|
Oracle Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance
The Oracle Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance (Recovery Appliance or ZDLRA) is a computing platform that includes Oracle Corporation (Oracle) Engineered Systems hardware and software built for backup and recovery of the Oracle Database. It performs continuous data protection, data validation , validates backups, automatically resolves many issues, and provides alerts when backups fail validation. It is designed for Oracle databases and works only on Oracle databases. It is considered a 3rd party backup and recovery product. It was introduced in 2014 as part of Oracle Corporation's family of "Engineered Systems" and shares components with the Oracle Exadata Database Machine, with an additional layer of software that provides specific features for backup, Data recovery, recovery, Replication (computing), replication, monitoring, and management. Like the Oracle Exadata Database Machine, it is periodically refreshed as a new interoperable and expandable “generation” based on ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Co-founded in 1977 in Santa Clara, California, by Larry Ellison, who remains executive chairman, Oracle was the List of the largest software companies, third-largest software company in the world in 2020 by revenue and market capitalization. The company's 2023 ranking in the Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 80. The company sells Database, database software, particularly Oracle Database, and cloud computing. Oracle's core application software is a suite of enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, Customer Experience Commerce (CX Commerce) and supply chain management (SCM) software. History Larry Ellison, Bob Miner, and Ed Oates co-founded Oracle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Linux
Oracle Linux (abbreviated OL, formerly known as Oracle Enterprise Linux or OEL) is a Linux distribution packaged and freely distributed by Oracle, available partially under the GNU General Public License since late 2006. It is, in part, compiled from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) source code, replacing Red Hat branding with Oracle's. It is also used by Oracle Cloud and Oracle Engineered Systems such as Oracle Exadata and others. Potential users can freely download Oracle Linux through Oracle's server, or from a variety of mirror sites, and can deploy and distribute it without cost. The company's ''Oracle Linux Support program'' aims to provide commercial technical support, covering Oracle Linux and existing RHEL or CentOS installations but without any certification from the former (i.e. without re-installation or re-boot). Oracle Linux had over 15,000 customers subscribed to the support program. RHEL compatibility Oracle Corporation distributes Oracle Linux with two Linux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Validation
In computing, data validation or input validation is the process of ensuring data has undergone data cleansing to confirm it has data quality, that is, that it is both correct and useful. It uses routines, often called "validation rules", "validation constraints", or "check routines", that check for correctness, meaningfulness, and security of data that are input to the system. The rules may be implemented through the automated facilities of a data dictionary, or by the inclusion of explicit application program validation logic of the computer and its application. This is distinct from formal verification, which attempts to prove or disprove the correctness of algorithms for implementing a specification or property. Overview Data validation is intended to provide certain well-defined guarantees for fitness and consistency of data in an application or automated system. Data validation rules can be defined and designed using various methodologies, and be deployed in various conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Exadata
Oracle Exadata (Exadata) is a computing system optimized for running Oracle Databases. Exadata is a combined database machine and software platform that includes scale-out x86-64 compute and storage servers, RoCE networking, RDMA-addressable memory acceleration, NVMe flash, and specialized software. Exadata was introduced in 2008 for on-premises deployment, and since October 2015, via the Oracle Cloud as a subscription service, known as the ''Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure,'' and ''Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure''. ''Exadata Cloud@Customer'' is a hybrid cloud (on-premises) deployment of Exadata Database Service. Starting December, 2023, Exadata Database Service became available for Microsoft Azure, Google and AWS public clouds within the ''Oracle Database@Azure'', ''Oracle Database@Google Cloud'' and ''Oracle Database@AWS'multicloud partnerships Use cases Exadata is designed to run all Oracle Database workloads, such as OLTP, Data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back up, back up", whereas the noun and adjective form is "wikt:backup, backup". Backups can be used to data recovery, recover data after its loss from File deletion, data deletion or Data corruption, corruption, or to recover data from an earlier time. Backups provide a simple form of IT disaster recovery; however not all backup systems are able to reconstitute a computer system or other complex configuration such as a computer cluster, active directory server, or database server. A backup system contains at least one copy of all data considered worth saving. The computer data storage, data storage requirements can be large. An information repository model may be used to provide structure to this storage. There are different types of data stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Recovery
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, overwritten or formatted data from computer data storage#Secondary storage, secondary storage, removable media or Computer file, files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, Magnetic-tape data storage, magnetic tapes, Compact disc, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronics, electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being Mount (computing), mounted by the host operating system (OS). Logical failures occur when the hard drive devices are functional but the user or automated-OS cannot retrieve or access data stored on them. Logical failures can occur due to corruption of the engineering chip, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication (computing)
Replication in computing refers to maintaining multiple copies of data, processes, or resources to ensure consistency across redundant components. This fundamental technique spans databases, file systems, and distributed systems, serving to improve availability, fault-tolerance, accessibility, and performance. Through replication, systems can continue operating when components fail ( failover), serve requests from geographically distributed locations, and balance load across multiple machines. The challenge lies in maintaining consistency between replicas while managing the fundamental tradeoffs between data consistency, system availability, and network partition tolerance – constraints known as the CAP theorem. Terminology Replication in computing can refer to: * ''Data replication'', where the same data is stored on multiple storage devices * ''Computation replication'', where the same computing task is executed many times. Computational tasks may be: ** ''Replicated in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gbit/s
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits ( bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multiples of bits per second (bit/s) and bytes per second (B/s). For example, the data rates of modern residential high-speed Internet connections are commonly expressed in megabits per second (Mbit/s). Standards for unit symbols and prefixes Unit symbol The ISQ symbols for the bit and byte are ''bit'' and ''B'', respectively. In the context of data-rate units, one byte consists of 8 bits, and is synonymous with the unit octet. The abbreviation bps is often used to mean bit/s, so that when a ''1 Mbps'' connection is advertised, it usually means that the maximum achievable bandwidth is 1 Mbit/s (one million bits per second), which is 0.125 MB/s ( megabyte per second), or about 0.1192 MiB/s ( mebibyte per second). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
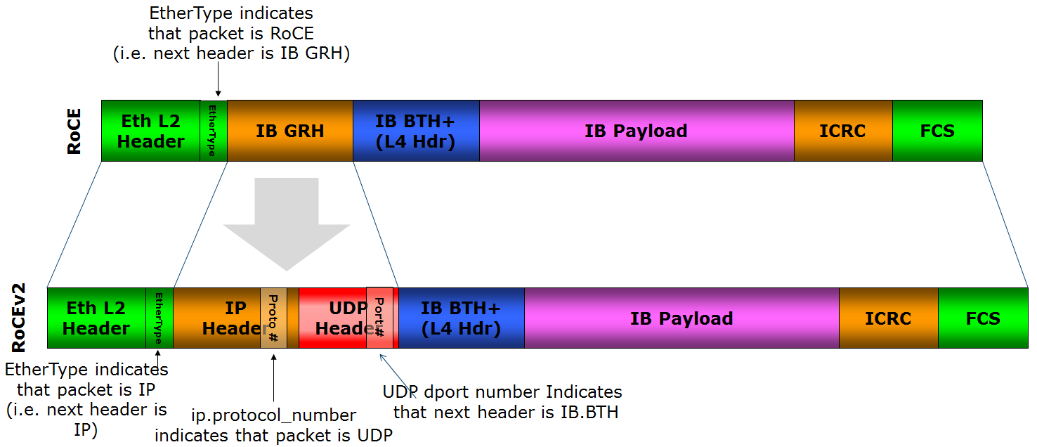
RDMA Over Converged Ethernet
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is a network protocol which allows remote direct memory access (RDMA) over an Ethernet network. There are multiple RoCE versions. RoCE v1 is an Ethernet link layer protocol and hence allows communication between any two hosts in the same Ethernet broadcast domain. RoCE v2 is an internet layer protocol which means that RoCE v2 packets can be routed. Although the RoCE protocol benefits from the characteristics of a converged Ethernet network, the protocol can also be used on a traditional or non-converged Ethernet network. Background Network-intensive applications like networked storage or cluster computing need a network infrastructure with a high bandwidth and low latency. The advantages of RDMA over other network application programming interfaces such as Berkeley sockets are lower latency, lower CPU load and higher bandwidth. The RoCE protocol allows lower latencies than its predecessor, the iWARP protocol. There are RoCE HCAs (Host Channel A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Direct Memory Access
In computing, remote direct memory access (RDMA) is a direct memory access from the memory of one computer into that of another without involving either one's operating system. This permits high-throughput, low- latency networking, which is especially useful in massively parallel computer clusters. Overview RDMA supports zero-copy networking by enabling the network adapter to transfer data from the wire directly to application memory or from application memory directly to the wire, eliminating the need to copy data between application memory and the data buffers in the operating system. Such transfers require no work to be done by CPUs, caches, or context switches, and transfers continue in parallel with other system operations. This reduces latency in message transfer. However, this strategy presents several problems related to the fact that the target node is not notified of the completion of the request (single-sided communications). Acceptance As of 2018 RDMA had achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Converged Ethernet
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks. Motivation Ethernet is the primary network protocol in data centers for computer-to-computer communications. However, Ethernet is designed to be a best-effort network that may experience packet loss when the network or devices are busy. In IP networks, transport reliability under the end-to-end principle is the responsibility of the transport protocols, such as the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). One area of evolution for Ethernet is to add extensions to the existing protocol suite to provide reliability without requiring the complexity of TCP. With the move to 10 Gbit/s and faster transmission rates, there is also a desire for finer granularity in control of bandwidth allocation and to ensure it is used more effectively. These enhancements are particularly im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfiniBand
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology. Between 2014 and June 2016, it was the most commonly used interconnect in the TOP500 list of supercomputers. Mellanox (acquired by Nvidia) manufactures InfiniBand host bus adapters and network switches, which are used by large computer system and database vendors in their product lines. As a computer cluster interconnect, IB competes with Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Intel Omni-Path. The technology is promoted by the InfiniBand Trade Association. History InfiniBand originated in 1999 from the merger of two competing designs: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |