|
Orrorin
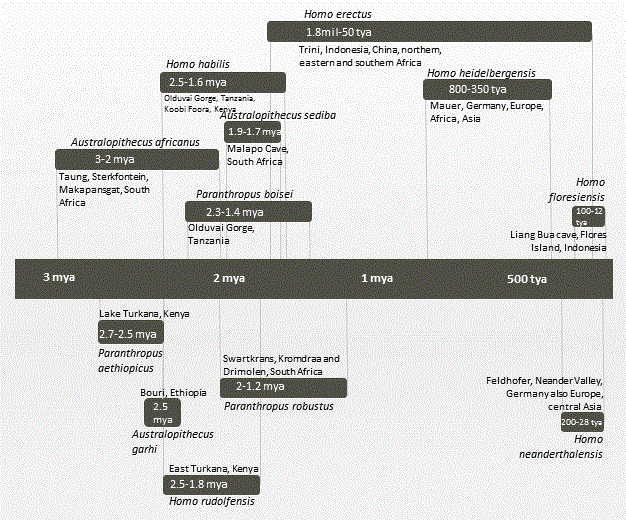
''Orrorin tugenensis'' is a postulated early species of Homininae, estimated at and discovered in 2000. It is not confirmed how ''Orrorin'' is related to modern humans. Its discovery was used to argue against the hypothesis that australopithecines are human ancestors, although this remains the most prevalent hypothesis of human evolution as of 2012. The name of genus ''Orrorin'' (plural ''Orroriek'') means "original man" in Tugen, and the name of the only classified species, ''O. tugenensis'', derives from Tugen Hills in Kenya, where the first fossil was found in 2000. As of 2007, 20 fossils of the species have been found. Fossils The 20 specimens found as of 2007 are believed to be from at least five individuals. They include: the posterior part of a mandible in two pieces; a symphysis and several isolated teeth; three fragments of femora; a partial humerus; a proximal phalanx; and a distal thumb phalanx. ''Orrorin'' had small teeth relative to its body size. Its dentition d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of ''Homo sapiens'' as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual development of traits such as human bipedalism and language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins, which indicate that human evolution was not linear but a web.Human Hybrids (PDF). Michael F. Hammer. ''Scientific American'', May 2013. The study of human evolution involves scientific disciplines, including [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tugen Hills
The Tugen Hills (also known as ''Saimo'') are a series of hills in Baringo County, Kenya. They are located in the central-western portion of Kenya. The Tugen Hills represent one of the few areas in Africa preserving a succession of deposits from the period of between 14 and 4 million years ago, making them an important location for the study of human (and animal) evolution. Excavations at the site conducted by Richard Leakey and others have yielded a complete skeleton of a 1.5-million-year-old elephant (1967), a new species of monkey (1969) and fossil remains of hominids from 1 to 2 million years ago. In 1974 Martin Pickford found a singular fossilised molar of a Orrorin tugenensis there, and that encouraged him to return 30 years later. In 1975, he named the fossilised finds ''Orrorin tugenensis'', which means: “Original man of Tugen Hills”. This hominid lived from 6.2 MYA to 5.6 MYA. Six-million-year-old hominid fossils were discovered here in 2000 by Brigitte Senut and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' (cladistically including the genus, genera ''Homo'', ''Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically includes the earlier ''Ardipithecus'', ''Orrorin'', ''Sahelanthropus'', and ''Graecopithecus''. All these closely related species are now sometimes collectively termed australopiths or homininians. They are the extinct, close relatives of humans and, with the extant genus ''Homo'', comprise the human clade. Members of the human clade, i.e. the Hominini after the split from the chimpanzees, are now called Hominina (''see Hominidae; Hominidae#Terminology, terms "hominids" and hominins''). While none of the groups normally directly assigned to this group survived, the australopiths do not appear to be literally extinct (in the sense of having no living descendants) as the genera ''Kenyanthropus'', ''Paranthropus'' and ''Homo'' probably emerged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australopithecus sediba''. Also the genera ''Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' emerged within ''Australopithecus''. ''Australopithecus'' is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes ''Ardipithecus'', though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of ''Australopithecus''. Species include ''Australopithecus garhi, A. garhi'', ''Australopithecus africanus, A. africanus'', ''Australopithecus sediba, A. sediba'', ''Australopithecus afarensis, A. afarensis, Australopithecus anamensis, A. anamensis, Australopithecus bahrelghazali, A. bahrelghazali'' and ''Australopithecus deyiremeda, A. deyiremeda''. Debate exists as to whether some ''Australopithecus'' species should be reclassified into ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homininae
Homininae (), also called "African hominids" or "African apes", is a subfamily of Hominidae. It includes two tribes, with their extant as well as extinct species: 1) the tribe Hominini (with the genus ''Homo'' including modern humans and numerous extinct species; the subtribe Hominina, comprising at least two extinct genera; and the subtribe Panina, represented only by the genus ''Pan'', which includes chimpanzees and bonobos)―and 2) the tribe Gorillini (gorillas). Alternatively, the genus '' Pan'' is sometimes considered to belong to its own third tribe, Panini. Homininae comprises all hominids that arose after orangutans (subfamily Ponginae) split from the line of great apes. The Homininae cladogram has three main branches, which lead to gorillas (through the tribe Gorillini), and to humans and chimpanzees via the tribe Hominini and subtribes Hominina and Panina (see the evolutionary tree below). There are two living species of Panina (chimpanzees and bonobos) and two living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachilos Footprints
The Trachilos footprints are possibly tetrapod footprints which show hominin-like characteristics from the late Miocene on the western Crete, close to the village of Trachilos, west of Kissamos, in the Chania Prefecture. Researchers describe the tracks as representing at least one apparent bipedal hominin or an unknown primate. The stratum in which the footprints were found was dated to about 5.7 million years ago, which predates the previously earliest discovered hominin footprints by about two million years. Later studies show that the footprints might be more than 6 million years old. The researchers of the tracks suggest that it may imply the possibility of hominin evolution outside of Africa, contrary to the current theory. Discovery The tracks were originally discovered by Gerard D. Gierliński, from the Polish Research Institute in Warsaw in 2002. During a visit to Trachilos on Crete, Gierliński found the tracks, and as he was not planning on staying in Trachilos, Gierl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
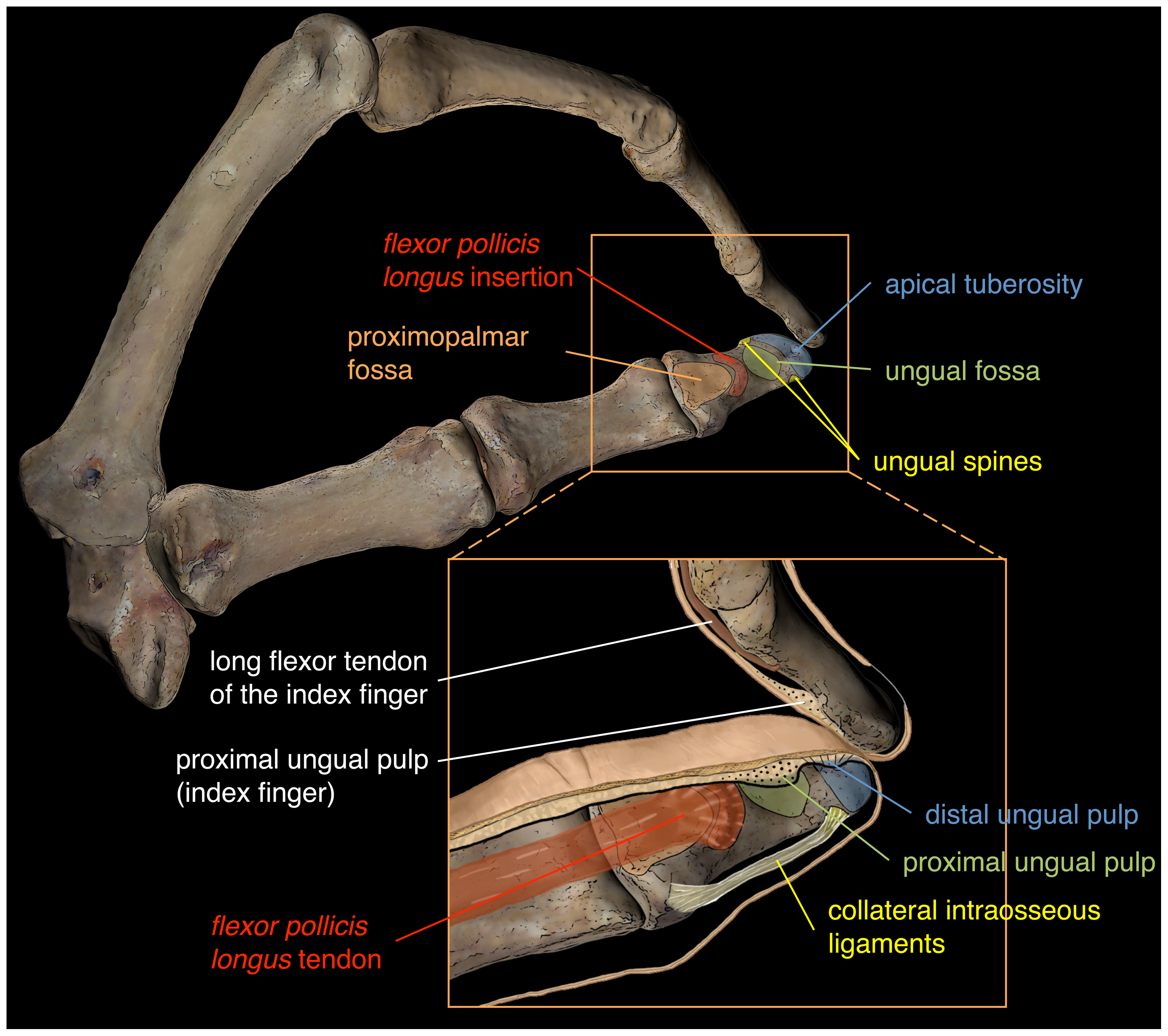
Distal Phalanx
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardipithecus
''Ardipithecus'' is a genus of an extinct hominine that lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene epochs in the Afar Depression, Ethiopia. Originally described as one of the earliest ancestors of humans after they diverged from the chimpanzees, the relation of this genus to human ancestors and whether it is a hominin is now a matter of debate. Two fossil species are described in the literature: '' A. ramidus'', which lived about 4.4 million years ago during the early Pliocene, and '' A. kadabba'', dated to approximately 5.6 million years ago (late Miocene). Initial behavioral analysis indicated that ''Ardipithecus'' could be very similar to chimpanzees, however more recent analysis based on canine size and lack of canine sexual dimorphism indicates that ''Ardipithecus'' was characterised by reduced aggression, and that they more closely resemble bonobos. Some analyses describe ''Australopithecus'' as being sister to ''Ardipithecus ramidus'' specifically. This mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bones
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-canine Megadontia
Post-canine megadontia is a relative enlargement of the molars and premolars compared to the size of the incisors and canines. This phenomenon is seen in some early hominid ancestors such as ''Paranthropus aethiopicus.'' Archaeological evidence The evidence for post-canine megadontia comes from measuring post-canine tooth surface area of hominid specimens and comparing these measurements to other hominid species. ''Australopithecus'', dated to have lived 2 to 3 million years ago, is the earliest hominid genus to demonstrate post-canine enlargement, with average post-canine tooth area ranging from approximately 460mm2 and going all the way up to the largest tooth area, 756mm2, which is seen in ''Paranthropus boisei'' . After ''Australopithecus'', a trend of steady decline in post-canine size is observed, starting in the genus ''Homo'' and culminating with ''Homo sapiens'' which has an average post-canine tooth area of only 334mm2. Studies of premolar size in hominid species that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microdontia
Microdontia is a condition in which one or more teeth appear smaller than normal. In the generalized form, all teeth are involved. In the localized form, only a few teeth are involved. The most common teeth affected are the upper lateral incisors and third molars. Teeth affected by microdontia may also have abnormal shape, and the abnormal size may affect the whole tooth, or only a part of the tooth. Definition Males tend to have larger teeth than females, and tooth size also varies by race. Abnormal tooth size is defined by some as when the dimensions are more than 2 standard deviations from the average. Microdontia is when the teeth are abnormally small, and macrodontia is when the teeth are abnormally large. Classification There are 3 types of microdontia: True generalized All the teeth are smaller than the normal size. True generalized microdontia is very rare, and occurs in pituitary dwarfism. Due to decreased levels of growth hormone the teeth fail to develop to a normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postcranium
Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated skeletal elements; these are referred to as ''postcrania''. There is some disagreement over whether the skull and skeleton belong to the same or different animals. One example is the case of a Cretaceous sauropod skull of ''Nemegtosaurus'' found in association with the postcranial skeleton ''Opisthocoelicaudia''. In paleoanthropological studies, reconstruction of relationship between various species/remains is considered to be better supported by cranial characters rather than postcranial characters. However, this assumption is largely untested. Notes Skeletal system {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |