|
Orellanine
Orellanine or orellanin is a mycotoxin found in a group of mushrooms known as the Orellani within the family Cortinariaceae. Structurally, it is a pyridine N-oxide, bipyridine N-oxide compound somewhat related to the herbicide diquat. History Orellanine first came to people's attention in 1952 when a mass poisoning of 102 people in Konin, Poland, resulted in 11 deaths. Orellanine comes from a class of mushrooms that fall under the genus ''Cortinarius,'' and has been found in the species ''Cortinarius orellanus, C. orellanus'', ''Cortinarius rubellus, rubellus'', ''henrici'', ''Cortinarius rainierensis, rainerensis'' and ''bruneofulvus''. Poisonings related to these mushrooms have occurred predominately in Europe where mushroom foraging was common, though cases of orellanine poisoning have been reported in North America and Australia as well. There are several reported cases of people ingesting orellanine-containing mushrooms after mistaking them for Edible mushroom, edible or Psilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orellanine Tautomerization
Orellanine or orellanin is a mycotoxin A mycotoxin (from the Greek μύκης , "fungus" and τοξικός , "poisonous") is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by fungi and is capable of causing disease and death in both humans and other animals. The term 'mycotoxin' is usually rese ... found in a group of mushrooms known as the Orellani within the family Cortinariaceae. Structurally, it is a bipyridine N-oxide compound somewhat related to the herbicide diquat. History Orellanine first came to people's attention in 1952 when a mass poisoning of 102 people in Konin, Poland, resulted in 11 deaths. Orellanine comes from a class of mushrooms that fall under the genus ''Cortinarius,'' and has been found in the species ''Cortinarius orellanus, C. orellanus'', ''Cortinarius rubellus, rubellus'', ''henrici'', ''Cortinarius rainierensis, rainerensis'' and ''bruneofulvus''. Poisonings related to these mushrooms have occurred predominately in Europe where mushroom foraging was common, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orellani
The Orellani are a group of seven related species in the genus ''Cortinarius'' that have been classified as a section of the subgenus ''Leprocybe'' or a subgenus in their own right. They are among world's most poisonous mushrooms as they contain the highly toxic compound orellanine. The best-known species are the deadly webcap ('' Cortinarius rubellus'', formerly also known as ''C. speciosissimus'' or ''C. orellanoides'') and the fool's webcap, '' C. orellanus''. The mushrooms' characteristics are quite common, making them difficult to identify, which often leads to fatal poisonings. Young examples of the species often have a veil between the cap of the mushroom and the stem. This veil looks like a cobweb, hence the name. The veil however partially or completely disappears in older specimens. Some other characteristics for each of the mushrooms are given below. Descriptions Deadly webcap ''(Cortinarius rubellus)'' ''Spore color'': Rusty brown to orange ''Cap'': 3–7 cm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called "total weed killers") kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields (per acre) of major crops by three to six times from 1900 to 2000. In the United States in 2012, about 91% of all herbicide usage, was determined by weight applied, in agriculture. In 2012, world pesticide expenditures totaled nearly US$24.7 billion; herbicides were about 44% of those sales and constituted the biggest portion, followed by insecticides, fungicides, and fumigants. Herbicide is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Ammonium Cation
In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure , where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphatase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life. Some such enzymes are integral membrane proteins (anchored within biological membranes), and move solutes across the membrane, typically against their concentration gradient. These are called transmembrane ATPases. Functions Transmembrane ATPases import metabolites necessary for cell metabolism and export toxins, wastes, and solutes that can hinder cellular processes. An important example is the sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ATPase) that maintains the cell membrane potential. Another example is the hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
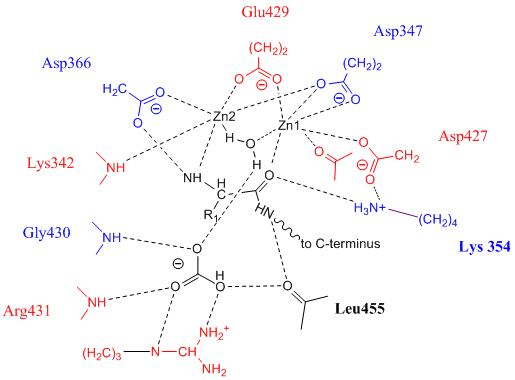
Leucyl Aminopeptidase
Leucyl aminopeptidases (, ''leucine aminopeptidase'', ''LAPs'', ''leucyl peptidase'', ''peptidase S'', ''cytosol aminopeptidase'', ''cathepsin III'', ''L-leucine aminopeptidase'', ''leucinaminopeptidase'', ''leucinamide aminopeptidase'', ''FTBL proteins'', ''proteinates FTBL'', ''aminopeptidase II'', ''aminopeptidase III'', ''aminopeptidase I'') are enzymes that preferentially catalyze the hydrolysis of leucine residues at the N-terminus of peptides and proteins. Other N-terminal residues can also be cleaved, however. LAPs have been found across superkingdoms. Identified LAPs include human LAP, bovine lens LAP, porcine LAP, ''Escherichia coli'' (''E. coli'') LAP (also known as PepA or XerB), and the solanaceous-specific acidic LAP (LAP-A) in tomato (''Solanum lycopersicum''). Enzyme description, structure, and active site The active sites in PepA and in bovine lens LAP have been found to be similar. Shown in the picture below is the proposed model for the active site of LAP-A i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-glutamyltransferase
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (also γ-glutamyltransferase, GGT, gamma-GT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; ) is a transferase (a type of enzyme) that catalyzes the transfer of gamma- glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathione to an acceptor that may be an amino acid, a peptide or water (forming glutamate). GGT plays a key role in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a pathway for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione as well as drug and xenobiotic detoxification. Other lines of evidence indicate that GGT can also exert a pro-oxidant role, with regulatory effects at various levels in cellular signal transduction and cellular pathophysiology. This transferase is found in many tissues, the most notable one being the liver, and has significance in medicine as a diagnostic marker. Nomenclature The name γ-glutamyltransferase is preferred by the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. The Expert Panel on Enzymes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function, but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of '' E. coli'' bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia. The level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is checked through the ALP test, which is often par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-competitive Inhibition
Non-competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme and binds equally well to the enzyme regardless of whether it has already bound the substrate. This is unlike competitive inhibition, where binding affinity for the substrate in the enzyme is decreased in the presence of an inhibitor. The inhibitor may bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already been bound, but if it has a higher affinity for binding the enzyme in one state or the other, it is called a mixed inhibitor. History During his years working as a physician Leonor Michaelis and a friend Peter Rona built a compact lab, in the hospital, and over the course of five years – Michaelis successfully became published over 100 times. During his research in the hospital, he was the first to view the different types of inhibition; specifically using fructose and glucose as inhibitors of maltase activity. Maltase breaks maltose into two units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as vitamins and hormones. A general name for this class of material is ''biological materials''. Biomolecules are an important element of living organisms. They are often endogeny (biology), endogenous, i.e. produced within the organism, but organisms usually also need exogeny, exogenous biomolecules, for example certain nutrients, to survive. Biomolecules and their organic reaction, reactions are studied in biology and its subfields of biochemistry and molecular biology. Most biomolecules are organic compounds, and just four chemical element, elements—oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen—make up 96% of the human body's mass. But many other elements, such as the various biometal (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |