|
Owl Nebula
The Owl Nebula (also known as Messier 97, M97 or NGC 3587) is a planetary nebula approximately 2,030 light years away in the constellation Ursa Major. Estimated to be about 8,000 years old, it is approximately circular in cross-section with a faint internal structure. It was formed from the outflow of material from the stellar wind of the central star as it evolved along the asymptotic giant branch. The nebula is arranged in three concentric shells, with the outermost shell being about 20–30% larger than the inner shell. The owl-like appearance of the nebula is the result of an inner shell that is not circularly symmetric, but instead forms a barrel-like structure aligned at an angle of 45° to the line of sight. The nebula holds about 0.13 solar masses () of matter, including hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur; all with a density of less than 100 particles per cubic centimeter. Its outer radius is around and it is expanding with velocities in the range of 27–39 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major (constellation)
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere, Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In Classical antiquity, antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism (astronomy), asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper", "the Wagon", "Charles's Wain", or "the Plough", among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the "Ursa Minor, Little Dipper". Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Beta Ursae Majoris, Merak (Alpha Ursae Majoris, α Ursae Majoris and Beta Ursae Majoris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstellar Disk
A Circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place, and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways. Young star According to the widely accepted model of star formation, sometimes referred to as the nebular hypothesis, a young star (protostar) is formed by the gravitational collapse of a pocket of matter within a giant molecular cloud. The infalling material possesses some amount of angular momentum, which results in the formation of a gaseous protoplanetary disc around the young, rotating star. The former is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Dipper
The Big Dipper (American English, US, Canadian English, Canada) or the Plough (British English, UK, Hiberno-English, Ireland) is an asterism (astronomy), asterism consisting of seven bright stars of the constellation Ursa Major; six of them are of second magnitude star, second magnitude and one, Megrez (δ), of third magnitude. Four define a "bowl" or "body" and three define a "handle" or "head". It is recognized as a distinct grouping in many cultures. The North Star (Polaris), the current northern pole star and the tip of the handle of the Little Dipper (Little Bear), can be located by extending an imaginary line through the front two stars of the asterism, Beta Ursae Majoris, Merak (β) and Alpha Ursae Majoris, Dubhe (α). This makes it useful in celestial navigation. Names and places The constellation of ''Ursa Major'' (Latin language, Latin: Greater Bear) has been seen as a bear, a wagon, or a ladle (spoon), ladle. The "bear" tradition is Proto-Indo-European mythology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbra, Penumbra And Antumbra
The umbra, penumbra and antumbra are three distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after impinging on an opaque object of lesser size. In cases of equal or smaller impinging objects, only an umbra and penumba are generated. Assuming no diffraction, for a collimated beam (such as a point source) of light, only the umbra is cast. These phenomena are generally observed within solar systems, as the size of the stars within the system are larger than the orbiting satellites, hence these terms are most often used for the shadows cast by celestial bodies, though they are sometimes used to describe levels of darkness, such as in sunspots. Umbra The umbra () is the innermost and darkest part of a shadow, where the light source is completely blocked by the occluding body. An observer within the umbra experiences a total occultation. The umbra of a round body occluding a round light source forms a right circular cone. When viewed from the cone's apex, the two bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Parsons, 3rd Earl Of Rosse
William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse (17 June 1800 – 31 October 1867), was an English engineer and astronomer. He built several giant telescopes. His 72-inch telescope, built in 1845 and colloquially known as the "Leviathan of Parsonstown", was the world's largest telescope, in terms of aperture size, until the early 20th century. From April 1807 until February 1841, he was styled as Baron Oxmantown. Life He was born in York, England, the son of Sir Lawrence Parsons, later 2nd Earl of Rosse, and Alice Lloyd. He was educated at Trinity College Dublin and Magdalen College, Oxford, graduating with first-class honours in mathematics in 1822. He inherited an earldom and a large estate in King's County (now County Offaly) in Ireland when his father, Lawrence, 2nd Earl of Rosse, died in February 1841. Lord Rosse married Mary Field, daughter of John Wilmer Field, on 14 April 1836. They had thirteen offspring, of which four sons survived to adulthood: * Lawrence, 4th Earl of Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Smyth
Admiral William Henry Smyth (21 January 1788 – 8 September 1865) was an English Royal Navy officer, hydrographer, astronomer and numismatist. He is noted for his involvement in the early history of a number of learned societies, for his hydrographic charts, for his astronomical work, and for a wide range of publications and translations. Origins William Henry Smyth was the only son of Joseph Smyth (died 1788) and Georgiana Caroline Pitt Pilkington (died 1838), the daughter of John Carteret Pilkington and the granddaughter of Laetitia Pilkington and her husband Matthew Pilkington. His father, Joseph Smyth, an American Loyalist from New Jersey who served as a lieutenant in the King's Royal Regiment of New York during the Revolutionary War, was the sixth son of Benjamin Smyth (died 1769), a landowner in what is now Blairstown, and his first wife Catherina Schoonhoven (died 1750). Never having known his father, the Admiral grew up with a half-brother Augustus Earle and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 109
Messier 109 (also known as NGC 3992 or the Vacuum Cleaner Galaxy) is a barred spiral galaxy exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the central bar approximately away in the northern constellation Ursa Major. M109 can be seen south-east of the star Phecda (γ UMa, Gamma Ursa Majoris). History Messier 109 was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781. Two years later Charles Messier catalogued the object, as an appended object to his publication. Between the 1920s through the 1950s, it was considered that Messier objects over 103 were not official, but later the additions, further referred target objects from Méchain, became more widely accepted. David H. Levy mentions the modern 110 object catalog while Sir Patrick Moore places the limit at 104 objects but has M105 to 109 listed as addenda. By the late 1970s all 110 objects are commonly used among astronomers and remain so. General information This galaxy is the most distant object in the Messier Catalog, followed by M9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ursae Majoris
Phecda , also called Gamma Ursae Majoris (γ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Gamma UMa, γ UMa), is a star in the constellation of Ursa Major. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified. Based upon parallax measurements with the ''Hipparcos'' astrometry satellite, it is located at a distance of around from the Sun. It is more familiar to most observers in the northern hemisphere as the lower-left star forming the bowl of the Big Dipper, together with Alpha Ursae Majoris (Dubhe, upper-right), Beta Ursae Majoris (Merak, lower-right) and Delta Ursae Majoris (Megrez, upper-left). Along with four other stars in this well-known asterism, Phecda forms a loose association of stars known as the Ursa Major moving group. Like the other stars in the group, it is a main sequence star, as the Sun is, although somewhat hotter, brighter and larger. Phecda is located in relatively close physical pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 108
Messier 108 (also known as NGC 3556, nicknamed the Surfboard Galaxy) is a barred spiral galaxy about 46 million light-years away from Earth in the northern constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 or 1782. From the Earth, this galaxy is seen almost edge-on. This galaxy is an isolated member of the Ursa Major Cloud of galaxies in the local supercluster. It has a morphological classification of type SBbc in the de Vaucouleurs system, which means it is a barred spiral galaxy with somewhat loosely wound arms. The maximum angular size of the galaxy in the optical band is 11 ′.1 × 4′.6, and it is inclined 75° to the line of sight. This galaxy has an estimated mass of 125 billion solar masses () and bears about 290 ± 80 globular clusters. Examination of the distribution of neutral hydrogen in this galaxy shows discrete shells of expanding gas extending for several kiloparsecs, known as H1 supershells. These may be driven by currents of dark mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
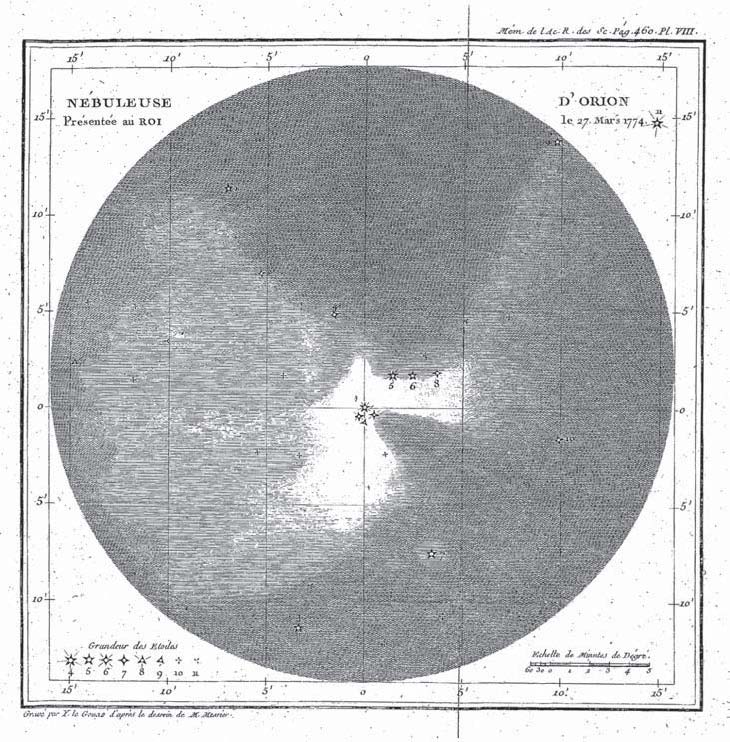
Messier Catalog
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters''). Because Messier was interested only in finding comets, he created a list of those non-comet objects that frustrated his hunt for them. This list, which Messier created in collaboration with his assistant Pierre Méchain, is now known as the ''Messier catalogue''. The Messier catalogue is one of the most famous lists of astronomical objects, and many objects on the list are still referenced by their Messier numbers. The catalogue includes most of the astronomical deep-sky objects that can be easily observed from Earth's Northern Hemisphere; many Messier objects are popular targets for amateur astronomers. A preliminary version of the catalogue first appeared in 1774 in the ''Memoirs'' of the French Academy of Sciences for the year 1771. The first version of Messier's catalogue contained 45 objects, which wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
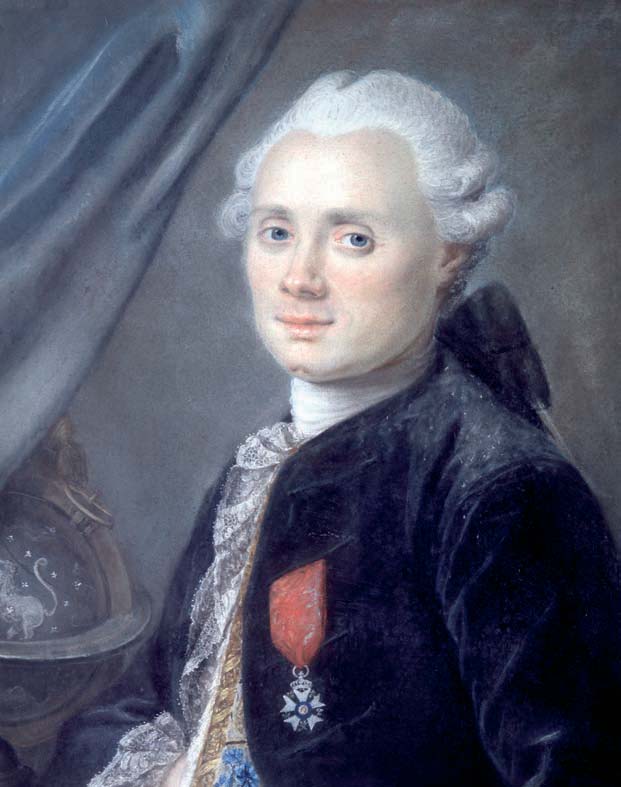
Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with the letter M and their number between 1 and 110. Messier's purpose for list of Messier objects, the catalogue was to help astronomical observers distinguish between permanent and transient astronomical event, transient visually diffuse astronomical object, objects in the sky. Biography Messier was born in Badonviller in the Lorraine region of Kingdom of France, France, in 1730, the tenth of twelve children of Françoise B. Grandblaise and Nicolas Messier, a Court usher. Six of his brothers and sisters died while young, and his father died in 1741. Charles' interest in astronomy was stimulated by the appearance of the Great Comet of 1744, great six-tailed comet in 1744 and by an annular solar eclipse visible from his hometown on 25 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |