|
Paratungstate
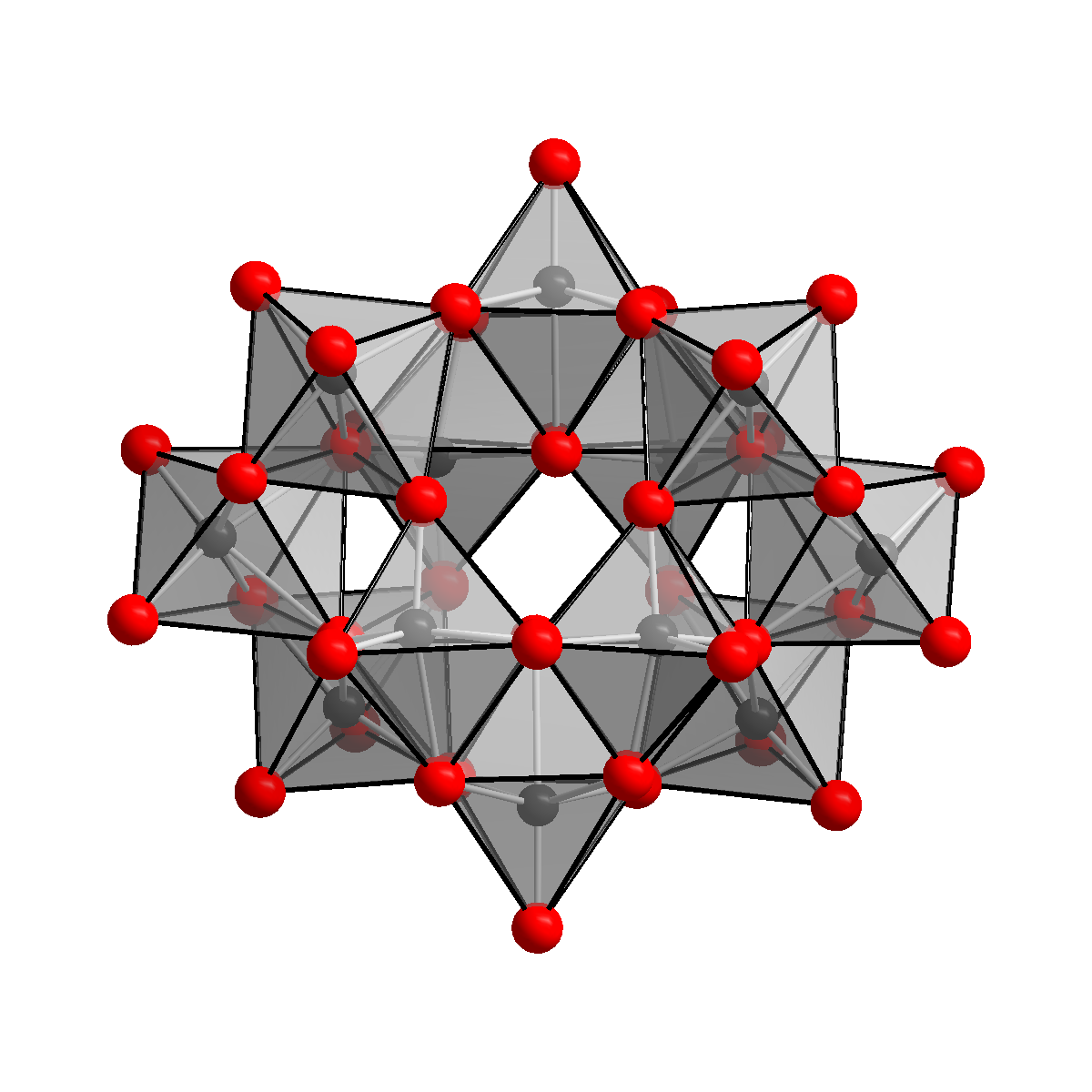
In chemistry, paratungstate refers to the anion with the formula [W12O42]12- and salts derived from this anion. The term also refers to protonated derivatives of this anion, including [H2W12O42]10-. Ammonium paratungstate (or APT), (NH4)10[H2W12O42] is a key intermediate in the purification of tungsten from its ores. The salt (NH4)10(W12O42)·4H2O has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The unprotonated anion [W12O42]12- has C2h symmetry group, symmetry. See also * Metatungstate [W12O40]8-, with idealized Td symmetry. References {{Authority control Tungstates Transition metal oxyanions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatungstate
In chemistry, metatungstate refers to the anion with the formula 12O40sup>8- and salts derived from this anion. The term also refers to protonated derivatives of this anion, including 2W12O40sup>6-. The unprotonated anion 12O40sup>12- has Td symmetry. See also * Paratungstate In chemistry, paratungstate refers to the anion with the formula 12O422- and salts derived from this anion. The term also refers to protonated derivatives of this anion, including 2W12O420-. Ammonium paratungstate (or APT), (NH4)10 2W12O42 ... [W12O42sup>12-, with idealized C2h symmetry. References {{Authority control Tungstates Transition metal oxyanions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Paratungstate
Ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is a white crystalline salt with the chemical formula (NH4)10(H2W12O42)·4H2O. It is described as "the most important raw material for all other tungsten products." Production From tungsten ores Tungsten ores, which are typically oxides, are digested in base to give solutions of tungstate together with many contaminating species. This crude extract is acidified and treated with sulfide Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds lar ... to separate molybdenum trisulfide. Upon further acidification APT eventually crystallizes. Laboratory methods If a calcined WO3 is used, refluxing the ammonia solution is advisable to accelerate its dissolution. Conversion to tungsten metal Heating ammonium paratungstate to its decomposition temperature of 600& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Group
In group theory, the symmetry group of a geometric object is the group of all transformations under which the object is invariant, endowed with the group operation of composition. Such a transformation is an invertible mapping of the ambient space which takes the object to itself, and which preserves all the relevant structure of the object. A frequent notation for the symmetry group of an object ''X'' is ''G'' = Sym(''X''). For an object in a metric space, its symmetries form a subgroup of the isometry group of the ambient space. This article mainly considers symmetry groups in Euclidean geometry, but the concept may also be studied for more general types of geometric structure. Introduction We consider the "objects" possessing symmetry to be geometric figures, images, and patterns, such as a wallpaper pattern. For symmetry of physical objects, one may also take their physical composition as part of the pattern. (A pattern may be specified formally as a scalar field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |