|
Pandoraviridae
''Pandoraviridae'' is a proposed family of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect amoebae. There is only one genus in this family: ''Pandoravirus''. Several species in this genus have been described, including '' Pandoravirus dulcis'', '' Pandoravirus salinus'' and '' Pandoravirus yedoma''. History The viruses were discovered in 2013. Description The viruses in this family are the second largest known virus (~1 micrometer) in capsid length, after ''Pithovirus'' (1.5 micrometer). ''Pandoravirus'' has the largest viral genome known, containing double-stranded DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ... of 1.9 to 2.5 megabase pairs. Evolution These viruses appear to be related to the phycodnaviruses. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q16987267 Nucleocytoplasmic larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocytoplasmic Large DNA Viruses
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are referred to as nucleocytoplasmic because they are often able to replicate in both the host's cell nucleus and cytoplasm. The phylum is notable for containing the giant viruses. There are nine families of NCLDVs that all share certain genomic and structural characteristics; however, it is uncertain whether the similarities of the different families of this group have a common viral ancestor. One feature of this group is a large genome and the presence of many genes involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Typically, viruses with smaller genomes do not contain genes for these processes. Most of the viruses in this family also replicate in both the host's nucleus and cytoplasm, thus the name nucleocytoplasmic. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pithovirus
''Alphapithovirus'', is a genus of giant virus known from two species, '' Alphapithovirus sibericum'', which infects amoebas, and '' Alphapithovirus massiliense''. It is DNA-based and is a member of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses clade. It was discovered in 2014, when a viable specimen was found in a 30,000-year-old ice core harvested from permafrost in Siberia, Russia. Description The genus name ''Alphapithovirus'', a reference to large storage containers of ancient Greece known as pithoi, was chosen to describe the new species. A specimen of ''Alphapithovirus'' measures approximately 1.5 μm (1500 nm) in length and 0.5 μm (500 nm) in diameter, making it one of the largest viruses yet found, second to Megaklothovirus. It is 50% larger in size than the '' Pandoraviridae'', the previous largest-known viruses, and is larger than '' Ostreococcus'', the smallest eukaryotic cell, although ''Pandoravirus'' has the largest viral genome, containing 1.9 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
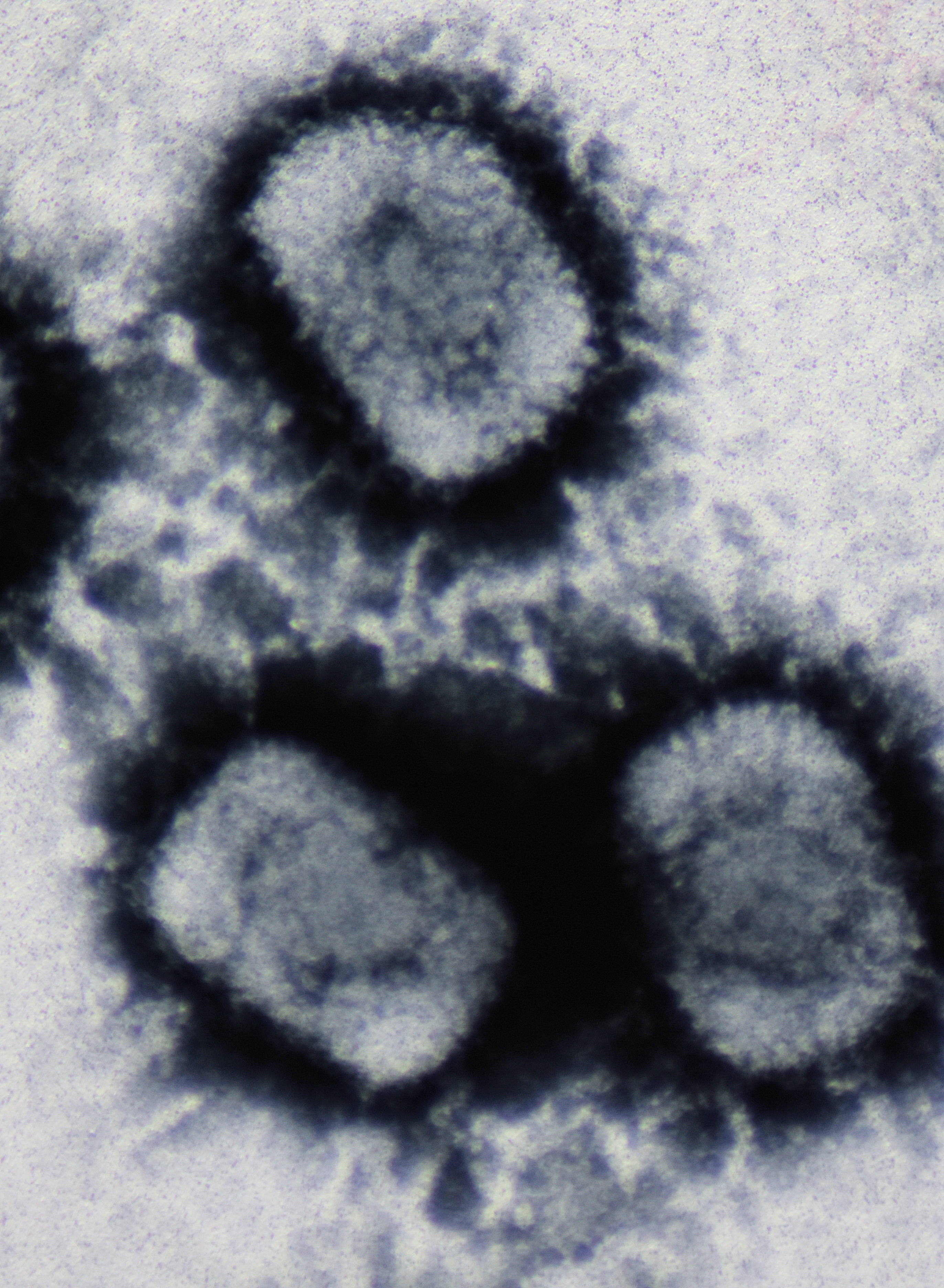
Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with the largest genome size (2.5 million base pairs) of any known viral genus. Discovery The discovery of Pandoraviruses by a team of French scientists, led by husband and wife Jean-Michel Claverie and Chantal Abergel, was announced in a report in the journal ''Science'' in July 2013. Other scientists had previously observed the pandoravirus particles, but owing to their enormous size they were not expected to be viruses. Patrick Scheid, a parasitologist from the Central Institute of the Bundeswehr Medical Service in Koblenz, Germany, found one in 2008, in an amoeba living in the contact lens of a woman with keratitis. Its development within the amoebal host was documented extensively. Unlike in other cases with such giant viruses, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycodnavirus
''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 faces). As of 2014, there were 33 species in this family, divided among 6 genera. This family belongs to a super-group of large viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Evidence was published in 2014 suggesting that specific strains of ''Phycodnaviridae'' might infect humans rather than just algal species, as was previously believed. Most genera under this family enter the host cell by cell receptor endocytosis and replicate in the nucleus. ''Phycodnaviridae'' play important ecological roles by regulating the growth and productivity of their algal hosts. Algal species such '' Heterosigma akashiwo'' and the genus '' Chrysochromulina'' can form dense blooms which can be damaging to fisheries, resulting in losses in the aquaculture i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DsDNA Viruses
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandoravirus Dulcis
''Pandoravirus dulcis'' is an egg-shaped virus of genus ''Pandoravirus'', that was discovered in a shallow lake at La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ... in 2013. The virus contains around 1.9 million DNA bases and about 1500 genes. It infects amoeba living in pond water. Along with '' Pandoravirus salinus'', and around one micrometre in size, it is one of the largest viruses ever identified. References 2013 in science Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses Unaccepted virus taxa {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandoravirus Salinus
''Pandoravirus salinus'' is a large virus of genus ''Pandoravirus'', found in the marine sediment layer of the Tunquen River in Chile, and is one of the largest viruses identified, along with '' Pandoravirus dulcis''. It is 2.5 million nucleobases long, encodes for about 2,500 genes, and is visible through an optical microscope The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of micros .... It was first identified in 2013. References 2013 in science Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses Unaccepted virus taxa {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandoravirus Yedoma
''Pandoravirus yedoma'' is a virus that originated 48,500 years ago which was discovered in the deep Siberian permafrost in 2022. The scientists also revived 13 new pathogens and characterized them as 'zombie viruses'. It has been shown to infect amoeba An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ... cells (particularly '' A. castellanii'') killing them in the process. References Bamfordvirae Unaccepted virus taxa {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI Unit, SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cell (biology), cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |