|
Overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of disease that will never cause symptoms or death during a patient's ordinarily expected lifetime and thus presents no practical threat regardless of being pathologic. Overdiagnosis is a side effect of screening for early forms of disease. Although screening saves lives in some cases, in others it may turn people into patients unnecessarily and may lead to treatments that do no good and perhaps do harm. Given the tremendous variability that is normal in biology, it is inherent that the more one screens, the more incidental findings will generally be found. For a large percentage of them, the most appropriate medical response is to recognize them as something that does not require intervention; but determining which action a particular finding warrants ("ignoring", watchful waiting, or intervention) can be very difficult, whether because the differential diagnosis is uncertain or because the risk ratio is uncertain (risks posed by intervention, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screening (medicine)
In medicine, screening is a strategy used to look for as-yet-unrecognised conditions or risk markers. This testing can be applied to individuals or to a whole population without symptoms or signs of the disease being screened. Screening Public health intervention, interventions are designed to identify conditions which could at some future point turn into disease, thus enabling earlier intervention and management in the hope to reduce mortality and suffering from a disease. Although screening may lead to an earlier diagnosis, not all screening tests have been shown to benefit the person being screened; overdiagnosis, misdiagnosis, and creating a false sense of security are some potential Adverse effect (medicine), adverse effects of screening. Additionally, some screening tests can be inappropriately overused. For these reasons, a test used in a screening program, especially for a disease with low Incidence (epidemiology), incidence, must have good Sensitivity (tests), sensitivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis. Diagnosis is often challenging because many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For example, redness of the skin ( erythema), by itself, is a sign of many disorders and thus does not tell the healthcare professional what is wrong. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. This involves the correlation of various pieces of information followed by the recognition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis Of Malaria
The mainstay of malaria diagnosis has been the microscopic examination of blood, utilizing blood films. Although blood is the sample most frequently used to make a diagnosis, both saliva and urine have been investigated as alternative, less invasive specimens. More recently, modern techniques utilizing antigen tests or polymerase chain reaction have been discovered, though these are not widely implemented in malaria endemic regions. Areas that cannot afford laboratory diagnostic tests often use only a history of subjective fever as the indication to treat for malaria. Blood films The most economic, preferred, and reliable diagnosis of malaria is microscopic examination of blood films because each of the four major parasite species has distinguishing characteristics. Two sorts of blood film are traditionally used. Thin films are similar to usual blood films and allow species identification because the parasite's appearance is best preserved in this preparation. Thick films allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Screening
The objective of cancer screening is to detect cancer before symptoms appear, involving various methods such as blood tests, urine tests, DNA tests, and medical imaging. The purpose of screening is early cancer detection, to make the cancer easier to treat and extending life expectancy. In 2019, cancer was the second leading cause of death globally; more recent data is pending due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Universal screening, also known as mass screening or population screening, involves the screening of individuals within certain age and gender groups, aiming to screen the population for particular cancers or cancer risk factors. Selective screening, also known as targeted screening, identifies individuals with a higher risk of developing cancer, including individuals with a family history (genetic risk) of cancer or individuals engaging in high-risk behaviors such as smoking. The act of cancer screening plays a pivotal role in both preventing cancer and providing early diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unnecessary Health Care
Unnecessary health care (overutilization, overuse, or overtreatment) is health care provided with a higher volume or cost than is appropriate. In the United States, where health care costs are the highest as a percentage of GDP, overuse was the predominant factor in its expense, accounting for about a third of its health care spending ($750 billion out of $2.6 trillion) in 2012. Factors that drive overuse include paying health professionals more to do more (fee-for-service), defensive medicine to protect against litigiousness, and insulation from price sensitivity in instances where the consumer is not the payer—the patient receives goods and services but insurance pays for them (whether public insurance, private, or both). Such factors leave many actors in the system (doctors, patients, pharmaceutical companies, device manufacturers) with inadequate incentive to restrain health care prices or overuse. This drives payers, such as national health insurance systems or the U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, typically blood tests that check for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Those with high levels of PSA in their blood are at increased risk for developing prostate cancer. Diagnosis requires a prostate biopsy, biopsy of the prostate. If cancer is present, the pathologist assigns a Gleason score; a higher score represents a more dangerous tumor. Medical imaging is performed to look for cancer that has spread outside the prostate. Based on the Gleason score, PSA levels, and imaging results, a cancer case is assigned a cancer staging, stage 1 to 4. A higher stage signifies a more advanced, more dangerous disease. Most prostate tumors remain small and cause no health problems. These are managed with active surveillance of prostate cancer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens exist on normal cells, cancer cells, parasites, viruses, fungus, fungi, and bacteria. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, antibodies are ''antigen-specific'', meaning that an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer screening is the screening process used to detect undiagnosed prostate cancer in men without signs or symptoms. When abnormal prostate tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat and cure, but it is unclear if early detection reduces mortality rates. Screening precedes a diagnosis and subsequent treatment. The digital rectal examination (DRE) is one screening tool, during which the prostate is manually assessed through the wall of the rectum. The second screening tool is the measurement of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood. The evidence remains insufficient to determine whether screening with PSA or DRE reduces mortality from prostate cancer. A 2013 Cochrane review concluded PSA screening results in "no statistically significant difference in prostate cancer-specific mortality...". The American studies were determined to have a high bias. European studies included in this review were of low bias and one reported "a significant reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral CT
X-ray computed tomography operates by using an X-ray generator that rotates around the object; X-ray detectors are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source. A visual representation of the raw data obtained is called a ''sinogram'', yet it is not sufficient for interpretation. Once the scan data has been acquired, the data must be processed using a form of tomographic reconstruction, which produces a series of cross-sectional images. In terms of mathematics, the raw data acquired by the scanner consists of multiple "projections" of the object being scanned. These projections are effectively the Radon transformation of the structure of the object. Reconstruction essentially involves solving the inverse Radon transformation. Structure In conventional CT machines, an X-ray tube and detector are physically rotated behind a circular shroud (see the image above right). An alternative, short lived design, known as electron beam tomography (EBT), used el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged airway cells gain the ability to multiply unchecked, causing the growth of a tumor. Without treatment, tumors spread throughout the lung, damaging lung function. Eventually lung tumors metastasize, spreading to other parts of the body. Early lung cancer often has no symptoms and can only be detected by medical imaging. As the cancer progresses, most people experience nonspecific respiratory problems: coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain. Other symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor. Those suspected of having lung cancer typically undergo a series of imaging tests to determine the location and extent of any tumors. Definitive diagnosis of lung cancer requires a biopsy of the suspected tumor be examined by a patholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
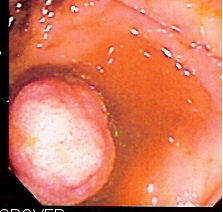
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of Cell (biology), cells (tumor) that does not Cancer invasion, invade neighboring tissue or Metastasis, metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to Cancer, malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower Cell growth, growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well Cell differentiation, differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface (fibrous sheath of connective tissue) or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include Melanocytic nevus, moles and uterine fibroids. Some forms of benign tumors may be harmful to health. Benign tumor growth causes a Mass effect (medicine), mass effect that can compress neighboring tissues. This can lead to nerve damage, blood flow reduction (Ischaemia, ischemia), tissue death (necrosis), or organ damage. The health effects of benign tumor growth may be more prominent if the tumor is contained within an enclosed space such as the cranium, respir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |