|
Pamukkale 30
Pamukkale, () meaning "cotton castle" in Turkish, is a natural site in Denizli Province in southwestern Turkey. The area is famous for a carbonate mineral left by the flowing of thermal spring water. It is located in Turkey's Inner Aegean region, in the River Menderes valley, which has a temperate climate for most of the year. The ancient Greek city of Hierapolis was built on top of the travertine formation which is in total about long, wide and high. It can be seen from the hills on the opposite side of the valley in the town of Denizli, 20 km away. This area has been drawing visitors to its thermal springs since the time of classical antiquity. The Turkish name refers to the surface of the shimmering, snow-white limestone, shaped over millennia by calcite-rich springs. Dripping slowly down the mountainside, mineral-rich waters collect in and cascade down the mineral terraces, into pools below. It was added as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988 along with Hierapoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierapolis
Hierapolis (; , lit. "Holy City") was a Hellenistic Greek city built on the site of a Phrygian cult center of the Anatolian mother goddess Cybele, in Phrygia in southwestern Anatolia, Turkey. It was famous for its hot springs, its high quality wool fabrics and dyes, and as the birthplace of the Stoic philosopher Epictetus. Its extensive remains are adjacent to modern Pamukkale in Turkey. The hot springs have been used as a spa since at least the 2nd century BCE, with many patrons retiring or dying there as evidenced by the large necropolis filled with tombs, most famously that of Marcus Aurelius Ammianos, which bears a relief depicting the earliest known example of a crank and rod mechanism, and the Tomb of Philip the Apostle. Hierapolis was added as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988. The Italian Archaeological Mission of Hierapolis of Frigia (MAIER) has operated at the site since 1957 and is currently directed bGrazia Semeraro Professor of Classical Archaeology at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denizli
Denizli is a city in Aegean Region, Aegean Turkey, and seat of the province of Denizli Province, Denizli. The city forms the urban part of the districts Merkezefendi and Pamukkale, Denizli, Pamukkale, with a population of 691 783 in 2024. Denizli has seen economic development in the last few decades, mostly due to textile production and exports. Denizli also attracts visitors to the nearby mineral-coated hillside hot spring of Pamukkale, and with red color thermal water spa hotels Karahayıt, just north of Pamukkale. Recently, Denizli became a major domestic tourism destination due to the various types of thermal waters in Sarayköy, Central/Denizli (where Karahayıt and Pamukkale towns are located), Akköy, Denizli, Akköy (Gölemezli), Buldan (Yenicekent), and Çardak districts. The ancient ruined city of Hierapolis, as well as ruins of the city of Laodicea on the Lycus, the ancient metropolis of Phrygia, are nearby. Also in the vicinity of Honaz, about west of Denizli is, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denizli Province
Denizli Province () () is a province and metropolitan municipality of Turkey in Western Anatolia, on high ground above the Aegean coast. Neighbouring provinces are Uşak to the north, Burdur, Isparta, Afyon to the east, Aydın, Manisa to the west and Muğla to the south. It is located between the coordinates 28° 30’ and 29° 30’ E and 37° 12’ and 38° 12’ N. Its area is 12,134 km2, and its population is 1,056,332 (2022). The provincial capital is the city of Denizli. Districts Geography Approximately 28-30% of the land is plain, 25% is high plateau and tableland, and 47% is mountainous. At 2571m Mount Honaz is the highest in the province, and indeed in Western Anatolia. Babadag in the Mentes range has a height of 2308 meters. The biggest lake in Denizli is Acıgöl, which means ''bitter lake'' and indeed industrial salts ( sodium sulphate) are extracted from this lake which is highly alkaline. There is a thermal spring to the west of Sarayköy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of the modern Middle East. Just beyond it lies southwestern Iran, where the region transitions into the Iranian plateau, Persian plateau, marking the shift from the Arab world to Iran. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran (southwest), Turkey (southeast), Syria (northeast), and Kuwait. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture". It is recognised as the cradle of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-speaking region of Babylonia. Its rulers established two important empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital of other empires, such as the Achaemenid Empire. Babylon was one of the most important urban centres of the ancient Near East, until its decline during the Hellenistic period. Nearby ancient sites are Kish, Borsippa, Dilbat, and Kutha. The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri (2217–2193 BC), of the Akkadian Empire. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
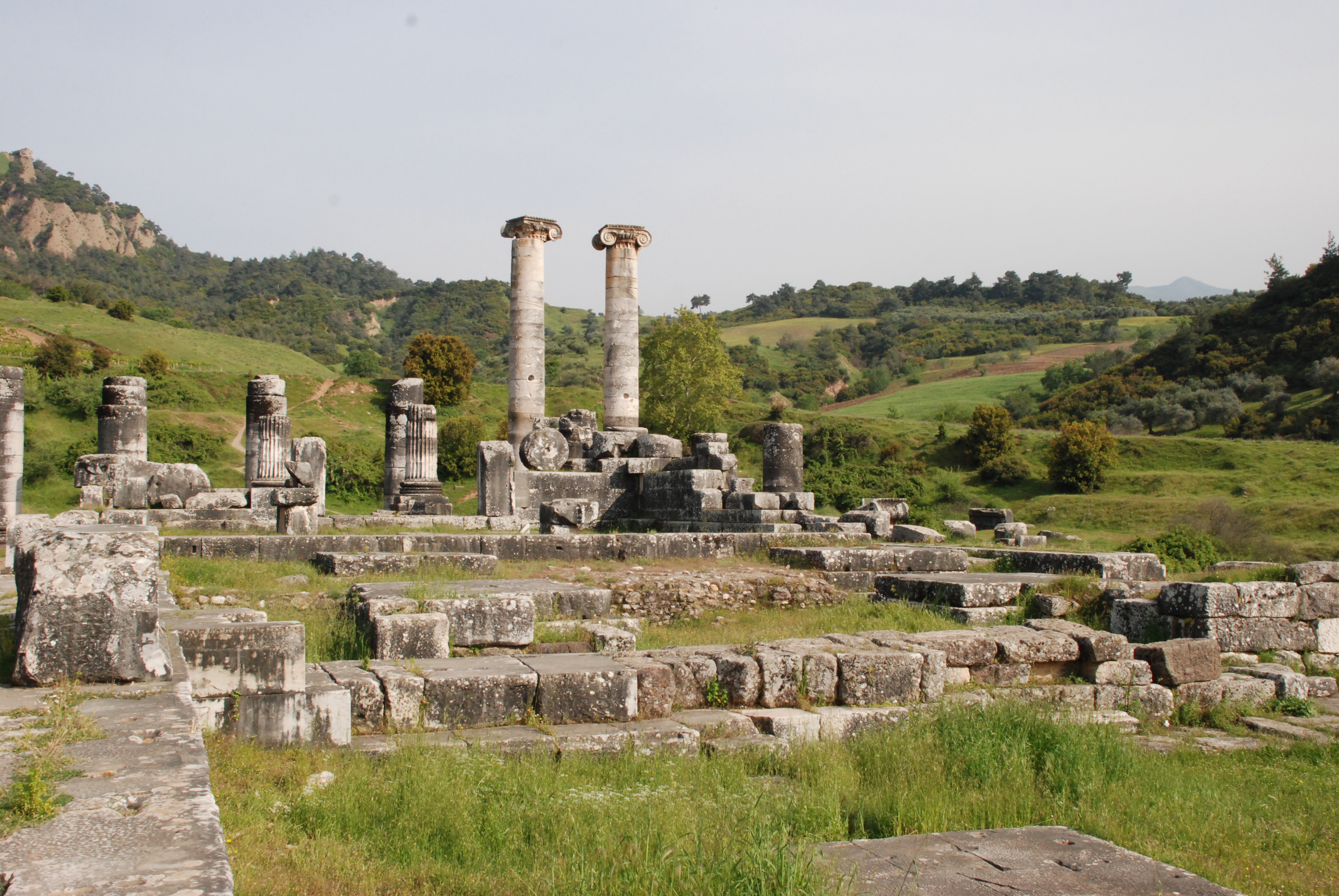
Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman Republic, Roman Asia (Roman province), province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak Province, Uşak, Manisa Province, Manisa and inland İzmir Province, İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of observing the Mosaic covenant, which they believe was established between God in Judaism, God and the Jewish people. The religion is considered one of the earliest monotheistic religions. Jewish religious doctrine encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. Among Judaism's core texts is the Torah—the first five books of the Hebrew Bible—and a collection of ancient Hebrew scriptures. The Tanakh, known in English as the Hebrew Bible, has the same books as Protestant Christianity's Old Testament, with some differences in order and content. In addition to the original written scripture, the supplemental Oral Torah is represented by later texts, such as the Midrash and the Talmud. The Hebrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
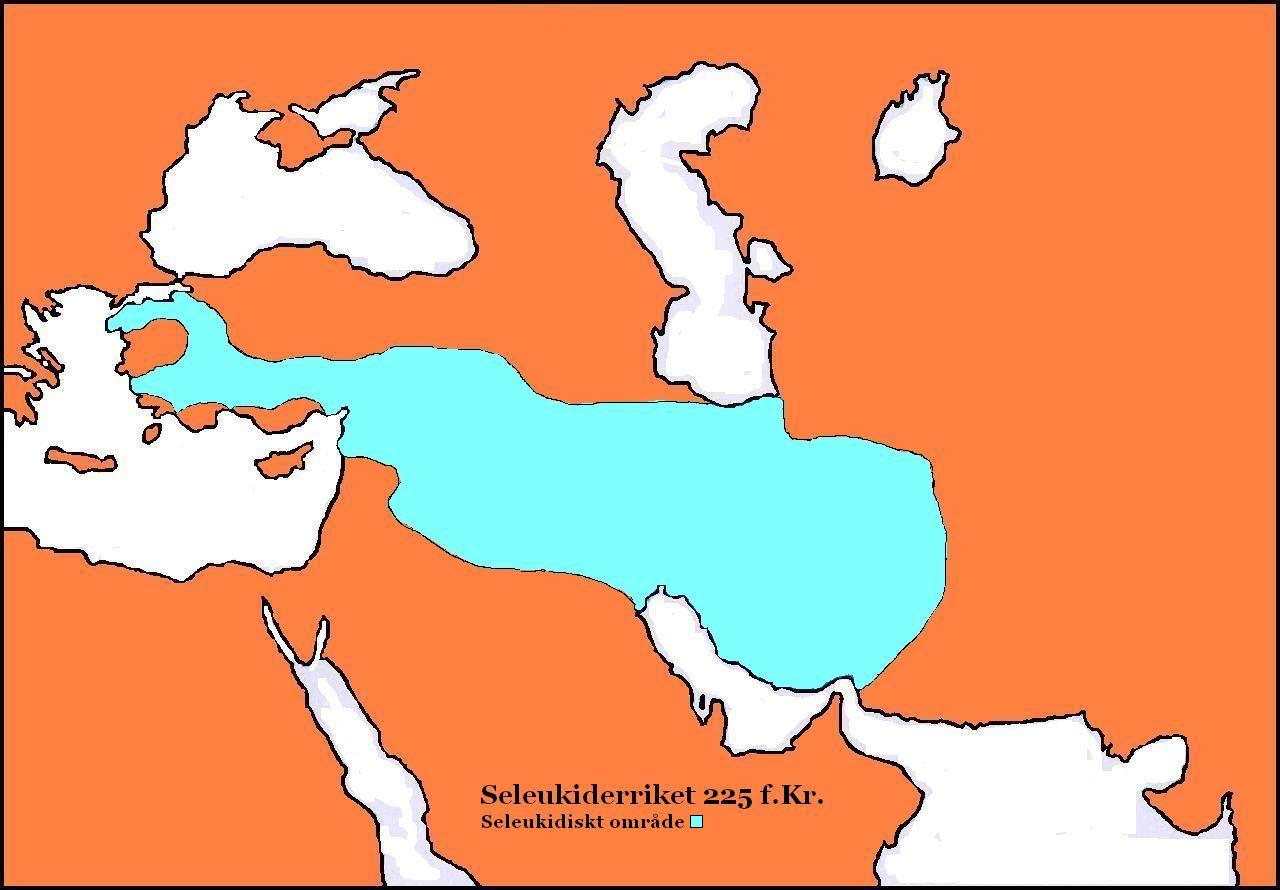
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in April/June 223 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for ' Great King'), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against the Roman Republic. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domination", he waged a four-year war against Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in modern-day Turkey in the early 2nd millennium BC. The Hittites formed a series of Polity, polities in north-central Anatolia, including the kingdom of Kussara (before 1750 BC), the Kültepe, Kanesh or Nesha Kingdom (–1650 BC), and an empire centered on their capital, Hattusa (around 1650 BC). Known in modern times as the Hittite Empire, it reached its peak during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed most of Anatolia and parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, bordering the rival empires of the Hurri-Mitanni and Assyrians. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Hittites were one of the dominant powers of the Near East, coming into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC. After receiving the Mesopotamian regions of Babylonia and Assyria in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, and Lebanon, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what are now modern Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pools In Hierapolis
Pool may refer to: Bodies of water * Swimming pool, usually an artificial structure containing a large body of water intended for swimming * Reflecting pool, a shallow pool designed to reflect a structure and its surroundings * Tide pool, a rocky pool on an ocean shore that remains filled with seawater when the tide goes out * Salt pannes and pools, a water-retaining depression located within salt and brackish marshes * Plunge pool, a small, deep body of water * Stream pool, a quiet slow-moving portion of a stream * Spent fuel pool, a storage facility for used fuel rods from a nuclear reactor * Vernal pools, seasonal pools of water that provide habitat for distinctive plants and animals. Sports and gambling * Pool (cards), the common pot for stakes or the stakes themselves in card games * Pool (dominoes), the stock or boneyard in dominoes * Pool (cue sports), a group of games played on a pool table * Pool (poker) or pot (poker), money wagered during a single hand of poker * Pool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TR Pamukkale Hierapolis Asv2020-02 Img07
TR or tr may stand for Arts and entertainment Gaming * ''Tomb Raider'', a video game franchise * Terminal Reality, an American video game developer * A currency in online game ''TalesRunner'' * Terran Republic (''PlanetSide''), a faction in the video game series ''PlanetSide'' Music * Korg TR, a variant of the Korg Triton music workstation synthesizer * Trill TRILL (Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links) is a networking protocol for optimizing bandwidth and resilience in Ethernet networks, implemented by devices called TRILL switches. TRILL combines techniques from bridging and routing, and ..., notation for musical ornament * TR-808, TR-909 etc., 1980s Roland drum machines Businesses and organizations * Scoot, IATA code since 2017 * Tiger Airways, IATA code between 2003 and 2017 * Tomahawk Railway, reporting mark * Transbrasil, IATA airline code until 2001 * Team Rubicon, commonly used abbreviation * Talyllyn Railway, a Welsh railway * Thomson Reuters, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |