|
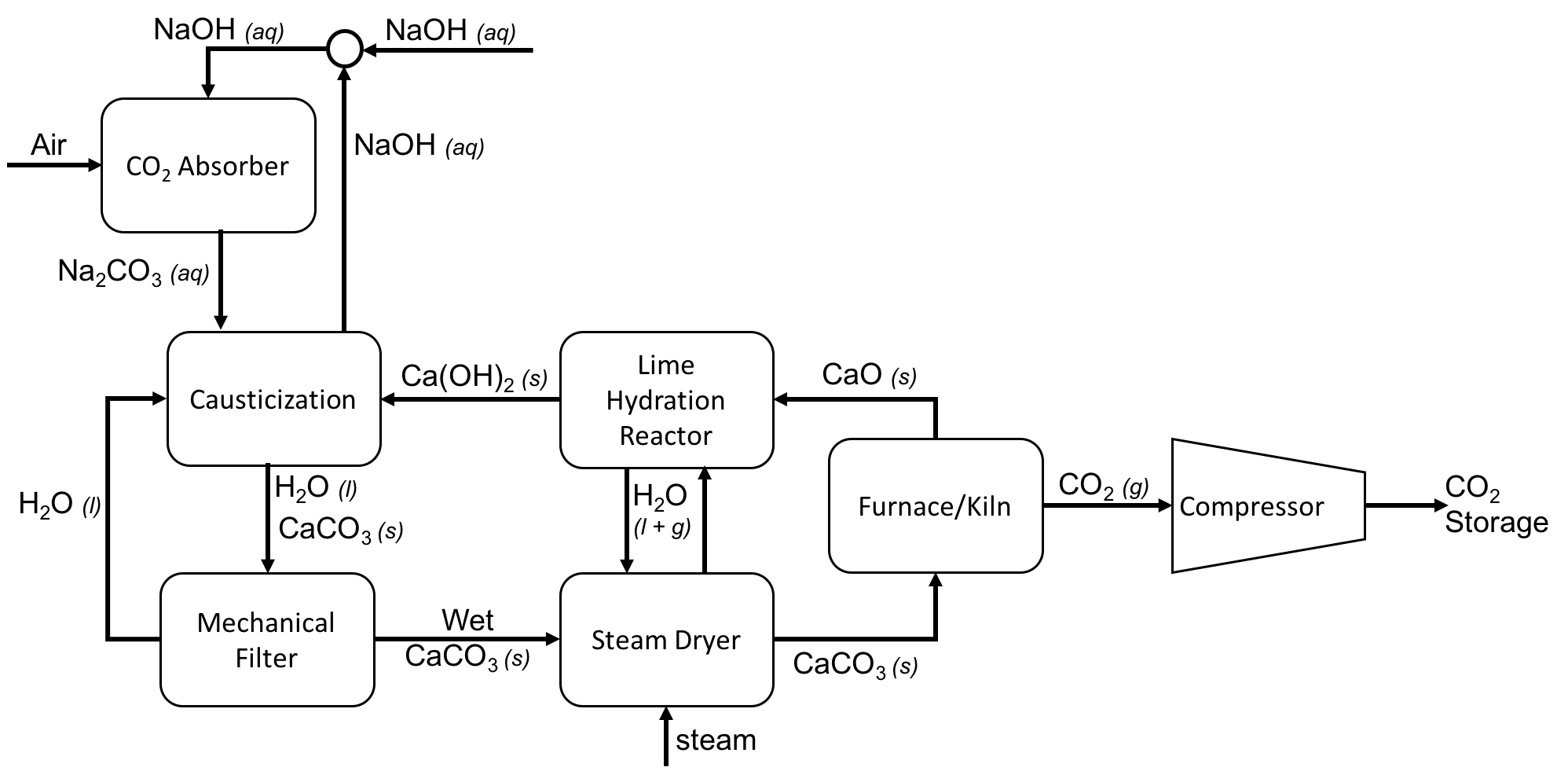
Orca (carbon Capture Plant)
The Orca carbon capture plant is a facility that uses direct air capture to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It was constructed by Climeworks and is joint work with Carbfix, an academic-industrial partnership that has developed a novel approach to capture . The plant uses dozens of large fans to pull in air and pass it through a filter. The filter is then released of the it contains through heat. The extracted is later mixed with water and pushed into the ground, using a technology from Carbfix. The plant started sequestering carbon dioxide in 2021. It is said to have cost between $10–15 million to build. It is located in Iceland and is the largest facility of its kind on earth. It is located about 50 kilometers outside Reykjavík next to the Hellisheiði Power Station, which is run by Reykjavík Energy. It was inaugurated on 8 September 2021 in presence of Katrín Jakobsdóttir, the Prime Minister of Iceland. Carbon offsetting potential Climeworks claims that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Air Capture
Direct air capture (DAC) is a process of capturing carbon dioxide () directly from the ambient air (as opposed to capturing from point sources, such as a cement factory or biomass power plant) and generating a concentrated stream of for sequestration or utilization or production of carbon-neutral fuel and windgas. Carbon dioxide removal is achieved when ambient air makes contact with chemical media, typically an aqueous alkaline solvent or sorbents. These chemical media are subsequently stripped of CO2 through the application of energy (namely heat), resulting in a CO2 stream that can undergo dehydration and compression, while simultaneously regenerating the chemical media for reuse. DAC was suggested in 1999 by Klaus S. Lackner and is still in development. Several commercial plants are planned or in operation in Europe and the US. Large-scale DAC deployment may be accelerated when connected with economical applications or policy incentives. In contrast to carbon capture a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climeworks
Climeworks AG is a Swiss company specializing in carbon dioxide air capture technology. The company filters directly from the ambient air through an adsorption-desorption process. Climeworks refers to the filtering of from the ambient air for underground storage as carbon dioxide removal. History Christoph Gebald and Jan Wurzbacher founded Climeworks in November 2009 as a spin-off from ETH Zurich. The two German founders were fellow students in mechanical engineering and had worked with technologies for chemical and physical in the context of their studies and subsequent doctorates. In 2011, Climeworks received capital from investors for the first time to develop a prototype with a modular structure. Since then, rapid scaling has led to their present module technology, which has been available since 2014. In the course of the enterprise's development, a partnership with the automaker Audi succeeded. Further support was provided by the Swiss Federal Office of Energy, which e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequestering Carbon
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in land use and agricultural practices, such as converting crop land into land for non-crop fast growing plants. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks, bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, enhanced weathering, direct air capture and water capture when combined with storage. Forests, kelp beds, and other forms of plant life absorb carbon dioxide from the air as they grow, and bind it into biomass. However, these biological stores are considered volatile carbon sinks as the long-term sequestration cannot be guaranteed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sport .... It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited, Scott Trust. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Economist Group, with its core editorial offices in the United States, as well as across major cities in continental Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. In 2019, its average global print circulation was over 909,476; this, combined with its digital presence, runs to over 1.6 million. Across its social media platforms, it reaches an audience of 35 million, as of 2016. The newspaper has a prominent focus on data journalism and interpretive analysis over original reporting, to both criticism and acclaim. Founded in 1843, ''The Economist'' was first circulated by Scottish economist James Wilson to muster support for abolishing the British Corn Laws (1815–1846), a system of import tariffs. Over time, the newspaper's coverage expanded furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reykjavík
Reykjavík ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxaflói bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a population of around 131,136 (and 233,034 in the Capital Region), it is the centre of Iceland's cultural, economic, and governmental activity, and is a popular tourist destination. Reykjavík is believed to be the location of the first permanent settlement in Iceland, which, according to Landnámabók, was established by Ingólfr Arnarson in 874 CE. Until the 18th century, there was no urban development in the city location. The city was officially founded in 1786 as a trading town and grew steadily over the following decades, as it transformed into a regional and later national centre of commerce, population, and governmental activities. It is among the cleanest, greenest, and safest cities in the world. History According to legend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellisheiði Power Station
The Hellisheiði Power Station ( is, Hellisheiðarvirkjun, ) is the eighth-largest geothermal power station in the world and largest in Iceland. The facility is located in Hengill, southwest Iceland, from the Nesjavellir Geothermal Power Station. The plant has a capacity of of electricity and th of hot water for Reykjavik's district heating. The power station is owned and operated by ON Power, a subsidiary of Reykjavík Energy. History Electricity production with two turbines commenced in 2006. In 2007, an additional low pressure steam turbine of was added. In 2008, two turbines were added with steam from Skarðsmýrarfjall Mountain. The hot water plant was introduced in 2010 and the last two high pressure 45 MW turbines were added in 2011. In order to reduce hydrogen sulphide pollution in the capital area a system was added to the plant in 2014 which reinjects non-condensable gases into the ground. Renewed drilling In 2016 the operator, ON, announced a program o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katrín Jakobsdóttir
Katrín Jakobsdóttir (; born 1 February 1976) is an Icelandic politician who has been serving as the prime minister of Iceland since 2017 and a member of the Althing for the Reykjavík North constituency since 2007. A graduate of the University of Iceland, she became deputy chairperson of the Left-Green Movement in 2003, and has been their chairperson since 2013. Katrín was Iceland's minister of education, science, and culture, and of Nordic co-operation from 2 February 2009 to 23 May 2013. She is Iceland's second female prime minister, after Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir. On 19 February 2020, she was named Chair of the Council of Women World Leaders. Education Born in Reykjavík, Katrín graduated from the University of Iceland in 1999 with a bachelor's degree, with a major in Icelandic and a minor in French. She went on to complete a Master of Arts degree in Icelandic literature at the University of Iceland in 2004, for a thesis on the work of popular Icelandic crime wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |