|
Omniscience
Omniscience () is the capacity to know everything. In Hinduism, Sikhism and the Abrahamic religions, this is an attribute of God. In Jainism, omniscience is an attribute that any individual can eventually attain. In Buddhism, there are differing beliefs about omniscience among different schools. Etymology The word ''omniscience'' derives from the Latin word ''sciens'' ("to know" or "conscious") and the prefix '' omni'' ("all" or "every"), but also means " all-seeing". In religion Buddhism The topic of omniscience has been much debated in various Indian traditions, but no more so than by the Buddhists. After Dharmakirti's excursions into the subject of what constitutes a valid cognition, Śāntarakṣita and his student Kamalaśīla thoroughly investigated the subject in the Tattvasamgraha and its commentary the Panjika. The arguments in the text can be broadly grouped into four sections: * The refutation that cognitions, either perceived, inferred, or otherwise, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded. Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actions that are freely chosen. It is also connected with the concepts of advice, persuasion, deliberation, and prohibition. Traditionally, only actions that are freely willed are seen as deserving credit or blame. Whether free will exists, what it is and the implications of whether it exists or not are some of the longest running debates of philosophy and religion. Some conceive of free will as the right to act outside of external influences or wishes. Some conceive free will to be the capacity to make choices undetermined by past events. Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with a libertarian model of free will. Ancient Greek philosophy identified this issue, which remains a major fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arihant (Jainism)
''Arihant'' ( pka, arihant, italic=yes, sa, अरिहन्त, lit=conqueror) is a jiva (soul) who has conquered inner passions such as attachment, anger, pride and greed. Having destroyed four inimical karmas, they realize pure self. ''Arihants'' are also called ''kevalins'' ( omniscient beings) as they possess '' kevala jnana'' (pure infinite knowledge). An ''arihant'' is also called a ''jina'' ("victor"). At the end of their life, ''arihants'' destroy remaining ''karmas'' and attain ''moksha'' (liberation) and become '' siddhas''. ''Arihantas'' have a body while ''siddhas'' are bodiless pure spirit. The Ṇamōkāra mantra, the fundamental prayer dedicated to ''Pañca-Parameṣṭhi'' (five supreme beings), begins with ''Ṇamō arihantāṇaṁ'', "obeisance to the arihants". ''Kevalins'' - omniscient beings - are said to be of two kinds # ''Tirthankara kevalī'': 24 human spiritual guides who after attaining omniscience teach the path to salvation. # ''Sāmānya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God In Islam
God in Islam ( ar, ٱللَّٰه, Allāh, contraction of '' al- ’Ilāh'', lit. "the God") is seen as the eternal creator and sustainer of the universe, who will eventually resurrect all humans. In Islam, God is conceived as a perfect, singular, immortal, omnipotent, and omniscient god, completely infinite in all of his attributes. Islam further emphasizes that God is most-merciful."Allah." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Encyclopædia Britannica According to Islamic theology, God has no physical body or gender, although he is always referred to with masculine grammatical articles, and there is nothing else like him in any way whatsoever. Therefore, Islam rejects the doctrine of the incarnation and the notion of a personal god as anthropomorphic, because it is seen as demeaning to the transcendence of God. The Quran prescribes the fundamental transcendental criterion in the following verse: " e isthe Creator of the heavens and the earth. He has made for you f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Of Providence
The Eye of Providence (or the All-Seeing Eye of God) is a symbol that depicts an eye, often enclosed in a triangle and surrounded by rays of light or glory, meant to represent divine providence, whereby the eye of God watches over humanity. A well-known example of the Eye of Providence appears on the reverse of the Great Seal of the United States, which is depicted on the United States one-dollar bill. Use by governments and confederations United States In 1782, the Eye of Providence was adopted as part of the symbolism featured on the reverse side of the Great Seal of the United States. It was first proposed as an element of the Great Seal by the first of three design committees in 1776, and is thought to be the suggestion of the artistic consultant, Pierre Eugene du Simitiere, Bureau of Public Affairs. July 2003.The Great Seal of the United States" Washington: U.S. Department of State Archive; See alsoGreat Seal" Bureau of Public Affairs. 2002. Both retrieved 6 Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predestination In Islam
''Qadar'' ( ar, قدر, Hans Wehr transliteration, transliterated ''qadar'', meaning literally "power",J. M. Cowan (ed.) (1976). ''The Hans Wehr Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic''. Wiesbaden, Germany: Spoken Language Services. but translated variously as: "Fate", "Divine Fore-ordainment", "Predestination," "Divine Decree", "Decree" of Allah", "Preordainment") is the concept of Divinity, Divine Destiny in Islam. As God is God in Islam#Omniscience, all-knowing and all-powerful, everything that has happened and will happen in the universe—including sinful human behavior—is not only known but commanded by him.#AGI1978, Guillaume, ''Islam'', 1978: p.132 At the same time, human beings are responsible for their actions, and will be rewarded or punished accordingly on Judgement Day in Islam, Judgement Day. Predestination/Divine Destiny is one of Sunni Islam's Iman (concept)#The Six Articles of Faith, six articles of faith, (along with belief in the Tawhid, Oneness of Allah, the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakyamuni Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and ''jhana''. He died in Kushina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Know
Knowledge can be defined as awareness of facts or as practical skills, and may also refer to familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often defined as true belief that is distinct from opinion or guesswork by virtue of justification. While there is wide agreement among philosophers that propositional knowledge is a form of true belief, many controversies in philosophy focus on justification: whether it is needed at all, how to understand it, and whether something else besides it is needed. These controversies intensified due to a series of thought experiments by Edmund Gettier and have provoked various alternative definitions. Some of them deny that justification is necessary and replace it, for example, with reliability or the manifestation of cognitive virtues. Others contend that justification is needed but formulate additional requirements, for example, that no defeaters of the belief are present or that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Theology
Christian theology is the theology of Christianity, Christian belief and practice. Such study concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theology, theologians use biblical exegesis, rationality, rational analysis and argument. Theologians may undertake the study of Christian theology for a variety of reasons, such as in order to: * help them better understand Christian tenets * make comparative religion, comparisons between Christianity and other traditions * Christian apologetics, defend Christianity against objections and criticism * facilitate reforms in the Christian church * assist in the evangelism, propagation of Christianity * draw on the resources of the Christian tradition to address some present situation or perceived need * education in Christian philosophy, especially in Neoplatonism, Neoplatonic philosophyLouth, Andrew. The Origins of the Christian Mystical Tradition: From Plato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrahamic Religions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religion Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...s centered around worship of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrews , Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran. Jewish tradition claims that the Twelve Tribes of Israel are descended from Abraham through his son Isaac and grandson Jacob, whose sons formed the nation of the Israelites in Canaan (or the Land of Israel); Islamic tradition claims that twelve Arab tribes known as the Ishmaelites are descended from Abraham through his son Ishmael in the Arabian Peninsula. In its early stages, Origins of Judaism , Israelite religion was derived from the Canaanite religion, Canaanite rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhakti
''Bhakti'' ( sa, भक्ति) literally means "attachment, participation, fondness for, homage, faith, love, devotion, worship, purity".See Monier-Williams, ''Sanskrit Dictionary'', 1899. It was originally used in Hinduism, referring to devotion and love for a personal god or a representational god by a devotee.Bhakti ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (2009) In ancient texts such as the '''', the term simply means participation, devotion and love for any endeavor, while in the '''', it connotes one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orozco Mural Omniciencia 1925 Azulejos
Orozco is of Spanish/Basque origin. Notable people with the surname include: * Ana María Orozco (born 1973), Colombian television actress * Andrés Orozco (born 1979), Colombian football defender * Antonio Orozco (born 1972), Spanish singer-songwriter * Aurora Estrada Orozco (1918–2011), Mexican American community leader * Caleb Orozco, LGBT activist in Belize * Daniel Orozco, an American writer of fiction * Danilo Orozco (1944–2013), Cuban musicologist * Edwin Orozco (born 1982), Colombian road cyclist * Esther Orozco (born 1945), Mexican biologist and researcher * Ezequiel Orozco (1988–2018), Mexican football player * Gabriel Orozco (born 1962), Mexican postminimalist artist * Germán Orozco (born 1976), Argentine field hockey defender * John Orozco (born 1992), American gymnast * Jonathan Orozco, Mexican football player * José Clemente Orozco (1883–1949), Mexican painter * Lisseth Orozco (born 1986), Colombian judoka * Michael Orozco Fiscal (born 1986), Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
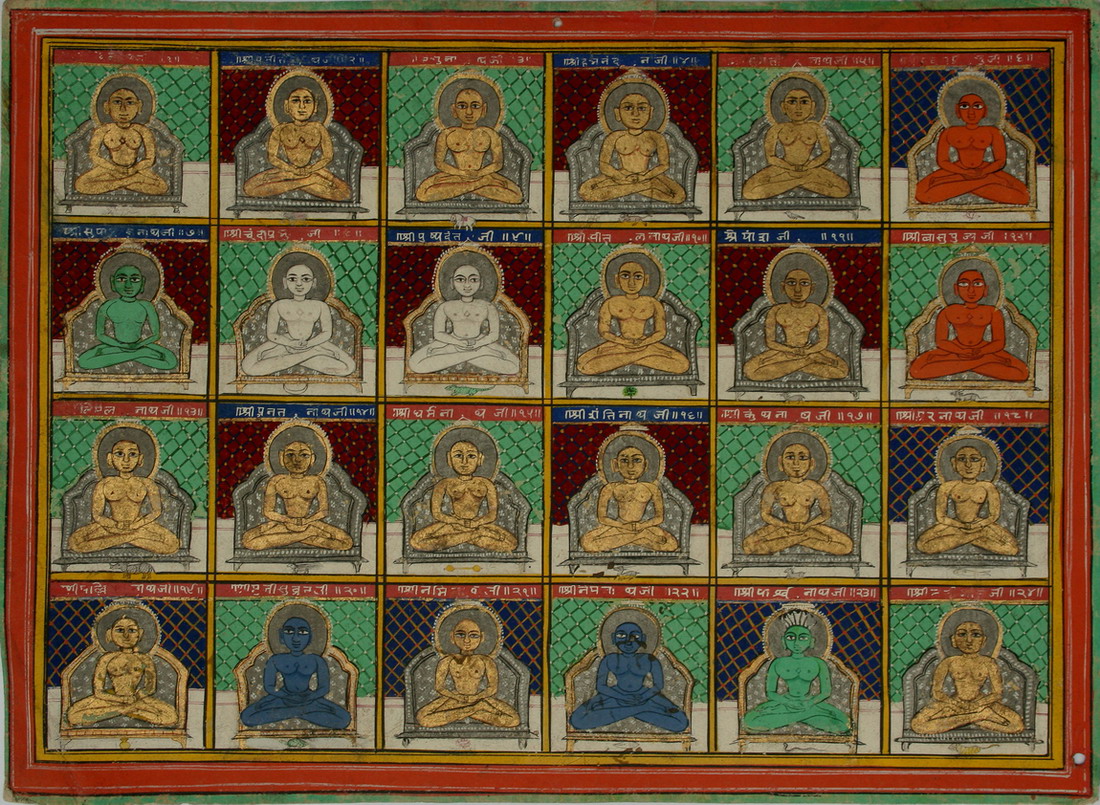
Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (Sanskrit: '; English language, English: literally a 'Ford (crossing), ford-maker') is a saviour and spiritual teacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', which is a fordable passage across the sea of interminable births and deaths, the ''Saṃsāra (Jainism), saṃsāra''. According to Jains, a ''Tirthankara'' is an individual who has conquered the ''saṃsāra'', the cycle of death and rebirth, on their own, and made a path for others to follow. After understanding the true nature of the self or soul, the ''Tīrthaṅkara'' attains ''Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). Tirthankara provides a bridge for others to follow the new teacher from ''saṃsāra'' to ''moksha'' (liberation). In Jain cosmology, the wheel of time is divided in two halves, Utsarpiṇī' or ascending time cycle and ''avasarpiṇī'', the descending time cycle (said to be current no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



.jpg)
