|
Nuclear Transport
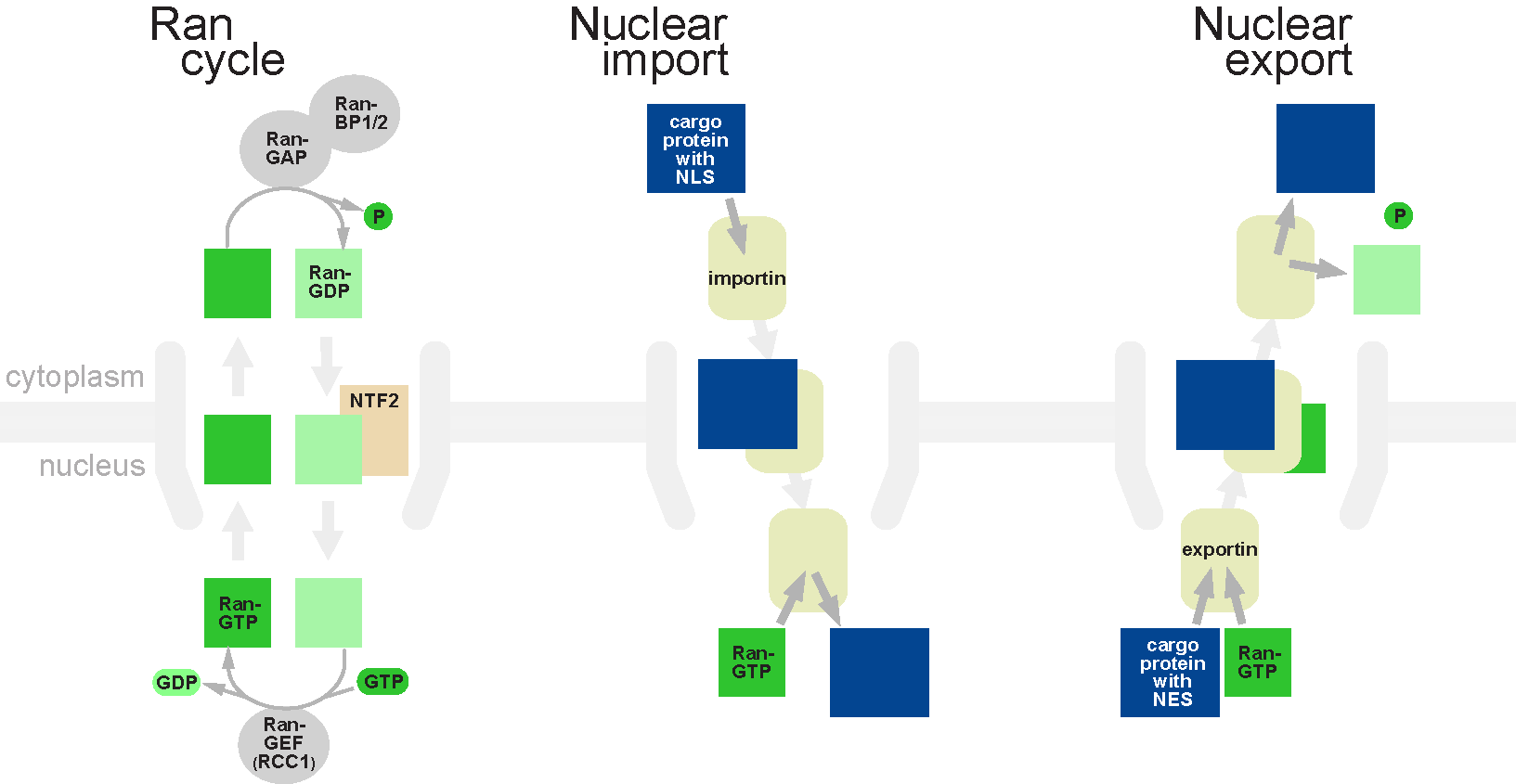
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit. Nuclear import Protein that must be imported to the nucleus from the cytoplasm carry nuclear localization signals (NLS) that are bound by importins. An NLS is a sequence of amino acids that acts as a tag. They are most commonly hydrophilic proteins containing lysine and arginine residues, although diverse NLS sequences have been documented. Proteins, transfer RNA, and assembled ribosomal subunits are exported from the nucleus due to association with exportins, which bind signaling sequences cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Membrane
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Export Signal
A nuclear export signal (NES) is a short target peptide containing 4 hydrophobic residues in a protein that targets it for export from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex using nuclear transport. It has the opposite effect of a nuclear localization signal, which targets a protein located in the cytoplasm for import to the nucleus. The NES is recognized and bound by exportins. NESs serve several vital cellular functions. They assist in regulating the position of proteins within the cell. Through this NESs affect transcription and several other nuclear functions that are essential to proper cell function. The export of many types of RNA from the nucleus is required for proper cellular function. The NES determines what type of pathway the varying types of RNA may use to exit the nucleus and perform their function and the NESs may effect the directionality of molecules exiting the nucleus. Structure Computer analysis of known NESs found the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modifications
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XPOT
Exportin-T is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''XPOT'' gene. This gene encodes a protein belonging to the RAN-GTPase exportin family that mediates export of tRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Translocation of tRNA to the cytoplasm occurs once exportin Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ... has bound both tRNA and GTP-bound RAN. References Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exportin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through nuclear pores which acts as a gateway into and out of the nucleus. Most proteins require karyopherins to traverse the nuclear pore. Karyopherins can act as ''importins'' (i.e. helping proteins get into the nucleus) or ''exportins'' (i.e. helping proteins get out of the nucleus). They belong to the nuclear pore complex family in the transporter classification database (TCDB). Energy for transport is derived from the Ran gradient. Upon stress, several karyopherins stop shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and are sequestered in stress granules, cytoplasmic aggregates of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Importin beta Importin beta is a variety of karyopherin that facilitates the transport of cargo proteins into the nucleus. Firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small GTPase
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases. A typical G-protein is active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP (i.e. when the GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP). The GDP can be then replaced by free GTP. Therefore, a G-protein can be switched on and off. GTP hydrolysis is accelerated by GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), while GTP exchange is catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). Activation of a GEF typically activates its cognate G-protein, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
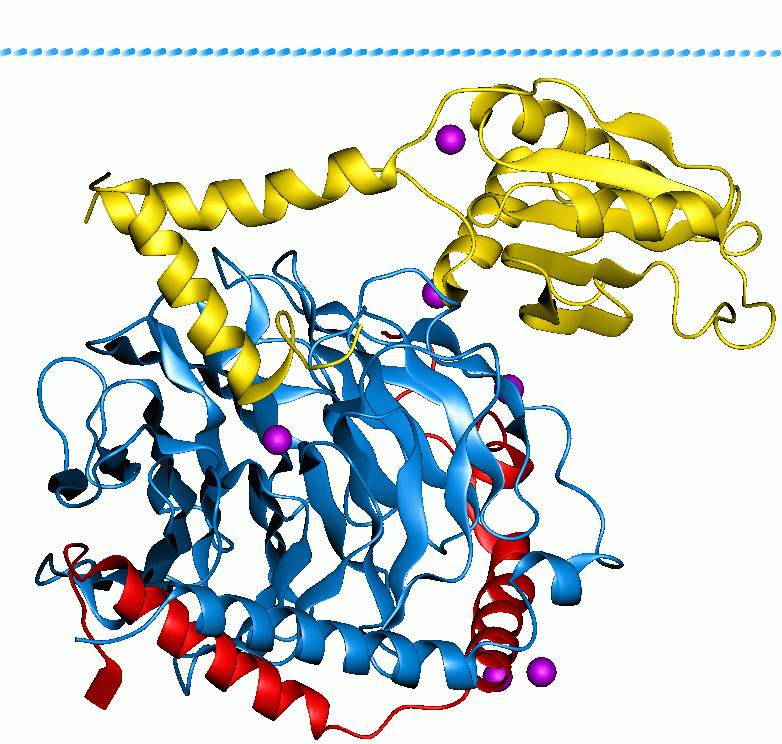
Ran (protein)
Ran (RAs-related Nuclear protein) also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily. Ran is a small G protein that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The Ran protein has also been implicated in the control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression, as mutations in Ran have been found to disrupt DNA synthesis. Function Ran cycle Ran exists in the cell in two nucleotide-bound forms: GDP-bound and GTP-bound. RanGDP is converted into RanGTP through the action of RCC1, the nucleotide exchange factor for Ran. RCC1 is also known as RanGEF (Ran Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor). Ran's intrinsic GTPase-activity is activated through interaction with Ran GTPase activating protein (RanGAP), facilita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |