|
Oriel Square
Oriel Square, formerly known as Canterbury Square, Hibbert, Christopher, ''The Encyclopedia of Oxford''. London: Pan Macmillan, 1988, pp. 295β296. . is a square in central Oxford Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ..., England, located south of the High Street, Oxford, High Street. The name was changed after the World War II, Second World War at the request of Oriel College, Oxford, Oriel College which maintained that the square had originally been known as Oriel Square. Location To the east at the southern end is the cobbled Merton Street and to the north are King Edward Street and Oriel Street. To the west at the northern end is Bear Lane. Oriel College, one of the older colleges of the University of Oxford, fronts onto the square to the east. Canterbury Gate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear Lane
Bear Lane is a short historic street in central Oxford, England. The lane is located just north of Christ Church. It runs between the junction of Blue Boar Street and Alfred Street to the west, and King Edward Street and the north of Oriel Square to the east. The south side of Bear Lane faces the back of Christ Church's Peckwater Quad while the north side opens onto a sizeable accommodation complex belonging to Lincoln College. The complex, known to students simply as ''Bear Lane'', houses over a hundred students and reaches all the way to High Street. The site was inherited by the College from Emmelina Carr in 1436. A residential centre for graduate studies was opened in 1977, designed by Geoffrey Beard. Further student accommodation for the College has been added between Bear Lane and the High Street to the north, completed in 1995. This building complex incorporates many historic features, including the Painted Room, which has 16th-century frescoes and panelling. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman, (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architecture, helping to save St Pancras railway station from demolition. He began his career as a journalist and ended it as one of the most popular British Poets Laureate and a much-loved figure on British television. Life Early life and education Betjeman was born in London to a prosperous silverware maker of Dutch descent. His parents, Mabel () and Ernest Betjemann, had a family firm at 34β42 Pentonville Road which manufactured the kind of ornamental household furniture and gadgets distinctive to Victorians. During the First World War the family name was changed to the less German-looking Betjeman. His father's forebears had actually come from the present day Netherlands more than a century earlier, setting up their home and business in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inspector Morse (TV Series)
Endeavour Morse, George Medal, GM, is the namesake character of the series of "Morse" detective novels by British author Colin Dexter, a Detective Chief Inspector in the Thames Valley Police in Oxford, England, Oxford, England. On television he was portrayed by John Thaw in a 33-episode drama series, ''Inspector Morse (TV series), Inspector Morse'' (1987β2000), and by Shaun Evans in the (2012β2023) prequel series ''Endeavour (TV series), Endeavour''. The older Morse is a senior Criminal Investigation Department (CID) officer, while the younger is a detective constable rising through the ranks with the Oxford City Police and, in later seasons, the Thames Valley Police. Morse presents, to some, a reasonably sympathetic personality, despite his sullen and snobbish temperament. He is known for his classic Jaguar Mark 2 (a Lancia in the early novels), thirst for English real ale, and love of classical music (especially opera and Richard Wagner, Wagner), poetry, art and cryptic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
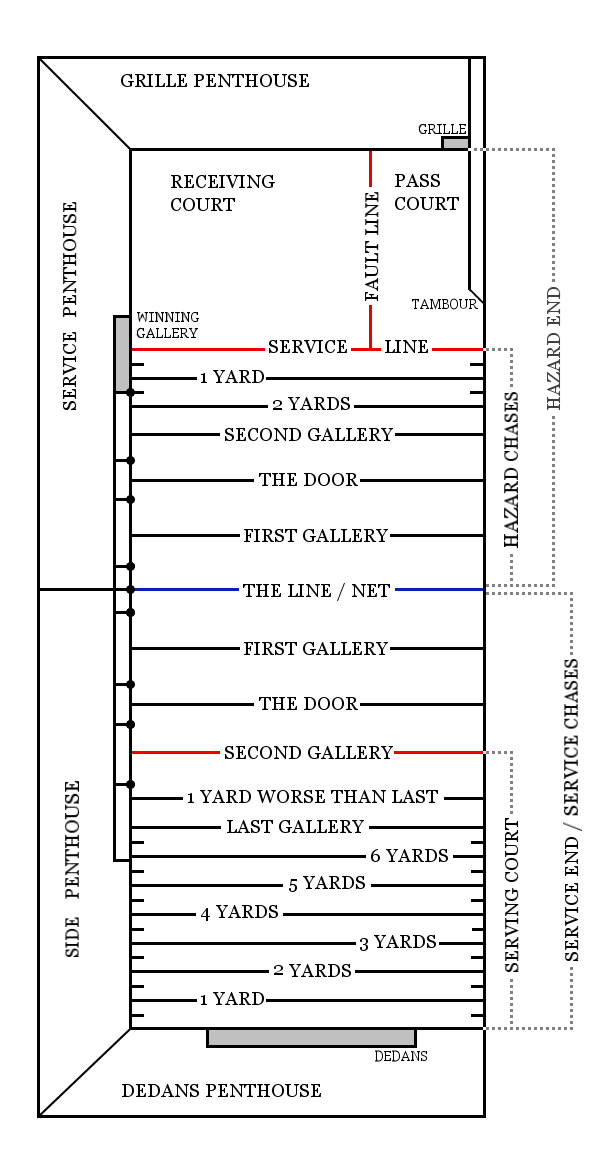
Merton Street Tennis Court
Merton Street tennis court is the home of the Oxford University Real Tennis Club. It stands on the north side of Merton Street in central Oxford, England, and forms part of Merton College. There has been a tennis court in Oxford since 1450 and one at the Merton Street site since c. 1494, according to one source. Alternatively, according to another source, Oxford has had a court since 1595 and one at this site when it was rebuilt in 1798. The Merton Street court, being early, has somewhat non-standard dimensions, and in particular an unusually flat tambour (a buttress used as part of the court). It is the smallest court in England and the second oldest. See also * Oriel Square tennis court __NOTOC__ The Oriel Square tennis court was a real tennis court that was located in Oriel Square, central Oxford, England. The ''Liber Albus'' mentions the Oriel court being in Vinehall Lane in 1577.Crossley, Alan (editor), 'Social and Cultural ... References Bibliography * ''Tennis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Tennis
Real tennis β one of several games sometimes called "the sport of kings" β is the original racquet sport from which the modern game of tennis (also called "lawn tennis") is derived. It is also known as court tennis in the United States, royal tennis in England and Australia, and ''courte-paume'' in France (to distinguish it from longue-paume, and in reference to the older, racquetless game of '' jeu de paume'', the ancestor of modern handball and racquet games). Many French real tennis courts are at ''jeu de paume'' clubs. The term ''real'' was first used by journalists in the early 20th century as a retronym to distinguish the ancient game from modern ''lawn'' tennis (even though, at present, the latter sport is seldom contested on lawns outside the few social-club-managed estates such as Wimbledon). There are just 45 active real tennis courts in the world, located in the United Kingdom, Australia, the United States and France. There are also currently six disu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriel Square Tennis Court
__NOTOC__ The Oriel Square tennis court was a real tennis court that was located in Oriel Square, central Oxford, England. The ''Liber Albus'' mentions the Oriel court being in Vinehall Lane in 1577.Crossley, Alan (editor), 'Social and Cultural Activities', ''A History of the County of Oxford: Volume 4: The City of Oxford'' (1979) β Oxford University PresBritish History Online Charles I of England, Charles I played tennis here with his nephew Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Prince Rupert in December 1642 and Edward VII of the United Kingdom, the future King Edward VII, accompanied by the Duke of Marlborough, played tennis here in 1859. The court survived until 1923, when it was used as a lecture hall by Oriel College, Oxford, Oriel College, though it may have seen earlier use as a theatre. The site is now the location of Oriel College's Harris Building, used for student accommodation, a seminar room and lecture theatre. The only active court left in the city is the Merton Street ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A420 Road
The A420 is a road between Bristol and Oxford in England. Between Swindon and Oxford it is a primary route. Route Since the opening of the M4 motorway in the 1970s, the road has been in two sections. The first section begins on Old Market Street near the centre of Bristol and passes through Kingswood before leaving the city on the east side. From here it travels eastward over the southern part of the Cotswolds, to the north of Bath, to Chippenham in Wiltshire. The second section begins at a junction with the A419 east of Swindon. It then travels under the Great Western Main Line at the twin-arch Acorn Bridge (the second arch was originally used by the Wilts & Berks Canal) and past Shrivenham and Watchfield (both bypassed in the 1980s), then on towards Faringdon in the Vale of White Horse. A further by-pass section, opened in 1979, avoids the centre of Faringdon, passing just south of Folly Hill and crossing the A417. The A420 then travels the corallian limestone ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ Church, Oxford
Christ Church (, the temple or house, ''wikt:aedes, Γ¦des'', of Christ, and thus sometimes known as "The House") is a Colleges of the University of Oxford, constituent college of the University of Oxford in England. Founded in 1546 by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII, the college is uniquely a joint foundation of the university and the cathedral of the Oxford diocese, Christ Church Cathedral, Oxford, Christ Church Cathedral, which also serves as the college chapel and whose Dean of Christ Church, Oxford, dean is ''ex officio'' the college head. As of 2022, the college had 661 students. Its grounds contain a number of architecturally significant buildings including Tom Tower (designed by Christopher Wren, Sir Christopher Wren), Tom Quad (the largest quadrangle in Oxford), and the Great Dining Hall, which was the seat of the Oxford Parliament (1644), parliament assembled by Charles I of England, King Charles I during the English Civil War. The buildings have inspired repli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II of England, Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English Ancient university, ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 Colleges of the University of Oxford, semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriel Street
Oriel Street is a narrow but historic street running between the High Street, Oxford, High Street to the north and Oriel Square to the south in central Oxford, England. The street is now blocked off to traffic by bollards at the High Street end. It passes between the main site of Oriel College, Oxford, Oriel College (hence its name) to the east and Oriel's newer "Island" site to the west. At the High Street end to the east is the 1911 ''Rhodes Building'', named after the former Oriel student Cecil John Rhodes, Cecil Rhodes, who went on to colonize the African state of Rhodesia (also named after him). History The name Oriel Street was in use by 1850. From 1210 it was called Schidyard Street, although the spelling changed over time, according to Thomas Hearne (antiquarian), Thomas Hearne in 1728 it was Sched Row β ''Writers' Row'',Christopher Hibbert, Hibbert, Christopher, ''The Encyclopedia of Oxford'' London: Macmillan Publishers, Macmillan 1988 p. 296 and between 1542 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |