|
Operation Popeye
Operation Sober Popeye (Project Controlled Weather Popeye / Motorpool / Intermediary-Compatriot) was a military cloud-seeding project carried out by the U.S. Air Force during the Vietnam War in 1967–1972. The highly classified program attempted to extend the monsoon season over specific areas of the Ho Chi Minh Trail, in order to disrupt North Vietnamese military supplies by softening road surfaces and causing landslides. The former U.S. Secretary of Defense, Robert S. McNamara, was aware that there might be objections raised by the international scientific community but said in a memo to the president that such objections had not in the past been a basis for prevention of military activities considered to be in the interests of U.S. national security. The chemical weather modification program was conducted from Thailand over Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam and allegedly sponsored by Secretary of State Henry Kissinger and the CIA without the authorization of then Secretary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud-seeding
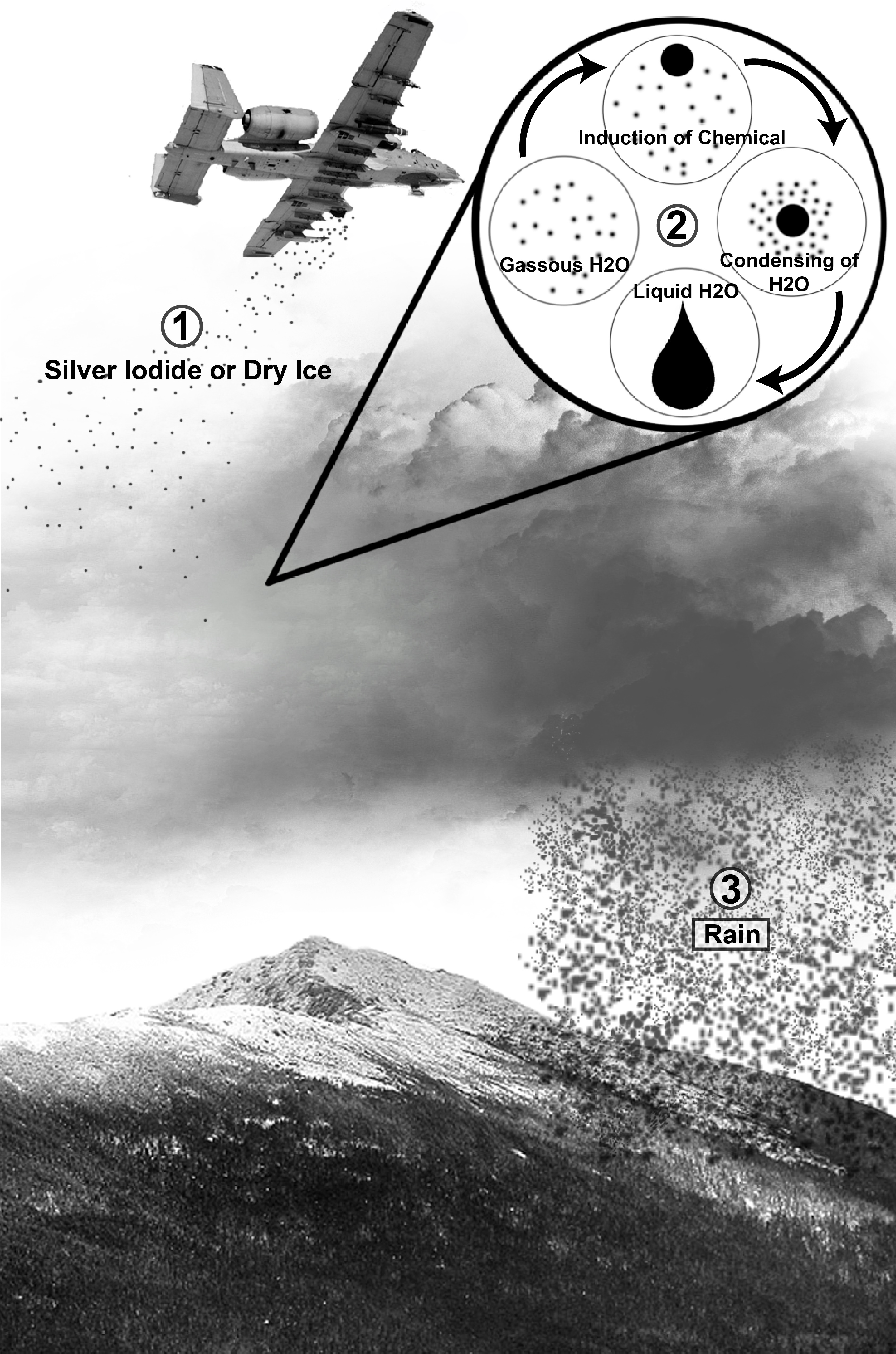
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud. Its effectiveness is debated; some studies have suggested that it is "difficult to show clearly that cloud seeding has a very large effect." The usual objective is to increase precipitation (rain or snow), either for its own sake or to prevent precipitation from occurring in days afterward. Methodologies Salts The most common chemicals used for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide and dry ice (solid carbon dioxide). Liquid propane, which expands into a gas, has also been used. This can produce ice crystals at higher temperatures than silver iodide. After promising research, the use of hygroscopic materials, such as table salt, is becoming more popular. When cloud seeding, increased snowfall t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud. Its effectiveness is debated; some studies have suggested that it is "difficult to show clearly that cloud seeding has a very large effect." The usual objective is to increase precipitation (rain or snow), either for its own sake or to prevent precipitation from occurring in days afterward. Methodologies Salts The most common chemicals used for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide and dry ice (solid carbon dioxide). Liquid propane, which expands into a gas, has also been used. This can produce ice crystals at higher temperatures than silver iodide. After promising research, the use of hygroscopic materials, such as table salt, is becoming more popular. When cloud seeding, increased sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Modification
Weather modification is the act of intentionally manipulating or altering the weather. The most common form of weather modification is cloud seeding, which increases rain or snow, usually for the purpose of increasing the local water supply. Weather modification can also have the goal of preventing damaging weather, such as hail or hurricanes, from occurring; or of provoking damaging weather against the enemy, as a tactic of military or economic warfare like Operation Popeye, where clouds were seeded to prolong the monsoon in Vietnam. Weather modification in warfare has been banned by the United Nations under the Environmental Modification Convention. History A popular belief in Northern Europe that shooting prevents hail caused many agricultural towns to fire cannons without ammunition. Veterans of the Seven Years' War, Napoleonic wars, and the American Civil War reported that rain fell after every large battle. After their stories were collected in ''War and Weather'', the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Warfare
Weather warfare is the use of weather modification techniques such as cloud seeding for military purposes. Background Use Prior to the Environmental Modification Convention signed in Geneva in 1977, the United States used weather warfare in the Vietnam War. Operation Popeye saw the use of cloud seeding over the Ho Chi Minh trail, increasing rainfall by an estimated thirty percent during 1967 and 1968. It was hoped that the increased rainfall would reduce the rate of infiltration down the trail.Transcript of the US Senate Hearing on Weather Modification of March 20, 1974 A research paper produced for the |
Environmental Modification Convention
The Environmental Modification Convention (ENMOD), formally the Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques is an international treaty prohibiting the military or other hostile use of environmental modification techniques having widespread, long-lasting or severe effects. It opened for signature on 18 May 1977 in Geneva and entered into force on 5 October 1978. The Convention bans weather warfare, which is the use of weather modification techniques for the purposes of inducing damage or destruction. The Convention on Biological Diversity of 2010 would also ban some forms of weather modification or geoengineering. Many states do not regard this as a complete ban on the use of herbicides in warfare, such as Agent Orange, but it does require case-by-case consideration. Parties The convention was signed by 48 states; 16 of the signatories have not ratified. As of 2022 the convention has 78 state parties. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claiborne Pell
Claiborne de Borda Pell (November 22, 1918 – January 1, 2009) was an American politician and writer who served as a U.S. Senator from Rhode Island for six terms from 1961 to 1997. He was the sponsor of the 1972 bill that reformed the Basic Educational Opportunity Grant, which provides financial aid funding to American college students; the grant was given Pell's name in 1980 in honor of his work in education legislation. A member of the Democratic Party, Pell is the longest serving U.S. Senator from Rhode Island. Early life and education Claiborne Pell was born on November 22, 1918, in New York City, the son of Matilda Bigelow and diplomat and congressman Herbert Pell. Pell's family members included John Francis Hamtramck Claiborne, George Mifflin Dallas, and Nathaniel Herbert Claiborne. He was a direct descendant of English mathematician John Pell and a descendant of Senator William C. C. Claiborne. The '' Congressional Record'' also reports that he was a direct des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentagon Papers
The ''Pentagon Papers'', officially titled ''Report of the Office of the Secretary of Defense Vietnam Task Force'', is a United States Department of Defense history of the United States in the Vietnam War, United States' political and military involvement in Vietnam from 1945 to 1967. Released by Daniel Ellsberg, who had worked on the study, they were first brought to the attention of the public on the front page of ''The New York Times'' in 1971. A 1996 article in ''The New York Times'' said that the ''Pentagon Papers'' had demonstrated, among other things, that the Presidency of Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson Administration had "systematically lied, not only to the public but also to Congress." The ''Pentagon Papers'' revealed that the U.S. had secretly enlarged the scope of its actions in the Vietnam War with coastal raids on North Vietnam and United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps attacks—none of which were reported in the mainstream media. For his disclosure of the ''Penta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Anderson (columnist)
Jack Northman Anderson (October 19, 1922 – December 17, 2005) was an American newspaper columnist, syndicated by United Features Syndicate, considered one of the founders of modern investigative journalism. Anderson won the 1972 Pulitzer Prize for National Reporting for his investigation on secret U.S. policy decision-making between the United States and Pakistan during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971. In addition to his newspaper career, Anderson also had a national radio show on the Mutual Broadcasting System, acted as Washington bureau chief of ''Parade'' magazine, and was a commentator on ABC-TV's ''Good Morning America'' for nine years. Among the exposés Anderson reported were the Nixon administration's investigation and harassment of John Lennon during its fight to deport Lennon; the continuing activities of fugitive Nazi officials in South America; and the savings and loan crisis. He revealed the history of a CIA plot to assassinate Fidel Castro and was credited for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; vi, Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed from 1945 to 1976 and was recognized in 1954. Both the North Vietnamese and South Vietnamese states ceased to exist when they unified as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. During the August Revolution following World War II, Vietnamese communist revolutionary Hồ Chí Minh, leader of the Việt Minh Front, declared independence on 2 September 1945, announcing the creation of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. The Việt Minh ("League for the Independence of Vietnam"), led by communists, was created in 1941 and designed to appeal to a wider population than the Indochinese Communist Party could command. From the very beginning, the DRV regime sought to consolidate power by purging other nationalist movements. Meanwhile, France moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udorn Royal Thai Air Force Base
Udorn Royal Thai Air Force Base (Udorn RTAFB) is a Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) base, the home of 23rd Wing Air Command. It is in the city of Udon Thani in northeastern Thailand and is the main airport serving the city and province. The RTAF 231 Squadron "Hunter" is assigned to Udorn, equipped with the Dassault/Dornier Alpha Jet-A. History Establishment Udorn RTAFB was established in the 1950s. The civil war inside Laos and fears of it spreading into Thailand led the Thai government to allow the United States to use covertly five Thai bases beginning in 1961 for the air defense of Thailand and to fly reconnaissance flights over Laos. Udorn was one of those bases. Under Thailand's "gentleman's agreement" with the US, RTAF bases used by the US Air Force (USAF) were considered RTAF bases and were commanded by Thai officers. Thai air police controlled access to the bases, along with USAF Security Police, who assisted them in base defense using sentry dogs, observation towers, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-4C Phantom
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American Tandem#Aviation, tandem two-seat, twinjet, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic aircraft, supersonic jet interceptor aircraft, interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 301. Proving highly adaptable, it entered service with the Navy in 1961 before it was adopted by the United States Marine Corps and the United States Air Force, and by the mid-1960s it had become a major part of their air arms. Phantom production ran from 1958 to 1981 with a total of 5,195 aircraft built, making it the List of most produced aircraft, most produced American supersonic military aircraft in history, and cementing its position as an iconic combat aircraft of the Cold War. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

