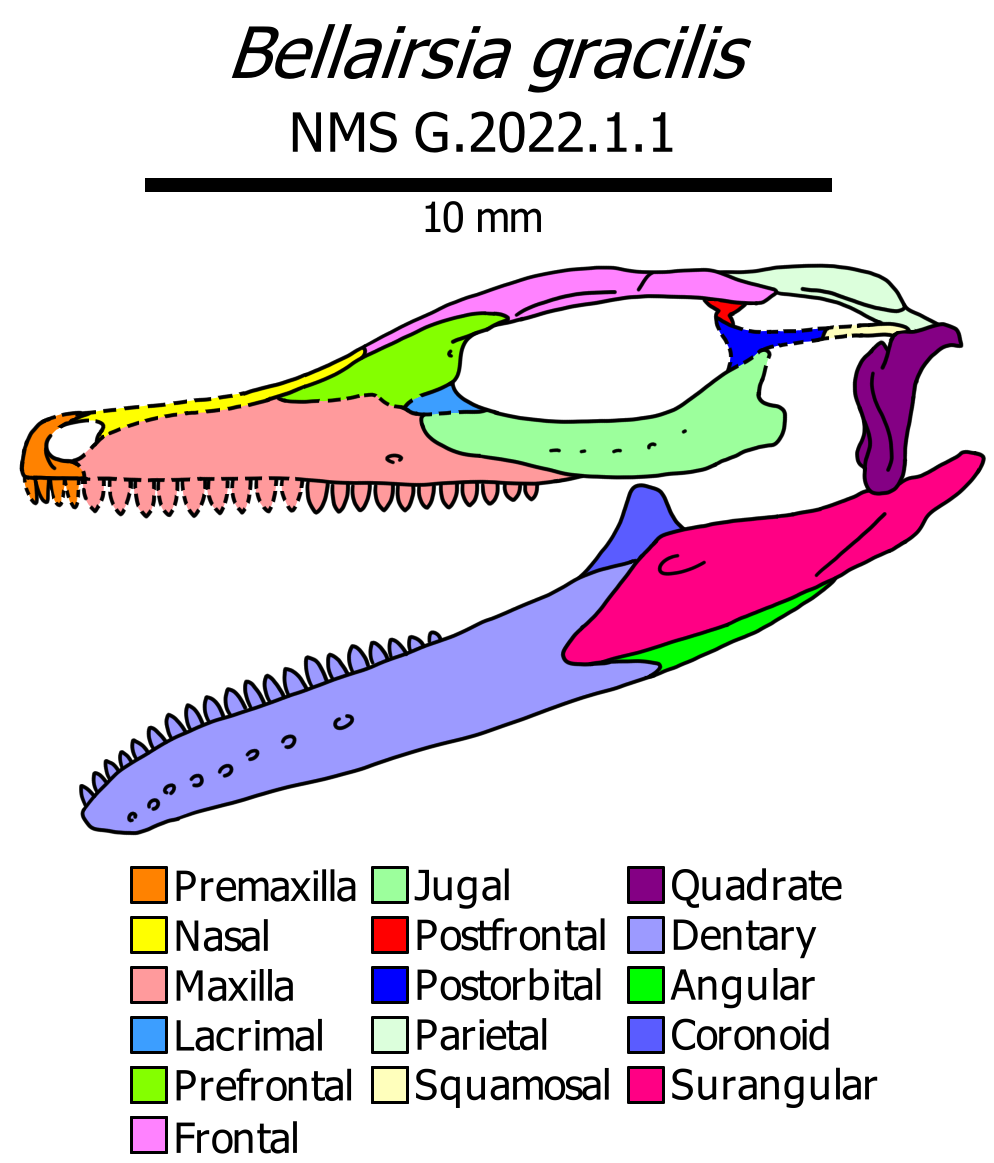
|
Palaeoxonodon
''Palaeoxonodon'' is an extinct genus of Cladotherian mammal from the Middle Jurassic of England and Scotland. Discovery The first fossils of ''Palaeoxonodon ooliticus'' were found in the Kirtlington cement quarry, Oxfordshire, England. This site was rich in Mesozoic mammal remains from the Bathonian Forest Marble Formation. Later, two more species of ''Palaeoxonodon'' were named from the same site, ''P. leesi'' and ''P. freemani''.Sigogneau-Russell D. 2003. Holotherian mammals from the Forest Marble(Middle Jurassic of England). ''Geodiversitas'', 25, 501–537. All of these fossils were individual teeth. However, a recent fossil recovered from the Kilmaluag Formation of Skye, Scotland comprised a lower jaw with five molar teeth, four premolars, a Canine tooth, canine and one incisor present. This more complete fossil suggests that the separate species previously named from England were in fact all the same species, ''P. ooliticus'', and only appeared different due to their diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmaluag Formation
The Kilmaluag Formation is a Middle Jurassic geologic formation in Scotland. It was formerly known as the Ostracod Limestone for the abundance of fossil freshwater ostracods within it. The Kilmaluag Formation is very fossiliferous, with ostracods, gastropods, bivalves, trace fossil burrows, and vertebrate fossil remains. Vertebrate fossils include fish, crocodylomorphs, mammals, small reptiles, amphibians and some large reptile remains including dinosaurs and pterosaurs.Panciroli E, RBJ Benson, S Walsh, RJ Butler, TA Castro, MEH Jones, SE. Evans. 2020Diverse vertebrate assemblage of the Kilmaluag Formation (Bathonian, Middle Jurassic) of Skye, Scotland Earth and Environmental Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh nline1-22 Geology The Kilmaluag Formation is Bathonian, and dates to around 167 million years old. It is part of the Great Estuarine Group of the Hebrides Basin, a series of sediments laid down as the land rose and fell in the area running between what is now m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitheriida
Amphitheriidae is a family of Mesozoic mammals restricted to the Middle Jurassic of Britain, with indeterminate members also possibly known from the equivalently aged Itat Formation in Siberia and the Anoual Formation of Morocco. They were members of Cladotheria, more derived than members of Dryolestida, and forming a close relationship with Peramuridae.Panciroli E; Roger B.J. Benson; Richard J. Butler (2018).New partial dentaries of amphitheriid mammalian Palaeoxonodon ooliticus from Scotland, and posterior dentary morphology in early cladotherians. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. in press. doi:10.4202/app.00434.2017. Amphitheriidae is the only family of the order Amphitheriida. Classification * Mammalia ** Yinotheria (monotremes and relatives) ** Theriimorpha ***†Eutriconodonta *** Theriiformes ****† Allotheria *****†Gondwanatheria *****† Multituberculata **** Trechnotheria ***** †Spalacotheriidae ***** †Zhangheotheriidae ***** Cladotheria ****** †Meridiole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitherium
''Amphitherium'' is an extinct genus of stem cladotherian mammal that lived during the Middle Jurassic of England. It was one of the first Mesozoic mammals ever described. A recent phylogenetic study found it to be the sister taxon of ''Palaeoxonodon''. It is found in the Forest Marble Formation and the Taynton Limestone Formation. Etymology ''Amphitherium'' comes from the Greek ''amphi'' meaning 'on both sides', and ''therion'' meaning 'wild beast'. This was in reference to de Blainville's incorrect belief that the original fossil jaw of this animal was not a mammal, but something in between mammals and reptiles. History The first jaws of mammals from the Mesozoic - including ''Amphitherium'' - were found in the Stonesfield Slate, part of the Taynton Limestone Formation near Stonesfield in England.Rudwick, M.J.S. 2008Worlds Before Adam/ref> These were bought by a student of the British paleontologist William Buckland. Although he thought the jaws were mammalian, the anatomis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Marble Formation
The Forest Marble is a geological formation in England. Part of the Great Oolite Group, it dates to the late Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Middle Jurassic, Europe)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 538–541. . Lithology The primary lithology of the formation typically consists of greenish grey variably calcareous silicate mudstone, with lenticular cross bedded limestone units deposited in a marine setting. Dinosaurian fauna Ornithischians Saurischians Microvertebrate fauna Despite the formation being nearly entirely marine, at several localities abundant remains of terrestrial microvertebrates are found, the primary locality being the Kirtlington Mammal Bed (designated 3p) in Kirtlington Quarry near Kirtlington, Oxfordshire. Another important locality is Watton Cliff near Eype in Dorset. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zatheria
Cladotheria is a clade (sometimes ranked as a legion) of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals (marsupials and placentals) and several extinct groups, such as the dryolestoids, amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to ''Mus musculus'' (the house mouse) than to the " symmetrodont" ''Spalacotherium tricuspidens''. Description Early cladotherians can be distinguished from other mammals by a number of derived traits (apomorphies). Their teeth differed from those of the " symmetrodonts" by the evolution of a talonid shelf ( hypoflexid) on the lower molars, which occluded with the paracone of the corresponding upper molars. A true talonid basin, allowing for the crushing and grinding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladotheria
Cladotheria is a clade (sometimes ranked as a legion) of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals (marsupials and placentals) and several extinct groups, such as the dryolestoids, amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to '' Mus musculus'' (the house mouse) than to the "symmetrodont" ''Spalacotherium tricuspidens''. Description Early cladotherians can be distinguished from other mammals by a number of derived traits ( apomorphies). Their teeth differed from those of the "symmetrodonts" by the evolution of a talonid shelf (hypoflexid) on the lower molars, which occluded with the paracone of the corresponding upper molars. A true talonid basin, allowing for the crushing and grin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladotherian
Cladotheria is a clade (sometimes ranked as a legion) of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals (marsupials and placentals) and several extinct groups, such as the dryolestoids, amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to ''Mus musculus'' (the house mouse) than to the " symmetrodont" ''Spalacotherium tricuspidens''. Description Early cladotherians can be distinguished from other mammals by a number of derived traits (apomorphies). Their teeth differed from those of the " symmetrodonts" by the evolution of a talonid shelf ( hypoflexid) on the lower molars, which occluded with the paracone of the corresponding upper molars. A true talonid basin, allowing for the crushing and grinding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic Scotland
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathonian Genera
In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age and stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.3 Ma to around 166.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds the Bajocian Age and precedes the Callovian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The Bathonian Stage takes its name from Bath, a spa town in England built on Jurassic limestone (the Latinized form of the town name is ''Bathonium''). The name was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist d'Omalius d'Halloy in 1843. The original type locality was located near Bath. The French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny was in 1852 the first to define the exact length of the stage. The base of the Bathonian is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Parkinsonia (Gonolkites) convergens'' in the stratigraphic column. The global reference profile for the base of the Bathonian (a GSSP) was ratified as Ravin du Bès, Bas-Auran area, Alpes de Haute Provence, France in 2009. The top of the Bathon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |