|
PDE6A
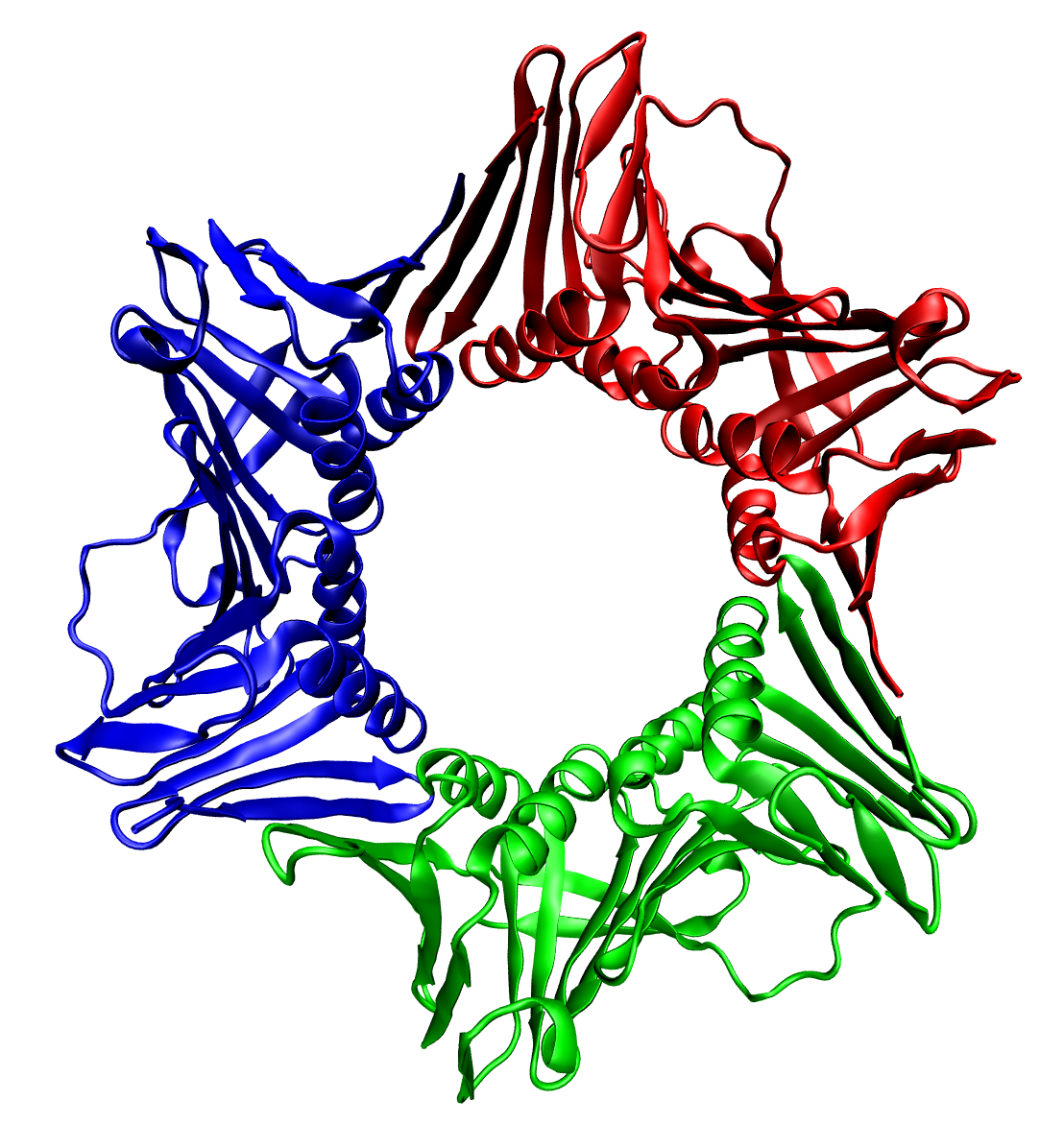
Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PDE6A'' gene. PDE6A encodes the cyclic-GMP (cGMP) specific phosphodiesterase 6A alpha subunit, expressed in cells of the retinal rod outer segment. The phosphodiesterase 6 holoenzyme is a heterotrimer composed of an alpha, beta, and two gamma subunits. cGMP is an important regulator of rod cell membrane current, and its dynamic concentration is established by phosphodiesterase 6A cGMP hydrolysis and guanylate cyclase cGMP synthesis. Mutations in PDE6A have been identified as one cause of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a member of a group of genetic disorders called inherited retinal dystrophy (IRD) that cause loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision (side and upper or lower visua .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in response to the binding of membrane-impermeable peptide hormones to the external cell surface. Through protein kinases activation, cGMP can relax smooth muscle. cGMP concentration in urine can be measured for kidney function and diabetes detection. History Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) research began after cGMP and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) were identified as cellular components and potentially involved with cellular regulation. Upon the synthesis of cGMP in 1960, progress rapidly spread in the understanding of regulation and effects of cGMP. Earl W. Sutherland received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his work with cAMP and secondary messengers. This award sparked extensive research into cAMP, while cGMP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNases, RNases, and restriction endonucleases (which all break the phosphodiester backbone of DNA or RNA), as well as numerous less-well-characterized small-molecule phosphodiesterases. The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases comprise a group of enzymes that degrade the phosphodiester bond in the second messenger molecules cAMP and cGMP. They regulate the localization, duration, and amplitude of cyclic nucleotide signaling within subcellular domains. PDEs are therefore important regulators of signal transduction mediated by these second messenger molecules. History These multiple forms (isoforms or subtypes) of phosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holoenzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotrimer
thumbnail, 400px, Trimeric form of a TNF-α mutant In biochemistry, a protein trimer is a macromolecular complex formed by three, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids. A protein trimer often occurs from the assembly of a protein's quaternary structure. The non-covalent interactions between the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on the polypeptides units help to stabilize the quaternary structure. Since a protein trimer is composed of multiple polypeptide subunits, it is considered an oligomer. A homotrimer would be formed by three identical molecules. A heterotrimer would be formed by three different macromolecules. Type II Collagen is an example of homotrimeric protein, while Type I collagen is an AAB-type heterotrimeric protein. An example of viral protein homotrimeric protein is mammarenavirus of Z matrix protein. Porins usually arrange themselves in membranes as trimers. __TOC__ Bacteriophage T4 tail fiber Multiple copies of a poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On average, there are approximately 92 million rod cells (vs ~4.6 million cones) in the human retina. Rod cells are more sensitive than cone cells and are almost entirely responsible for night vision. However, rods have little role in color vision, which is the main reason why colors are much less apparent in dim light. Structure Rods are a little longer and leaner than cones but have the same basic structure. Opsin-containing disks lie at the end of the cell adjacent to the retinal pigment epithelium, which in turn is attached to the inside of the eye. The stacked-disc structure of the detector portion of the cell allows for very high efficiency. Rods are much more common than cones, with about 120 million rod cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanylate Cyclase
Guanylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.2, also known as guanyl cyclase, guanylyl cyclase, or GC; systematic name GTP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-GMP-forming)) is a lyase enzyme that converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and pyrophosphate: : GTP = 3′,5′-cyclic GMP + diphosphate It is often part of the G protein signaling cascade that is activated by low intracellular calcium levels and inhibited by high intracellular calcium levels. In response to calcium levels, guanylate cyclase synthesizes cGMP from GTP. cGMP keeps cGMP-gated channels open, allowing for the entry of calcium into the cell. Like cAMP, cGMP is an important second messenger that internalizes the message carried by intercellular messengers such as peptide hormones and nitric oxide and can also function as an autocrine signal. Depending on cell type, it can drive adaptive/developmental changes requiring protein synthesis. In smooth muscle, cGMP is the signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |