia esculenta'' (taro) ** ''Eleocharis dulcis'' (Chinese water chestnut) ** ''Ensete'' spp. (enset) ** '' Nymphaea'' spp. (waterlily) ** '' Pteridium esculentum'' ** ''Sagittaria'' spp. (arrowhead or wapatoo) ** ''Typha spp. ** '' Xanthosoma'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
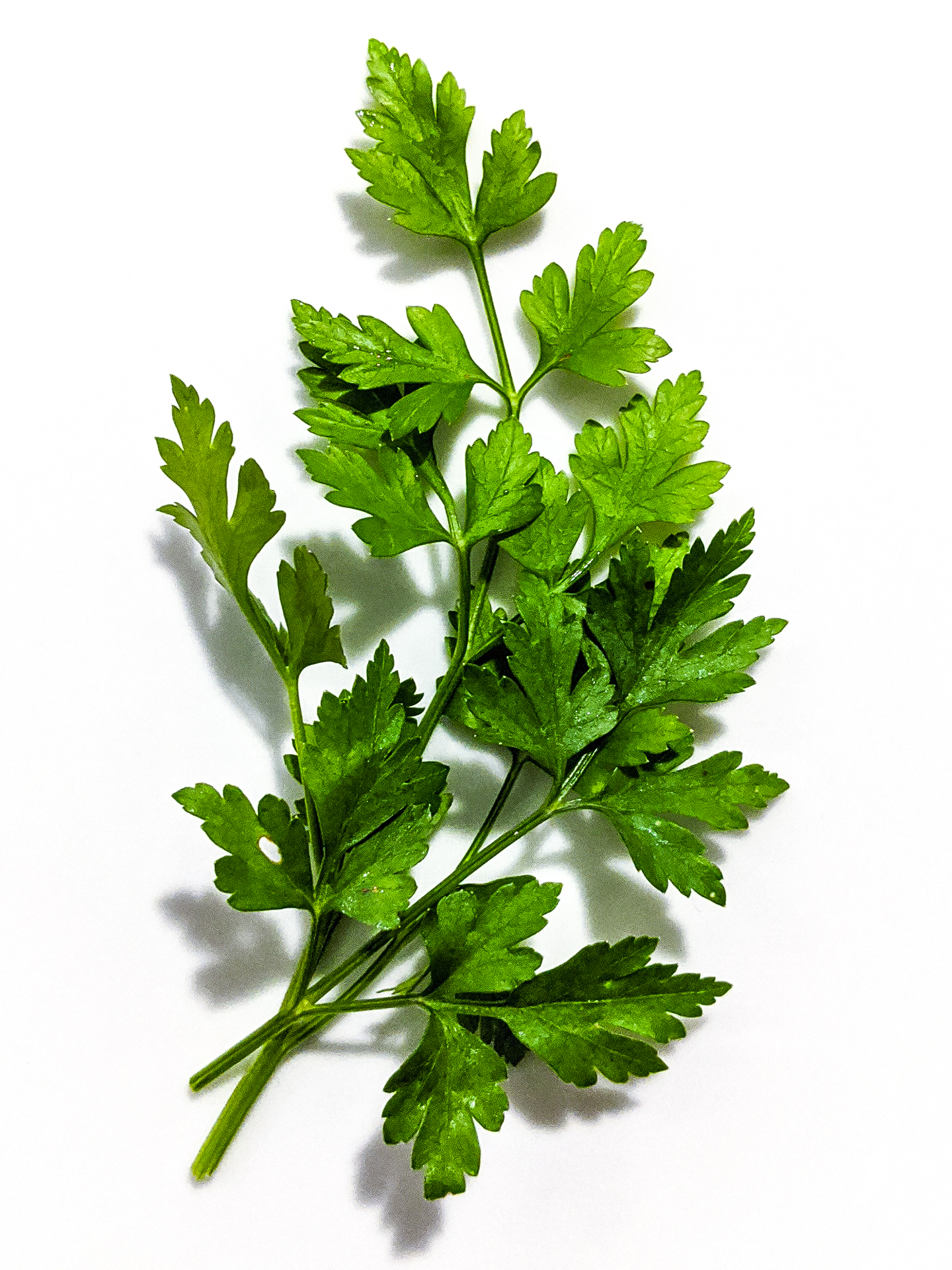 |
Parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum''), is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to Greece, Morocco and the former Yugoslavia. It has been introduced and naturalisation (biology), naturalized in Europe and elsewhere in the world with suitable climates, and is widely cultivated as an herb and a vegetable. It is believed to have been originally grown in Sardinia, and was cultivated in around the 3rd century BC. Linnaeus stated its wild habitat to be Sardinia, whence it was brought to England and apparently first cultivated in Britain in 1548, though literary evidence suggests parsley was used in England in the Middle Ages as early as the Anglo-Saxon period. Parsley is widely used in European cuisine, European, Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern, and American cuisine. Curly-leaf parsley is often used as a garnish (food), garnish. In Central European cuisine, central Europe, Eastern European cuisine, eastern Europe, and southern Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. The group was formerly called Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms are by far the most diverse group of Embryophyte, land plants with 64 Order (biology), orders, 416 Family (biology), families, approximately 13,000 known Genus, genera and 300,000 known species. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody Plant stem, stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. Angiosperms are distinguished from the other major seed plant clade, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Taproot
A taproot is a large, central, and dominant root from which other roots sprout laterally. Typically a taproot is somewhat straight and very thick, is tapering in shape, and grows directly downward. In some plants, such as the carrot, the taproot is a storage organ so well developed that it has been cultivated as a vegetable. The taproot system contrasts with the adventitious- or fibrous-root system of plants with many branched roots, but many plants that grow a taproot during germination go on to develop branching root structures, although some that rely on the main root for storage may retain the dominant taproot for centuries—for example, ''Welwitschia''. Description Dicots, one of the two divisions of flowering plants (angiosperms), start with a taproot, which is one main root forming from the enlarging radicle of the seed. The tap root can be persistent throughout the life of the plant but is most often replaced later in the plant's development by a fibrous root system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, Essential nutrients cannot be biosynthesis, synthesized in the organism in sufficient quantities for survival, and therefore must be obtained through the Diet (nutrition), diet. For example, vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others; it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance but is in the second. Most vitamins are not single molecules, but groups of related molecules called vitamers. For example, there are eight vitamers of vitamin E: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The term ''vitamin'' does not include the three other groups of essential nutrients: mineral (nutrient), minerals, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. Major health organizations list thirteen vitamins: * Vitamin A (all-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Foods are also treated with antioxidants to prevent Food spoilage, spoilage, in particular the rancidification of Vegetable oil, oils and fats. In Cell (biology), cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol, or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, inhibit damage from oxidative stress. Known diet (nutrition), dietary antioxidants are vitamins vitamin A, A, vitamin C, C, and vitamin E, E, but the term has also been applied to various compounds that exhibit antioxidant properties in vitro, having little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Dietary Mineral
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element. Some "minerals" are essential for life, but most are not. ''Minerals'' are one of the four groups of essential nutrients; the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. The five major minerals in the human body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and magnesium. The remaining minerals are called " trace elements". The generally accepted trace elements are iron, chlorine, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, iodine, selenium, and bromine; there is some evidence that there may be more. The four organogenic elements, namely carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen ( CHON), that comprise roughly 96% of the human body by weight, are usually not considered as minerals (nutrient). In fact, in nutrition, the term "mineral" refers more generally to all the other functional and structural elements found in living organisms. Plants obtain minerals from soil. Animals ingest plants, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |