|
Open Desktop Workstation
The Open Desktop Workstation, also referred to as ODW is a PowerPC based computer, by San Antonio-based Genesi. The ODW has an interchangeable CPU card allowing for a wide range of PowerPC microprocessors from IBM and Freescale Semiconductor. It is a standardized version of the Pegasos II. It was the first open-source based PowerPC computer and gave PowerPC a host/target development environment. Genesi released the complete specification (design and component listing) free of charge. The ODW-derived Home Media Center won the Best in Show award at the Freescale Technology Forum in 2005. It also features an ATI certification and a "Ready for IBM Technology" certification. It supports a variety of operating systems such as MorphOS, Linux, QNX and OpenSolaris. Manufacturing of the ODW was discontinued in favor of the EFIKA architecture. Specification * Freescale 1.0 GHz MPC7447 processor * 512 MB DDR RAM (two slots, up to 2 GB) * 80 GB ATA100 hard disk * D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegasos 1
Pegasos may refer to: * Pegasus, a winged horse in Greek mythology * Genesi Pegasos Pegasos is a discontinued brand of computer systems produced by Genesi USA, Inc., and designed by their research and design partner bplan GmbH based in Frankfurt, Germany. It is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC ..., a brand of computer systems produced by Genesi * Pegasos Swiss Association, a nonprofit group supporting assisted suicide See also * Pegasus (other) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
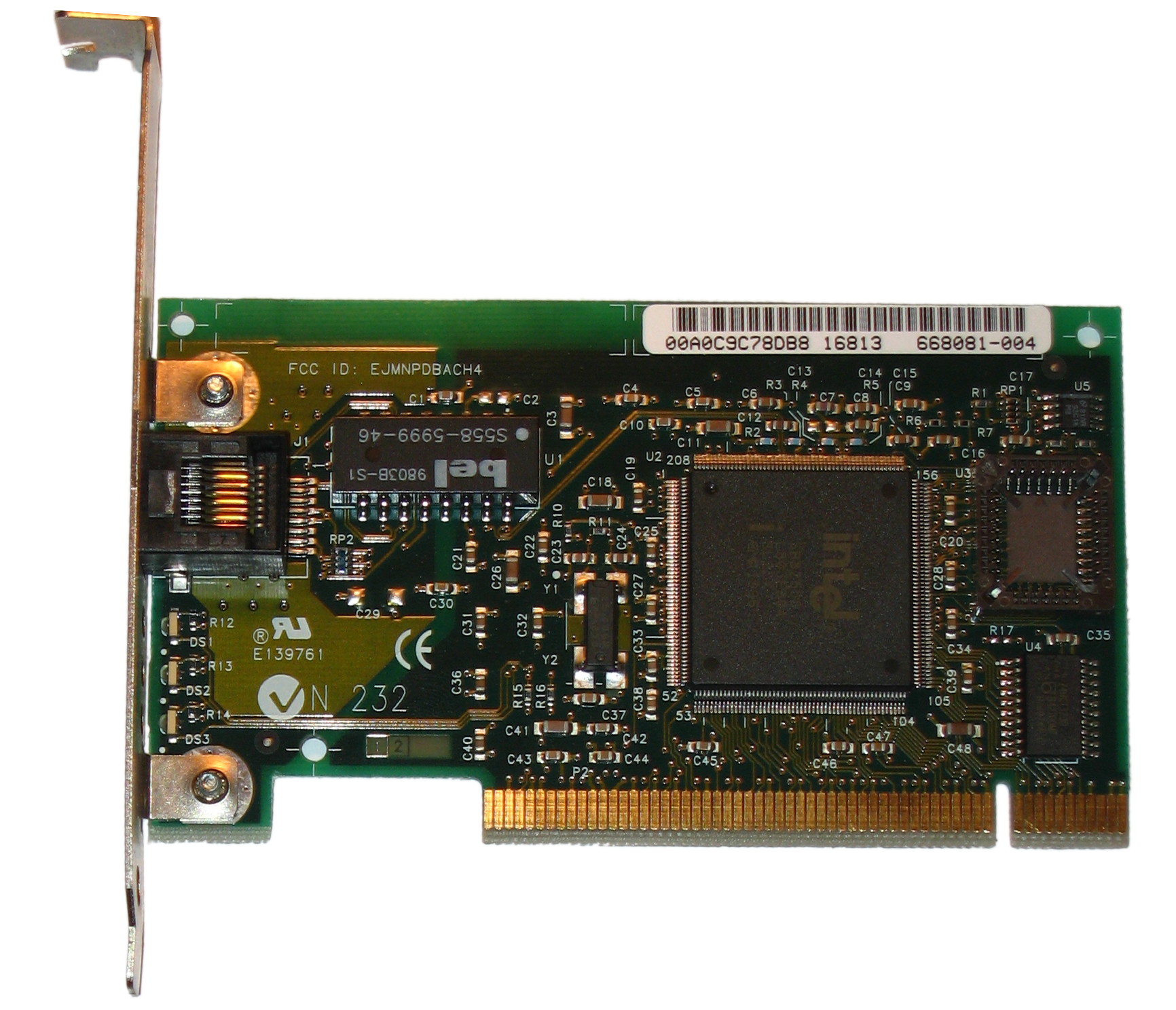
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Port
The game port is a device port that was found on IBM PC compatible and other computer systems throughout the 1980s and 1990s. It was the traditional connector for joystick input, and occasionally MIDI devices, until made obsolete by USB in the late 1990s. Originally located on a dedicated Game Control Adapter expansion card, the game port was later integrated with PC sound cards, and still later on the PC's motherboard. During the transition to USB, many input devices used the game port and a USB adapter dongle was included for systems without a game port. History Pre-IBM game ports At the time IBM was developing its game port, there was no industry standard for controller ports, although the Atari joystick port was close. It was introduced in 1977 with the Atari Video Computer System, and was later used on the VIC-20 (1980), Commodore 64 (1982), and Amstrad's PC1512 (1986). In contrast with the IBM design, the Atari port was primarily designed for digital inputs (includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S/PDIF
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a type of digital audio interface used in consumer audio equipment to output audio over relatively short distances. The signal is transmitted over either a coaxial cable using RCA connector, RCA or BNC connector, BNC connectors, or a fibre-optic cable using TOSLINK connectors. S/PDIF interconnects components in home theaters and other digital high-fidelity systems. S/PDIF is based on the AES3 interconnect Technical standard, standard. S/PDIF can carry two channels of uncompressed PCM audio or Audio compression (data), compressed 5.1 surround sound; it cannot support lossless surround formats that require greater bandwidth (computing), bandwidth. S/PDIF is a data link layer protocol as well as a set of physical layer specifications for carrying digital audio signals over either optical or electrical cable. The name stands for Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format but is also known as Sony/Philips Digital Interface. Sony and Philips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AC'97
AC'97 (''Audio Codec '97;'' also MC'97 for ''Modem Codec '97'') is an audio codec standard developed by Intel Architecture Labs and various codec manufacturers in 1997. The standard was used in motherboards, modems, and sound cards. The specification covers two types of components, and the AC-Link digital interface between them: # an AC'97 ''digital controller'' (DC97), which is typically built into the southbridge of the chipset, and # an AC'97 audio and/or modem ''codec'', available from several vendors, which contains the analog components of the architecture. AC'97 defines a high-quality, 16- or 24- bit audio architecture with 5.1 surround sound support for the PC. AC'97 supports a 96 kHz sampling rate at 24-bit stereo resolution and a 48 kHz sampling rate at 24-bit stereo resolution for multichannel recording and playback. Integrated audio is implemented with the AC'97 Codec on the motherboard, a communications and networking riser card, or an audio/modem r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. The first standard for faster 10 Gigabit Ethernet was approved in 2002. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented Physical layer, physical and Data link layer, link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to . The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet Ethernet physical layer, physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of . The Classic Ethernet, prior Ethernet speed was . Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The ''100'' in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of , while the ''BASE'' refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash (''T'' or ''F'') refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character (''X'', ''4'', etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where ''X'' is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FireWire
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. It is most commonly known by the name FireWire (Apple), though other brand names exist such as i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx ( Texas Instruments). The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber versions. The 1394 interface is comparable to USB. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices. History and development FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PS/2 Connector
The PS/2 port is a 6-pin mini-DIN connector used for connecting keyboards and mice to a PC compatible computer system. Its name comes from the IBM Personal System/2 series of personal computers, with which it was introduced in 1987. The PS/2 mouse connector generally replaced the older DE-9 RS-232 "serial mouse" connector, while the PS/2 keyboard connector replaced the larger 5-pin/180° DIN connector used in the IBM PC/AT design. The PS/2 keyboard port is electrically and logically identical to the IBM AT keyboard port, differing only in the type of electrical connector used. The PS/2 platform introduced a second port with the same design as the keyboard port for use to connect a mouse; thus the PS/2-style keyboard and mouse interfaces are electrically similar and employ the same communication protocol. However, unlike the otherwise similar Apple Desktop Bus connector used by Apple, a given system's keyboard and mouse port may not be interchangeable since the two devices use d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Serial Bus
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical interfaces, and communication protocols to and from ''hosts'', such as personal computers, to and from peripheral ''devices'', e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate ''hubs'', which multiply the number of a host's ports. Introduced in 1996, USB was originally designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces such as serial ports, parallel ports, game ports, and Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) ports. Early versions of USB became commonplace on a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, and power banks. USB has since evolved into a standard to replace virtually all common ports on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Video
S-Video (also known as separate video, Y/C, and erroneously Super-Video) is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it is improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels. The Atari 800 was the first to introduce separate Chroma/Luma output in late 1979. However, S-Video was not widely adopted until JVC's introduction of the S-VHS (Super-VHS) format in 1987, which is why it is sometimes incorrectly referred to as ''Super-Video''. The S-video format was widely adopted in consumer equipment due to its improvements over composite video. However, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the IBM PC compatible industry within three years. The term can now refer to the computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector, or the Graphics display resolution, resolution characteristic of the VGA hardware. VGA was the last IBM graphics standard to which the majority of IBM PC compatible computer manufacturers conformed, making it the Lowest common denominator#Colloquial usage, lowest common denominator that virtually all post-1990 PC graphics hardware can be expected to implement. VGA was adapted into many extended forms by third parties, collectively known as Super VGA, then gave way to custom graphics processing units which, in addition to their proprietary interfaces and capabilities, continue to implement common VGA graphics modes and interfaces to the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |