|
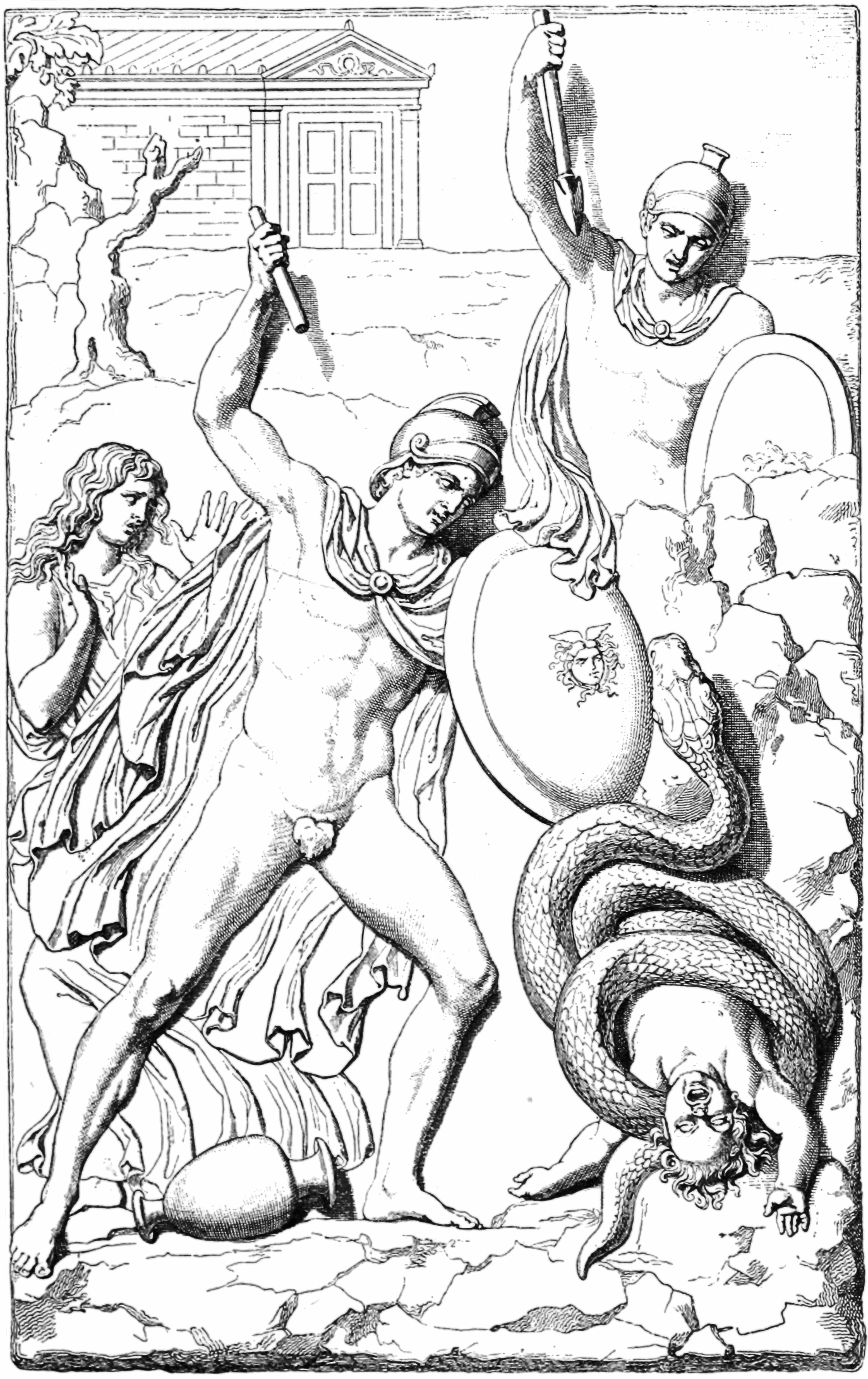
Opheltes
In Greek mythology, Opheltes (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλτης), also called Archemorus (Αρχέμορος, Beginning of Doom), was a son of Lycurgus of Nemea. His mother is variously given as Eurydice, Nemea, or Amphithea. As an infant, he was killed by a serpent at Nemea. Funeral games were held in the boy's honor, and these were supposed to have been the origin of the Nemean Games. Family According to Euripides, Opheltes' parents were Lycurgus, the priest of Zeus at Nemea, and Euridice. However Hyginus' Latin text calls Opheltes' father "Lycus", rather than Lycurgus—probably an error—and here he is a king, rather than a priest. The Latin poet Statius, following Euripides, has Lycurgus and Euridice as the parents of Opheltes, however for Statius, Lycurgus is both the king of Nemea, and the priest of Zeus. In agreement with Euripides, Apollodorus also says that Opheltes, "afterwards called Archemorus", was the son of Lycurgus (his father being Pheres, the son of Creth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archemoros 119
In Greek mythology, Opheltes (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλτης), also called Archemorus (Αρχέμορος, Beginning of Doom), was a son of Lycurgus of Nemea. His mother is variously given as Eurydice, Nemea, or Amphithea. As an infant, he was killed by a serpent at Nemea. Funeral games were held in the boy's honor, and these were supposed to have been the origin of the Nemean Games. Family According to Euripides, Opheltes' parents were Lycurgus, the priest of Zeus at Nemea, and Euridice. However Hyginus' Latin text calls Opheltes' father "Lycus", rather than Lycurgus—probably an error—and here he is a king, rather than a priest. The Latin poet Statius, following Euripides, has Lycurgus and Euridice as the parents of Opheltes, however for Statius, Lycurgus is both the king of Nemea, and the priest of Zeus. In agreement with Euripides, Apollodorus also says that Opheltes, "afterwards called Archemorus", was the son of Lycurgus (his father being Pheres, the son of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycurgus (of Nemea)
In Greek mythology, Lycurgus (; Ancient Greek: Λυκοῦργος ''Lykoûrgos'', Ancient Greek: ), also spelled Lykurgos or Lykourgos, was the son of Pheres, and the husband of Eurydice (or Amphithea) by whom he was the father of Opheltes. In the earliest account, Lycurgus was a priest of Nemean Zeus, while in later accounts he was a king of Nemea. When the army of the Seven against Thebes was passing through Nemea on its way to Thebes, Lycurgus' infant son Opheltes was killed by a serpent, through the negligence of his nursemaid Hypsipyle. The child's funeral games were said to have been the origin of the Nemean Games and Lycurgus' tomb was said to be in the grove of Nemean Zeus. Family According to Euripides, Lycurgus was from the Asopus river valley to west of Nemea, and he and his wife Euridice, were the parents of Opheltes. Hyginus also has Eurydice as the mother of Opheltes, however Hyginus' Latin text has Opheltes' father being a king of Nemea named "Lycus", rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypsipyle
In Greek mythology, Hypsipyle (Ancient Greek: Ὑψιπύλη) was a queen of Lemnos, and the daughter of King Thoas of Lemnos, and the granddaughter of Dionysus and Ariadne. When the women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, Hypsipyle saved her father Thoas. She ruled Lemnos when the Argonauts visited the island, and had two sons by Jason, the leader of the Argonauts. Later the women of Lemnos discovered that Thoas had been saved by Hypsipyle and she was sold as a slave to Lycurgus, the king of Nemea, where she became the nurse of the king's infant son Opheltes, who was killed by a serpent while in her care. She is eventually freed from her servitude by her sons. Family Hypsipyle's father was Thoas, who was the son of Dionysus and Ariadne. According to the ''Iliad'', Hypsipyle was the mother, by Jason, of Euneus. Later sources say that Hypsipyle had, in addition to Euneus, a second son by Jason. In Euripides' partially preserved play '' Hypsipyle'', she and Jason had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Against Thebes
The Seven against Thebes were seven champions in Greek mythology who made war on Thebes. They were chosen by Adrastus, the king of Argos, to be the captains of an Argive army whose purpose was to restore Oedipus' son Polynices to the Theban throne. Adrastus, although always the leader of the expedition against Thebes, was not always counted as one of the Seven champions. Usually the Seven were Polynices, Tydeus, Amphiaraus, Capaneus, Parthenopaeus, Hippomedon, and Adrastus or Eteoclus, whenever Adrastus is excluded. They tried and failed to take Thebes, and all but Adrastus died in the attempt. On their way to Thebes, the Seven stopped at Nemea, where they held funeral games for the infant Opheltes, which became the origin of the Nemean Games. Before arriving at Thebes, Adrastus sent Tydeus on ahead to resolve the dispute through negotiation, which failed. At Thebes, Capaneus was struck down by Zeus' thunderbolt while attempting to scale the city walls. Tydeus was mortal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; la, Thēbaïs, lit=Song of Thebes) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 12 books and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Vergil's ''Aeneid'' and the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic structure which is held together by subtle links between individual epis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemean Games
The Nemean Games ( grc-gre, Νέμεα or Νέμεια) were one of the four Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece, and were held at Nemea every two years (or every third). With the Isthmian Games, the Nemean Games were held both the year before and the year after the Ancient Olympic Games and the Pythian Games in the third year of the Olympiad cycle. Like the Olympic Games, they were held in honour of Zeus. They were said to have been founded by Heracles after he defeated the Nemean lion; another myth said that they originated as the funeral games of a child named Opheltes. However, they are known to have existed only since the 6th century BC (from 573 BC, or earlier). The winners received a wreath of wild celery leaves from the city of Argos. History The various legends concerning its origin are related in the ''argumenta'' of the scholiasts to the ''Nemea'' of Pindar, with which may be compared Pausanias, and Apollodorus. All these legends, however, agree in stating that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemea
Nemea (; grc, Νεμέα; grc-x-ionic, Νεμέη) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional unit of Corinthia. The small village of Archaia Nemea (formerly known as "Iraklion") is immediately southwest of the archaeological site, while the new town of Nemea lies to the west. Here, in Greek mythology, Heracles overcame the Nemean Lion, and here, during Antiquity, the Nemean Games were held (ending c. 235 BC) and were celebrated in the eleven Nemean odes of Pindar. Myth, legend and history In Greek mythology, Nemea was ruled by king Lycurgus and queen Eurydice. Nemea was famous in Greek myth as the home of the Nemean Lion, which was killed by the hero Heracles,In the late 2nd century CE, the traveller Pausanias was shown the lion's cave, fifteen furlongs from the sanctuary (Pausanias, ''Description of Greece'', II.15.2–.4). and as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphithea
Amphithea ( grc, Ἀμφιθέα) is the name of several women in Greek mythology: * Amphithea, who was, according to some, the wife of Lycurgus, king of Nemea, and mother of Opheltes (later called Archemorus). * Amphithea, daughter of Pronax, son of King Talaus of Argos, and thus, sister to Lycurgus. She married Adrastus and was the mother of Argia, Deipyle, Aegiale, Aegialeus and Cyanippus. Another account refers to her as the wife of Dion and the mother of Carya, Lyco and Orphe. * Amphithea, wife of Autolycus and mother of Anticlea (the mother of Odysseus), Polymede (possible mother of Jason), and a number of sons, including Aesimus (the father of Sinon). * Amphithea, wife of Aeolus the Etrurian king, and mother of six sons and six daughters, the youngest boy being Macareus, who made his sister Canace pregnant. Both he and his sister killed themselves. * Amphithea, an alternate name for Hemithea, the sister of Tenes.Stephanus of Byzantium, s.v. ''Tenedos'' Notes Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius ( Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, the '' Silvae''; and an unfinished epic, the '' Achilleid''. He is also known for his appearance as a guide in the ''Purgatory'' section of Dante's epic poem, the ''Divine Comedy''. Life Family background Information about Statius' life is almost entirely drawn from his ''Silvae'' and a mention by the satirist Juvenal. He was born to a family of Greek-Campanian origin; his Roman cognomen suggests that at some time an ancestor of his was freed and adopted the name of his former master, although neither Statius nor his father were slaves. The poet's father (whose name is unknown) was a native of Velia but later moved to Naples and spent time in Rome where he taught with marked success. From boyhood to adulthood, Statius' father proved hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opheltius
In Greek mythology, Opheltius (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλέστης), is the name of two soldiers in the Trojan War on each side of the conflict: *Opheltius, a defender of Troy killed by Euryalus. *Opheltius, an Achaean killed by Hector.Parada, s.v. Opheltius 2; Homer, ''Iliad'11.299–302/ref> Notes References * Homer, ''The Iliad with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, Ph.D. in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924Online version at the Perseus Digital Library * Parada, Carlos, ''Genealogical Guide to Greek Mythology'', Jonsered, Paul Åströms Förlag, 1993. . {{Greek myth index Characters in Greek mythology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurydice (Greek Myth)
In Greek mythology, Eurydice (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρυδίκη , ''Eurydikē'' "wide justice", derived from ''ευρυς eurys'' "wide" and ''δικη dike'' "justice), may refer to the following characters: * Eurydice, one of the 50 Nereids, sea-nymph daughters of the 'Old Man of the Sea' Nereus and the Oceanid Doris. * Eurydice, wife of King Aeolus of Aeolia and mother of his sons, Sisyphus, Salmoneus and Cretheus.Euripides, ''Melanippe Wise'' test. i (Collard and Cropp, pp. 572, 573) She may be identical to Enarete, the daughter of Deïmachus, who was commonly called the mother of these progeny. Apollodorus1.7.3/ref> * Eurydice, a Libyan princess as one of the 50 Danaïdes, daughter of King Danaus and the naiad Polyxo, who married (and murdered) Dryas. * Eurydice, one of the Cadmiades, the six daughters of Cadmus and Harmonia in a rare version of the myth. Her sisters were Ino, Agaue, Semele, Kleantho and Eurynome. * Eurydice, a Spartan princess as the daughter of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
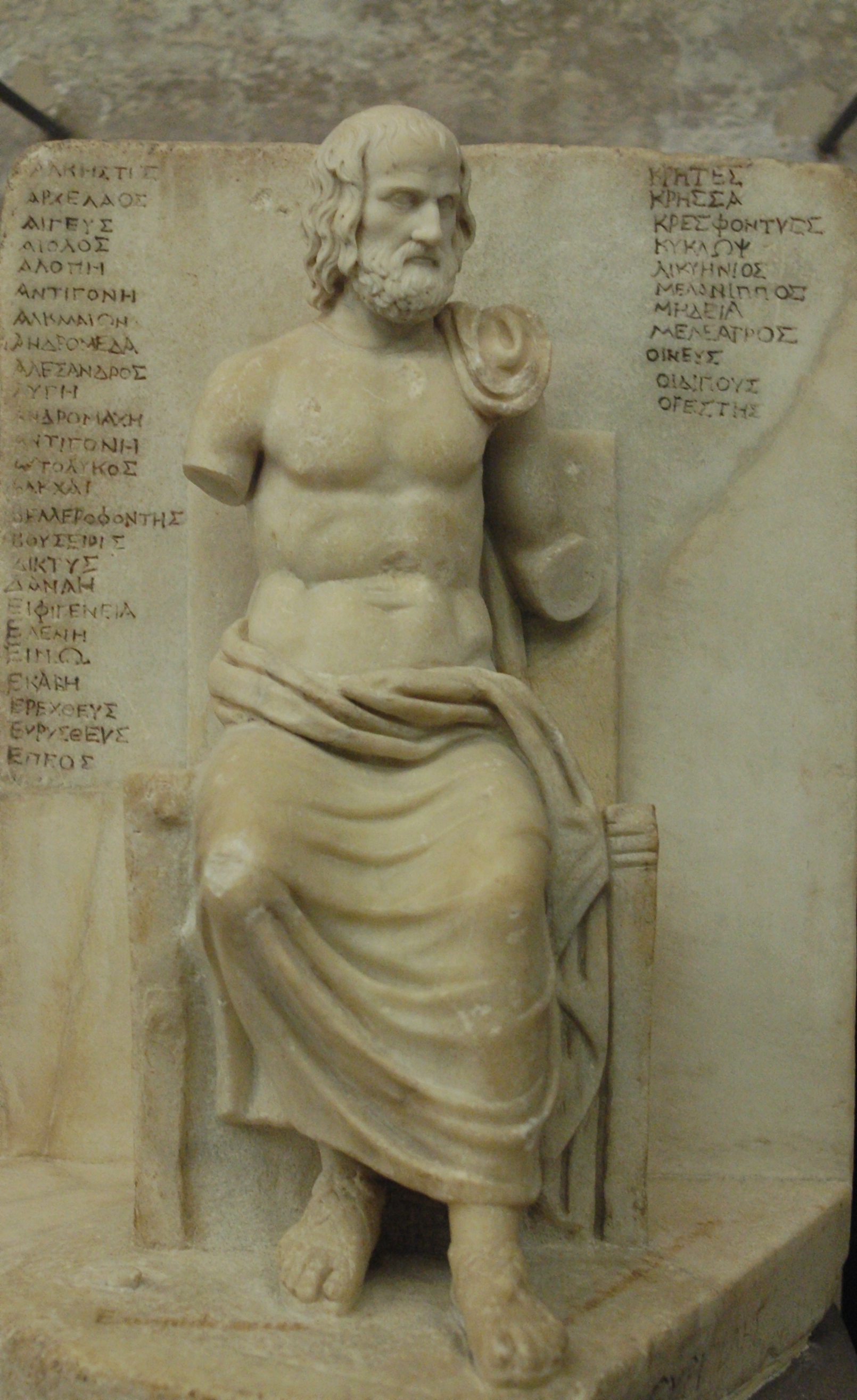
Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the '' Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete ('' Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |