|
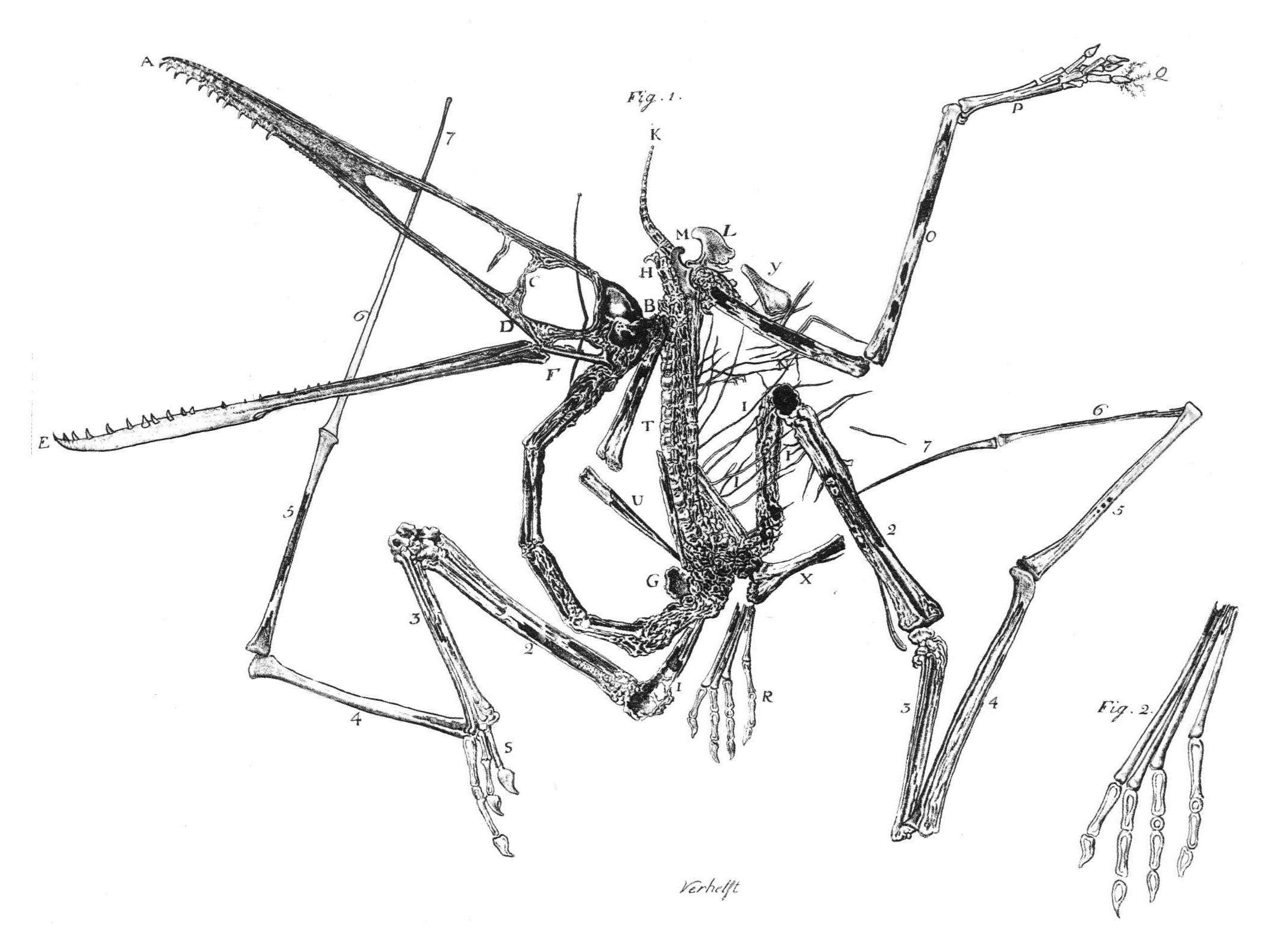
Ostromia
''Ostromia crassipes'' (''Thick-foot of John Ostrom'') is the single species of the anchiornithid theropod dinosaur genus ''Ostromia''. Recovered from the Late Jurassic Painten Formation of Germany, it was named by Christian Foth and Oliver Rauhut in 2017. Discovery and naming The holotype was discovered near Riedenburg, Germany in 1855 and it was originally misidentified as a species of a pterodactyloid pterosaur and named ''Pterodactylus crassipes'' in 1857. In 1970 it was identified as an ''Archaeopteryx'' by paleontologist John Ostrom, who called it the "Haarlem specimen", since it was kept in the Teylers Museum in Haarlem. In 2017 Christian Foth and Oliver Rauhut concluded it was more closely related to the Chinese ''Anchiornis'' and introduced the generic name ''Ostromia'', named after Ostrom. The only known specimen is fairly incomplete compared to most specimens of ''Archaeopteryx'', as it only preserves limb bones, cervical vertebrae and ribs. Most bones are also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchiornithidae
Anchiornithidae is a family of small Paraves, paravian dinosaurs. Anchiornithids have been classified at varying positions in the paravian tree, with some scientists classifying them as a distinct family, a basal subfamily of Troodontidae, members of Archaeopterygidae, or an assemblage of dinosaurs that are an evolutionary grade within Avialae or Paraves. Description Anchiornithids share many general features with other paravians, including early avialans. They were small and lightly-built feathered carnivores, similar in biology to ''Archaeopteryx'', early Dromaeosauridae, dromaeosaurids like ''Microraptor'', and particularly troodontids. They are almost exclusively known from Late Jurassic Chinese deposits, although ''Ostromia'' was discovered in Germany and ''Yixianosaurus'' (a putative member of the group only known from forelimbs) is believed to hail from the early Cretaceous. Most had long legs, arms, and hands, although some (''Eosinopteryx'') had slightly reduced foreli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ostrom
John Harold Ostrom (February 18, 1928 – July 16, 2005) was an American paleontologist who revolutionized the modern understanding of dinosaurs. Ostrom's work inspired what his pupil Robert T. Bakker has termed a " dinosaur renaissance". Beginning with the discovery of ''Deinonychus'' in 1964, Ostrom challenged the widespread belief that dinosaurs were slow-moving lizards (or "saurians"). He argued that ''Deinonychus'', a small two-legged carnivore, would have been fast-moving and warm-blooded. Further, Ostrom's work made zoologists question whether birds should be considered an order of Reptilia instead of their own class, Aves. The idea that dinosaurs were similar to birds was first proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in the 1860s, but was dismissed by Gerhard Heilmann in his influential book '' The Origin of Birds'' (1926). Prior to Ostrom's work, the development of birds was generally believed to have split off early on from that of dinosaurs. Ostrom showed more bird-like tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird'') is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaîos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" or "wing". Between the late 19th century and the early 21st century, ''Archaeopteryx'' was generally accepted by palaeontologists and popular reference books as the oldest known bird (member of the group Avialae). Older potential avialans have since been identified, including ''Anchiornis'', ''Xiaotingia'', '' Aurornis'', and '' Baminornis''. ''Archaeopteryx'' lived in the Late Jurassic around 150 million years ago, in what is now southern Germany, during a time when Europe was an archipelago of islands in a shallow warm tropical sea, much closer to the equator than it is now. Similar in size to a Eurasian magpie, with the largest individuals possibly attaining the size of a raven, the largest species of ''Archaeopteryx'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from ) is a genus of extinct pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile and one of the first prehistoric reptiles to ever be discovered. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pteros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painten Formation
The Painten Formation is a geologic formation in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic period.Painten Formation at .org Description It is roughly contemporary with the Altmühltal Formation (which includes the true Solnhofen limestone), as they both underlay the |
2017 In Archosaur Paleontology
The year 2017 in archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 11,700 years ago. The year 2017 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs. This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2017. General research * A study on the evolution of forelimb anatomy, musculature and joint ranges of motion from early archosaurs to sauropodomorph dinosaurs based on data from ''Mussaurus patagonicus'' and extant freshwater crocodile is published by Otero ''et al.'' (201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing ( ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bone
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and big toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal phalange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |