|
October Revolution Island
October Revolution Island (Russian: Остров Октябрьской Революции, ''Ostrov Oktyabrskoy Revolyutsii'') is the largest island of the Severnaya Zemlya group in the Russian Arctic. It is named after the October Revolution which led to the former Russian Empire becoming a Socialist country. The area of this island has been estimated at making it the 59th largest island in the world. It rises to a height of on Mount Karpinsky. Half the island is covered with glaciers reaching down into the sea. In the sections free from ice, the vegetation is desert or tundra. Geography October Revolution Island houses five domed ice caps; clockwise from north, they are named: Rusanov, Karpinsky, University, Vavilov and Albanov. The Rusanov and Karpinsky ice caps, located on the eastern side of the island, feed with glaciers the Matusevich Fjord of the Laptev Sea and the Marat Fjord of the Shokalsky Strait.Mark Nuttall, ''Encyclopedia of the Arctic'', p. 1887 The K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets. Description Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features (i.e., they will lie over the top of mountains). By contrast, ice masses of similar size that ''are'' constrained by topographical features are known as ice fields. The ''dome'' of an ice cap is usually centred on the highest point of a massif. Ice flows away from this high point (the ice divide) towards the ice cap's periphery. Ice caps have significant effects on the geomorphology of the area that they occupy. Plastic moulding, gouging and other glacial erosional features become present upon the glacier's retreat. Many lakes, such as the Great Lakes in North America, as well as numerous valleys have been formed by glacial action over hundreds of thousands of years. On Earth, there are about of total ice mass. The average te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Glacier
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
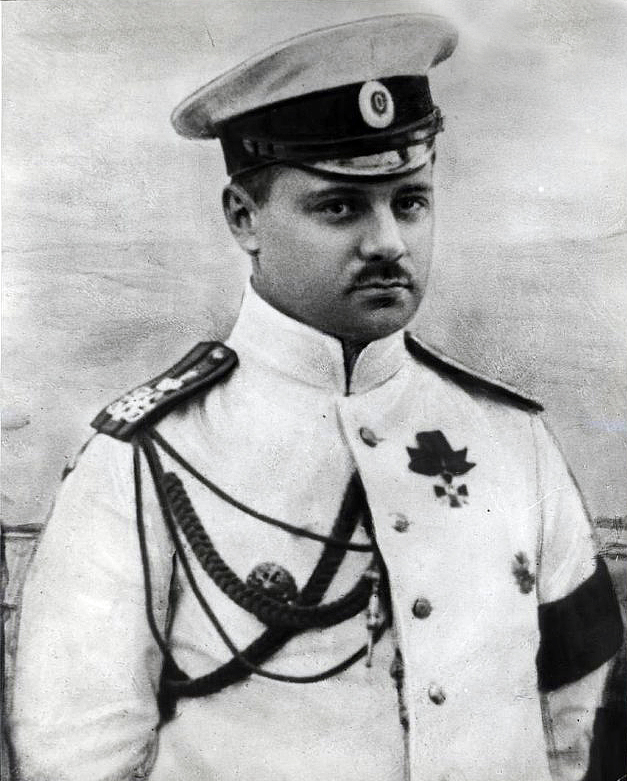
Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky (russian: Бори́с Андре́евич Вильки́цкий) (22 March (3 April N.S.) 1885, Pulkovo – 6 March 1961) was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky. Career Born in Pulkovo, Tsarskoselsky Uyezd (now part of Saint Petersburg), Vilkitsky graduated from the Naval Academy in Saint Petersburg in 1908. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. In 1913—1915 he led the Arctic hydrographic expedition on the ships ''"Taimyr"'' and ''"Vaigach"'' with the purpose of further exploration of the Northern Sea Route. In 1913, Vilkitsky's expedition discovered Emperor Nicholas II Land (russian: Земля Императора Николая II, ''Zemlya Imperatora Nikolaya II'') —later renamed 'Severnaya Zemlya', perhaps one of the most important Russian discoveries in the Arctic at the time. Other discoveries were an island that now bears his name ( Vilkitsky Island), as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape October
Cape October (russian: Мыс Октябрьский; ''Mys Oktyabr’skiy'') is a headland in Severnaya Zemlya, Russia. History This cape was named during the 1930–1932 expedition to the archipelago led by Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev after the month of the 1917 Russian Revolution. Thelodonti fossils from the Upper Silurian have been found in the area of the headland, as well as extinct marine mollusks of the Hiatellidae family. Geography Cape October is located in a low-lying unglaciated area of the northern part of October Revolution Island north of the Albanov Glacier. It faces the Red Army Strait opposite the Academy of Sciences Glacier on Komsomolets Island shore.GoogleEarth Visoky Island lies about east and Bolshoy Izvestnikovky Island about to the southwest of the cape, near the confluence with the Yuny Strait. See also *List of research stations in the Arctic References External linksRussian scientists have found a sharp decrease in the concentration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer Island (Russia)
Pioneer Island is part of the Severnaya Zemlya group in the Russian Arctic. It measures in area. The island was discovered by Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev during their 1930-32 expedition. This island contains the Pioneer Glacier. Geological and biological data: & See also * List of islands of Russia A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby unio ... References External links * {{coord, 79.917, N, 92.033, E, display=title, source:dewiki Islands of the Kara Sea Islands of Severnaya Zemlya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army Strait
Red Army Strait (russian: Пролив Красной Армии, ''Proliv Krasnoy Army'') is a strait in Severnaya Zemlya, Russia. It is named after the Red Army (Krasnaya Armiya). Geography The Red Army Strait is wide. It separates Komsomolets Island in the north from October Revolution Island in the south and connects the Kara Sea in the west with the Laptev Sea in the east. The Yuny Strait, separating Pioneer Island from Komsomolets Island, branches to the northwest in the eastern part of the strait. The huge Academy of Sciences Glacier reaches the shore all along the northern side of the strait, while the smaller Rusanov Glacier flanks the eastern part of its southern shore. Cape October is located in the northern shore of October Revolution Island, facing the Red Army Strait. Visoky Island lies about east and Bolshoy Izvestnikovky Island Bolshoi (, meaning ''big'', ''large'', ''great'', ''grand'', etc.) may refer to: *Bolshoi Theatre, a ballet and opera theatre in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Rusanov
Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov (russian: Влади́мир Алекса́ндрович Руса́нов; – ca. 1913) was a Russian geologist and Arctic explorer. Early life Rusanov was born in a merchant's family in Oryol, Russia. His early life was marred by hardship when his father went bankrupt before dying while Rusanov was still a child. Rusanov's widowed mother struggled to bring up the family but managed to send her son to the Oryol Gymnasium (Grammar School). Rusanov however began to be involved with Marxist revolutionaries. He was arrested by the police who while they could not prove anything informed the gymnasium leading to his expulsion. Rusanov therefore joined a theological seminary. Rusanov entered the natural sciences faculty at Kiev University in 1897. At Kiev he was involved in Marxist activities and was again expelled and briefly imprisoned. While in jail he was inspired by books about Fridjtof Nansen's Arctic voyages and resolved to become a polar explorer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerian Albanov
Valerian Ivanovich Albanov (russian: Валериа́н Ива́нович Альбанов; 26 May 1881 – 1919) was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of two survivors of the Brusilov expedition of 1912, which killed 22. Early life Albanov was born in 1881 in Voronezh and was raised by his uncle in the city of Ufa. At the age of seventeen he entered the Naval College at Saint Petersburg, from which he graduated in 1904. Brusilov expedition He served on board a number of ships before signing on as navigator aboard the , under Captain Georgy Brusilov, for an intended expedition to traverse the Northern Sea Route – a feat which only once before had been successfully completed, by explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The expedition was ill-planned and ill-executed by Brusilov, and the ''Svyataya Anna'' became locked in the sea ice of the Kara Sea in October 1912. Supplies were abundant, so officers and crew prepared themselves for wintering, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malyutka Glacier
The 9M14 Malyutka (russian: Малютка, links=no; "Little one", NATO reporting name: AT-3 Sagger) is a manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided missile of the Soviet Union and is probably the most widely produced ATGM of all time—with Soviet production peaking at 25,000 missiles a year during the 1960s and 1970s. In addition, copies of the missile have been manufactured under various names by at least six countries. Although they have been supplanted by more advanced anti-tank guided missiles, the Malyutka and its variants have seen widespread use in nearly every regional conflict since the 1960s. Development Development began in July 1961 with the government assigning the project to two design teams: Tula and Kolomna. The requirements were: * Vehicle mountable and/or man portable * Range of 3,000 meters * Armor penetration of 200 millimetres at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shokalsky Strait
Shokalsky Strait (russian: Пролив Шокальского) is a strait in Severnaya Zemlya, Russia. Geography The Shokalsky Strait is an up to a 50 km-wide strait that separates Bolshevik Island from October Revolution Island, connecting the Kara Sea in the west with the Laptev Sea in the east. It is named after Russian oceanographer Yuly Shokalsky Some fjords of Severnaya Zemlya have their mouths in the strait, such as Marat Fjord in October Revolution Island's eastern shore, as well as Partizan Fjord, Spartak Fjord and Thaelmann Fjord in Bolshevik Island northwestern coast. Cape Baranov and its adjacent Prima Polar Station are located in the northern part of Bolshevik Island facing the Shokalsky Strait.GoogleEarth The Krasnoflotskiye Islands are located at the western end of the strait.GoogleEarth See also *Mikoyan Bay Mikoyan Bay (russian: Залив Микояна, ''Zaliv Mikoyana'') is a bay in Severnaya Zemlya, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. GoogleEarth It is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marat Fjord
Marat Fjord (russian: Фьорд Марата, ''Fiord Marata''), is a fjord in Severnaya Zemlya, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia.GoogleEarth It is blocked by ice most of the year. History Although the shore of the island further north had been visited by Boris Vilkitsky's Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition in 1913, Vilkitsky surveyed the eastern shores of what is now known as Severnaya Zemlya in a fragmentary way —he did not explore the Shokalsky Strait and assumed that the whole of Severnaya Zemlya was one single landmass. This fjord was first surveyed and put in the map at the time of the 1931 expedition led by Soviet researchers Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev that explored for the first time Severnaya Zemlya. The fjord was named after prominent revolutionary figure Jean-Paul Marat (1743–1793). As in Matusevich Fjord further north, more accurate cartographic work of the fjord area was carried out by the 1950 expedition led by B.V. Zubov and A.I. Stepanov AI using ae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east. The sea is named after the Russian explorers Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev; formerly, it had been known under various names, the last being Nordenskiöld Sea (russian: link=no, мо́ре Норденшёльда), after explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The sea has a severe climate with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) over more than nine months per year, low water salinity, scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, and low depths (mostly less than 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |