|
Panzer Leader (book)
''Panzer Leader'' (original , literally "Memories of a Soldier") is an autobiography by German General Heinz Guderian, written during his imprisonment by the Allies after the Second World War. The most prominent English language version is the 1952 translation by Constantine Fitzgibbon published in the United Kingdom by Michael Joseph and the United States by E. P. Dutton, with a foreword by B. H. Liddell Hart. The Da Capo Press editions have an additional introduction by Kenneth Macksey. ''Panzer Leader'' and its subsequent editions sold over 180,000 copies worldwide by the 1970s. It eventually reached its 18th printing in Germany in 2003. Themes ''Panzer Leader'' acted as a memoir for Guderian to provide insight to various events that Guderian was involved in before and during the Second World War, providing his own comments and thoughts for each event. The most prominent themes discussed by Guderian are his involvement in the creation of Germany's armoured forces in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian (; 17 June 1888 – 14 May 1954) was a German general during World War II who later became a successful memoirist. A pioneer and advocate of the "blitzkrieg" approach, he played a central role in the development of the panzer division concept. After serving in the military since leaving school, including in World War I, in 1936, he became the Inspector of Motorized Troops. At the beginning of World War II, Guderian led an Panzer corps, armoured corps in the Invasion of Poland. During the Battle of France, Invasion of France, he commanded the armoured units that attacked through the Ardennes forest and overwhelmed the Allied defenses at the Battle of Sedan (1940), Battle of Sedan. He led the 2nd Panzer Army during Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union. The campaign ended in failure after the German offensive Operation Typhoon failed to capture Moscow, and after a disagreement with Hitler, Guderian was dismissed. In early 1943, Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands) and French Third Republic, France. The plan for the invasion of the Low Countries and France was called (Case Yellow or the Manstein plan). (Case Red) was planned to finish off the French and British after the Dunkirk evacuation, evacuation at Dunkirk. The Low Countries and France were defeated and occupied by Axis troops down to the Demarcation line (France), Demarcation line. On 3 September 1939, French declaration of war on Germany (1939), France and United Kingdom declaration of war on Germany (1939), Britain declared war on Nazi Germany, over the German invasion of Poland on 1 September. In early September 1939, the French army began the limited Saar Offensive but by mid-October had withdrawn to the start line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
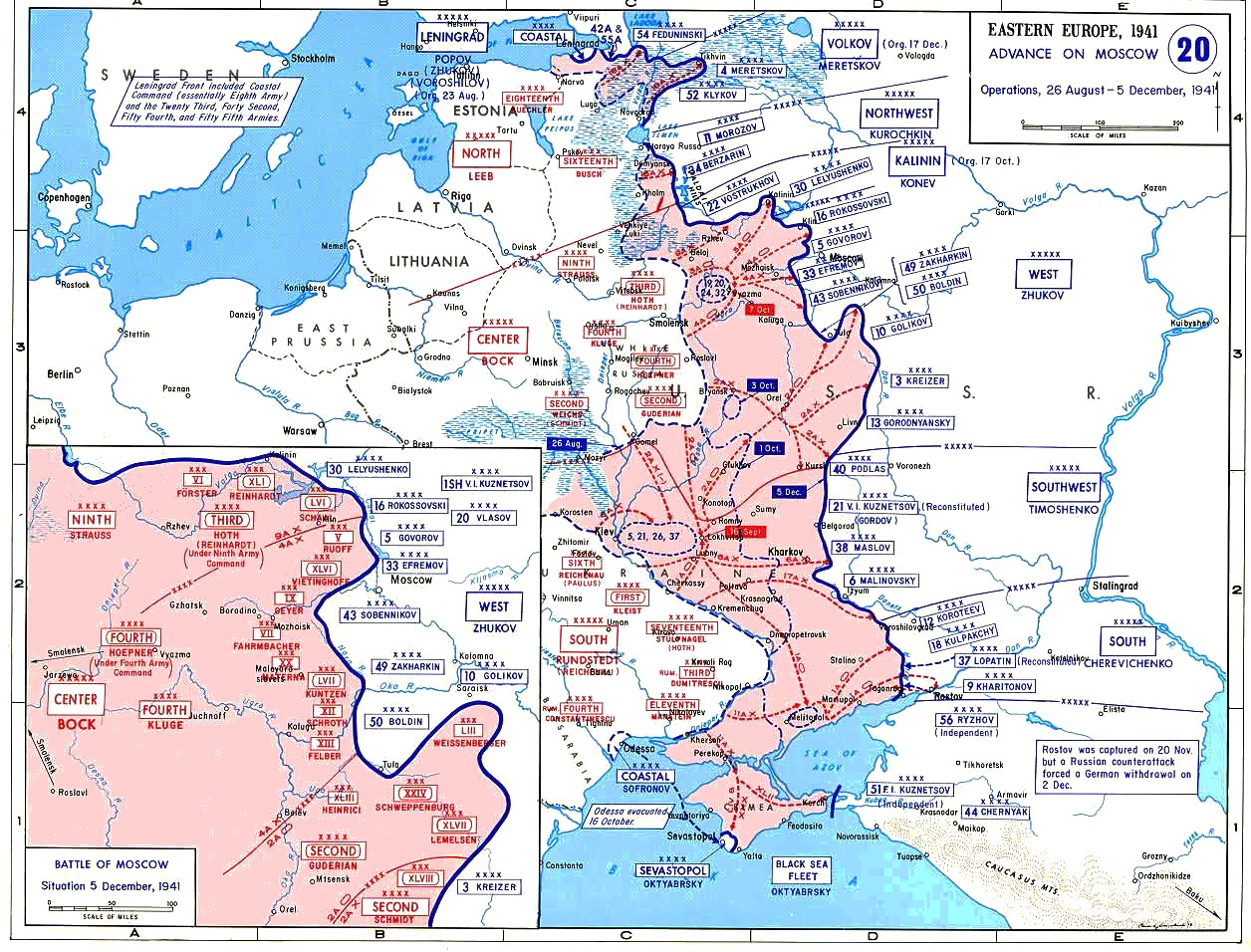
Battle Of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary military and political objectives for Axis forces in their invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd and 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front south of Tula, by the 2nd Panzer Army, while the 4th Army advanced directly towards Moscow from the west. Initially, the Soviet forces conducted a strategic defence of Moscow Oblast by constructing three defensive belts, deploying newly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre () was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created during the planning of Operation Barbarossa, Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, as one of the three German Army formations assigned to the invasion. After Army Group North was trapped in the Courland Pocket in mid-1944, it was renamed to Army Group Courland and the first Army Group Centre was renamed "Army Group North". The second iteration of Army Group Centre was formed by the redesignation of Army Group A as the replacement for the first Army Group Centre. Formation and Command The army group was officially created by Adolf Hitler when he issued Führer Directive 21 on 18 December 1940, ordering German forces to prepare for an attack on Soviet Russia in 1941. The first commanding officer of Army Group Centre was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, who would lead it until he was relieved on 18 December 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rostov (1941)
The Battle of Rostov (1941) took place on the Eastern Front of World War II around Rostov-on-Don and was fought between Army Group South of Nazi Germany and the Southern Front of the Soviet Union. The battle comprised three phases: the German Sea of Azov Offensive Operation by Army Group South (General Gerd von Rundstedt) (begun on 12 September 1941),p.87, Haupt, Army Group South the Soviet Rostov Defensive Operation (5 November 1941 – 16 November 1941) by the Southern Front (General Yakov Timofeyevich Cherevichenko), and the Rostov Offensive Operation (27 November 1941 – 2 December 1941) executed by the same Soviet Front. After forcing their way across the Mius River on 17 November, the German forces captured 10,000 Soviet troops and took Rostov on 21 November. Six days later the Southern Front, reinforced with the newly raised 37th Army, counterattacked from the north and threatened to surround the overstretched German III Motorized Army Corps. Rundstedt then order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group South
Army Group South () was the name of one of three German Army Groups during World War II. It was first used in the 1939 September Campaign, along with Army Group North to invade Poland. In the invasion of Poland, Army Group South was led by Gerd von Rundstedt and his chief of staff Erich von Manstein. Two years later, Army Group South became one of three army groups into which Germany organised their forces for Operation Barbarossa. Army Group South's principal objective was to capture Soviet Ukraine and its capital Kiev. In September 1944, Army Group South Ukraine was renamed Army Group South in Eastern Hungary. It fought in Western Hungary until March 1945 and retired to Austria at the end of the Second World War, where it was renamed Army Group Ostmark on 2 April 1945. Operation Barbarossa Ukraine was a major center of Soviet industry and mining and had the good farmland required for Hitler's plans for ''Lebensraum'' ('living space'). Army Group South was to advance up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (1935–1945)
The German Army (, ; ) was the Army, land forces component of the ''Wehrmacht'', the regular armed forces of Nazi Germany, from 1935 until it effectively ceased to exist in 1945 and then was formally dissolved in August 1946. During World War II, a total of about 13.6 million Wehrmacht foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts served in the German Army. Only 17 months after Adolf Hitler announced the German rearmament programme in 1935, the army reached its projected goal of 36 Division (military), divisions. During the autumn of 1937, two more corps were formed. In 1938 four additional corps were formed with the inclusion of the five divisions of the Austrian Armed Forces, Austrian Army after the Anschluss, annexation of Austria by Germany in March. During the period of its expansion under Hitler, the German Army continued to develop concepts pioneered during World War I, combining ground and air units into combined arms forces. Coupled with operational and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberkommando Des Heeres
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat at Moscow in December 1941. During World War II, OKH had the responsibility of strategic planning of Armies and Army Groups. The General Staff of the OKH managed operational matters. Each German Army also had an Army High Command ( or AOK). The Armed Forces High Command () then took over this function for theatres other than the Eastern front. The OKH commander held the title of Commander-in-chief of the Army (). After the Battle of Moscow, the OKH commander Field marshal Walther von Brauchitsch was removed from office, and Hitler appointed himself as Commander-in-Chief of the Army. From 1938, OKH was, together with () and () formally subordinated to the . OKH vs OKW OKH had been independent until February 1938, when Hitler creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German General Staff
The German General Staff, originally the Prussian General Staff and officially the Great General Staff (), was a full-time body at the head of the Prussian Army and later, the Imperial German Army, German Army, responsible for the continuous study of all aspects of war, and for drawing up and reviewing plans for mobilization or campaign. It existed unofficially from 1806, and was formally established by law in 1814. The first Staff (military), general staff in existence, it was distinguished by the formal selection of its officers by intelligence and Merit system, proven merit rather than patronage or wealth, and by the exhaustive and rigorously structured training which its staff officers undertook. The Prussian General Staff also enjoyed greater freedom from political control than its contemporaries, and this autonomy was enshrined in law on the unification of Germany and the establishment of the German Empire in 1871. It came to be regarded as the home of Militarism#Germany, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War II)
The Western Front was a European theatre of World War II, military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, French Third Republic, France, and Nazi Germany, Germany. The Italian campaign (World War II), Italian front is considered a separate but related theatre. The Western Front's 1944–1945 phase was officially deemed the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater by the United States, whereas Italy fell under the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army, Mediterranean Theater along with the North African campaign. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of Luxembourg, Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |