|
Orodromeus Fossil
''Orodromeus'' (meaning "Mountain Runner") is a genus of herbivorous orodromine thescelosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America. Only one species is known, the type species ''Orodromeus makelai''. Discovery and naming The remains of ''Orodromeus'' were discovered by Robert Makela during the excavation in Teton County, Montana, of the '' Egg Mountain'' brooding colony of a much larger relative, ''Maiasaura''. The type species, ''Orodromeus makelai'' and ''Orodromeus niedae'', were named and shortly described by Jack Horner and David B. Weishampel in 1988. The generic name is derived from Greek ὄρος, ''oros'', "mountain", in reference to the Egg Mountain site, and δρομεύς, ''dromeus'', "runner", referring to the cursorial habits of the animal. The specific name honoured the late Makela.Horner, J. and Weishampel, D., 1988, "A comparative embryological study of two ornithischian dinosaurs", ''Nature'' (London), 332(No. 6161): 256-257 (1988) The hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiasaura
''Maiasaura'' (from the Greek ''μαῖα'', meaning "midwife" and ''σαύρα'', the feminine form of ''saurus'', meaning "reptile") is a large herbivorous saurolophine hadrosaurid ("duck-billed") dinosaur genus that lived in the area currently covered by the state of Montana and the Canadian province of Alberta, in the Upper Cretaceous Period (mid to late Campanian), from 86.3 to 70.6 million years ago.Horner, J. R., Schmitt, J. G., Jackson, F., & Hanna, R. (2001). Bones and rocks of the Upper Cretaceous Two Medicine-Judith River clastic wedge complex, Montana. In Field trip guidebook, Society of Vertebrate Paleontology 61st Annual Meeting: Mesozoic and Cenozoic Paleontology in the Western Plains and Rocky Mountains. Museum of the Rockies Occasional Paper (Vol. 3, pp. 3-14). ''Maiasaura peeblesorum'' is the state fossil of Montana. The first remains of ''Maiasaura'' ''peeblesorum'' were discovered in the Two Medicine Formation near Chouteau, Montana in 1978 by Bynum, Montana r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
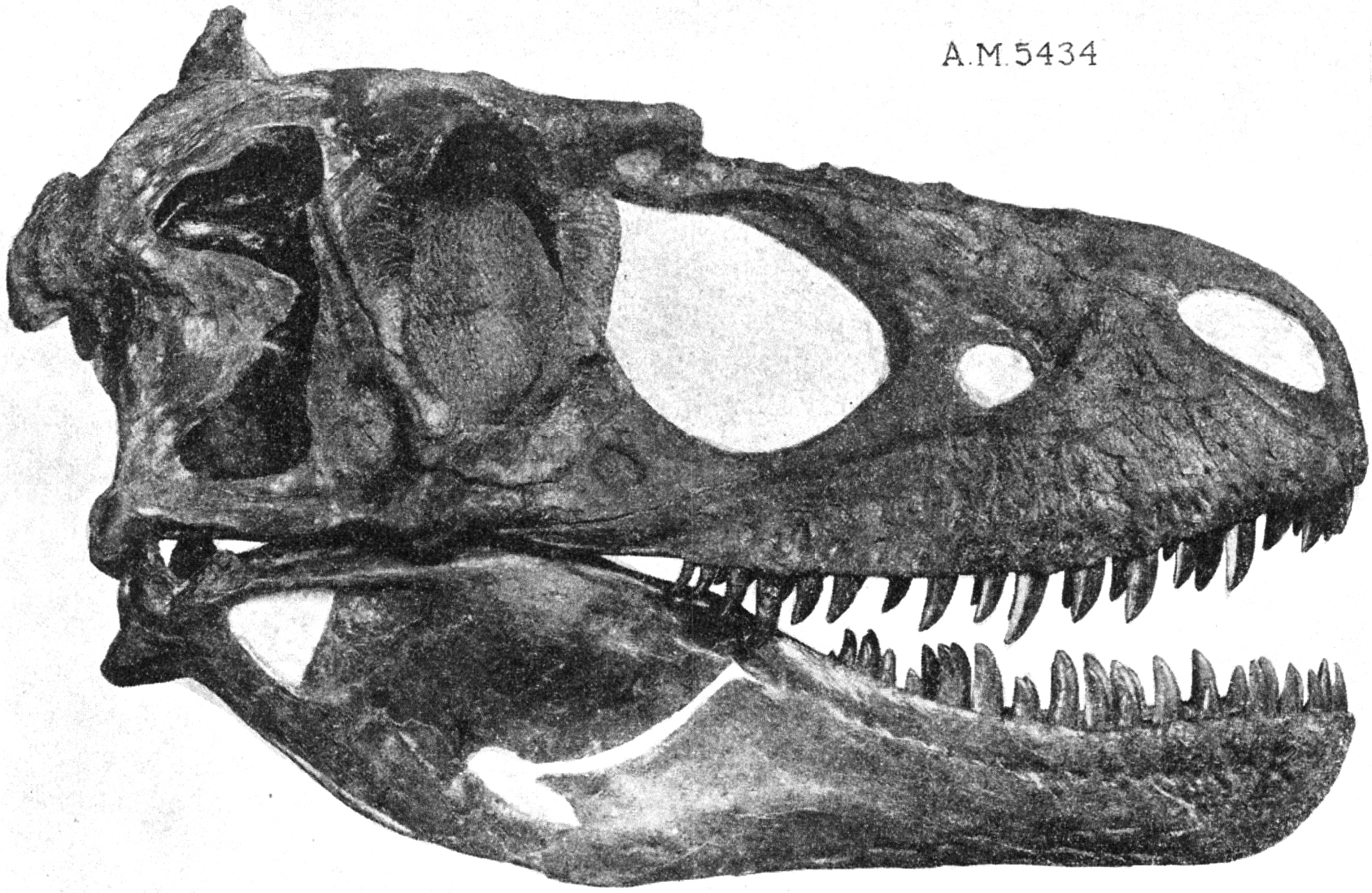
Daspletosaurus
''Daspletosaurus'' ( ; meaning "frightful lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Laramidia between about 77 and 74.4 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus ''Daspletosaurus'' contains three named species. Fossils of the earlier type species, ''D. torosus'', have been found in Alberta, while fossils of a later species, ''D. horneri'', have been found only in Montana. ''D. wilsoni'' has been suggested as an intermediate species between ''D. torosus'' and ''D. horneri'' that evolved through anagenesis, though further research may be required to definitively support the theory. There are also multiple specimens which may represent new species of ''Daspletosaurus'' from Alberta and Montana, but these have not been formally described. The taxon '' Thanatotheristes'' has been suggested to represent a species of ''Daspletosaurus'', ''D. degrootorum'', but this has not been widely supported. ''Daspletosaurus'' is closely related to the much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an animal moves by means of its two rear (or lower) Limb (anatomy), limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' and ''pes'' 'foot'). Types of bipedal movement include walking or running (a bipedal gait) and jumping, hopping. Several groups of modern species are habitual bipeds whose normal method of locomotion is two-legged. In the Triassic period some groups of archosaurs (a group that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs) developed bipedalism; among the dinosaurs, all the early forms and many later groups were habitual or exclusive bipeds; the birds are members of a clade of exclusively bipedal dinosaurs, the theropods. Within mammals, habitual bipedalism has evolved multiple times, with the Macropodidae, macropods, Dipodomyinae, kangaroo rats and mice, springhare, Hopping mouse, hopping mice, pangolins and hominin apes (austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenonychosaurus
''Stenonychosaurus'' (meaning "narrow claw lizard") is a disputed genus of troodontidae, troodontid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada, as well as possibly the Two Medicine Formation. The type and only species, ''S. inequalis'', was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. ''S. inequalis'' was reassigned in 1987 by Phil Currie to the genus ''Troodon'', which was reverted by the recognition of ''Stenonychosaurus'' as a separate genus from the possibly nomen dubium, dubious ''Troodon'' in 2017 by Evans ''et al.'' and also later in the same year by Van der Reest and Currie. History of discovery The first specimens currently assigned to ''Troodon'' that were not teeth were both found by Sternberg in 1928, in the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta. The first was named ''Stenonychosaurus inequalis'' by Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, frag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troodontidae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discoveries of complete and articulated specimens (including specimens which preserve feathers, eggs, embryos, and complete juveniles), have helped to increase understanding about this group. Anatomical studies, particularly studies of the most primitive troodontids, like '' Sinovenator'', demonstrate striking anatomical similarities with ''Archaeopteryx'' and primitive dromaeosaurids, and demonstrate that they are relatives comprising a clade called Paraves. Evolution The oldest definitive troodontid known is '' Hesperornithoides'' from the Late Jurassic of Wyoming. The slightly older '' Koparion'' of Utah is only represented by a single tooth, and small maniraptoran teeth from the Middle Jurassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been previously described or related species. For a species to be considered valid, a species description must follow established guidelines and naming conventions dictated by relevant nomenclature codes. These include the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) for animals, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) for plants, and the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) for viruses. A species description often includes photographs or other illustrations of type material and information regarding where this material is deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages ( limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hindlimb With reference to quadrupeds, the term hindleg or back leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term lower limb is often used. Location It is located on the limb of an animal. Hindlimbs are present in a large number of quadrupeds. Though it is a posterior limb, it can cause lameness in some animals. The way of walking through hindlimbs are called bipedalism. Benefits of hindlimbs Hindlimbs are helpful in many ways, some examples are: Frogs Frogs can easily adapt at the surroundings using hindlimbs. The main reason is it can jump high to easily escape to its predator and also to catch prey. It can perform some tricks using the hindlimbs such as the somersault a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch (eggs)
A clutch of eggs is the group of eggs produced by birds, amphibians, or reptiles, often at a single time, particularly those laid in a nest. In birds, destruction of a clutch by predators (or removal by humans, for example the California condor breeding program) results in ''double-clutching''. The technique is used to double the production of a species' eggs, in the California condor case, specifically to increase population size. Size Clutch size differs greatly between species, sometimes even within the same genus. It may also differ within the same species due to many factors including habitat, health, nutrition, predation pressures, and time of year. Clutch size variation can also reflect variation in optimal reproduction effort. In birds, clutch size can vary within a species due to various features (age and health of laying female, ability of male to supply food, and abundance of prey), while some species are determinant layers, laying a species-specific number of egg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype (biology), isotype nor a syntype). Often there is more than one paratype. Paratypes are usually held in museum research collections. The exact meaning of the term ''paratype'' when it is used in zoology is not the same as the meaning when it is used in botany. In both cases however, this term is used in conjunction with ''holotype''. Zoology In zoological nomenclature, a paratype is officially defined as "Each specimen of a type series other than the holotype.", ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' In turn, this definition relies on the definition of a "type series". A type series is the material (specimens of organisms) that was cited in the original publication of the new species or subspecies, and was not excluded from being type material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Million Years Ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds. Usage Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya or Ma. Together they make a reference system, one to a quantity, the other to a particular point in a year numbering system that is ''time before the present''. Myr is deprecated in geology, but in astronomy ''Myr'' is standard. Where "myr" ''is'' seen in geology, it is usually "Myr" (a unit of mega-years). In astronomy, it is usually "Myr" (Million years). Debate In geology, a debate remains open concerning the use of ''Myr'' (duration) plus ''Mya'' (million years ago) versus using only the term ''Ma''. In either case, the term '' Ma'' is used in geology literature conforming to ISO 31-1 (now ISO 80000-3) and NIST 811 recommended practices. Traditional style geology literature is written: The "ago" is implied, so that any s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |