|
Northrop T37
The Northrop-Hendy T37 Turbodyne (company designation N-10) was an American turboprop engine developed by the Turbodyne Division of Northrop in the late 1940s. Design and development Turbodyne I Northrop undertook a private venture to develop a turboprop engine from 1939 and was awarded a joint US Army/US Navy contract in 1941 for design, analysis and fabrication of a research compressor for the proposed engine. The contract was amended later to call for construction of two complete engine prototypes. Northrop had neither the space or expertise to fabricate the engines in a reasonable time-scale so they joined forces with the Joshua Hendy Iron Works in 1944 to form the Northrop-Hendy company. the two prototype engines were completed and test run in late 1944, but the first engine compressor failed, destroying the engine. Meanwhile the USN cancelled their interest in the engine in 1945, leaving the US Army to carry on. Testing continued with the second engine until that too fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft/page Content
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough energy to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtained by extracting additional power (beyond that necessary to drive the compressor) from turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop B-35
The Northrop YB-35, Northrop designation N-9 or NS-9, were experimental heavy bomber aircraft developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Army Air Forces during and shortly after World War II. The airplane used the radical and potentially very efficient flying wing design, in which the tail section and fuselage are eliminated and all payload is carried in a thick wing. Only prototypes and pre-production aircraft were built, although interest remained strong enough to warrant further development of the design as a jet bomber, under the designation YB-49.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 93, 95, 103–6, Cypress, CA, 2013. . Design and development The B-35 was the brainchild of Jack Northrop, who made the flying wing the focus of his work during the 1930s. In 1941 before the USA entered World War II, Northrop and Consolidated Vultee Corporation had been commissioned to develop a large wing-onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Hendy Iron Works
The Joshua Hendy Iron Works was an American engineering company that existed from the 1850s to the late 1940s. It was at one time a world leader in mining technology and its equipment was used in the construction of the Panama Canal, amongst other major projects. The company went on to serve many different markets during the course of its existence, but is perhaps best remembered today for its contribution to the American shipbuilding industry during World War II. Beginnings The company was named for its founder Joshua Hendy. Born in Cornwall, England in 1822, Hendy at the age of 13 migrated with two brothers to South Carolina in the United States. Joshua married and became a blacksmith in Houston, Texas. After the death of his wife and two children from yellow fever, he sailed round Cape Horn to San Francisco in 1849 to participate in the California Gold Rush. Hendy built California's first redwood lumber mill, the Benicia Sawmill (the region is now known as the Hendy Woods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Wing
A flying wing is a tailless fixed-wing aircraft that has no definite fuselage, with its crew, payload, fuel, and equipment housed inside the main wing structure. A flying wing may have various small protuberances such as pods, nacelles, blisters, booms, or vertical stabilizers. Similar aircraft designs, that are not technically flying wings, are sometimes casually referred to as such. These types include blended wing body aircraft and lifting body aircraft, which have a fuselage and no definite wings. A pure flying wing is theoretically the lowest drag design configuration for a fixed wing aircraft. However, because it lacks conventional stabilizing surfaces and the associated control surfaces, in its purest form the flying wing suffers from being unstable and difficult to control. The basic flying wing configuration became an object of significant study during the 1920s, often in conjunction with other tailless designs. In the Second World War, both Nazi Germany and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cargo Aircraft
A cargo aircraft (also known as freight aircraft, freighter, airlifter or cargo jet) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is designed or converted for the carriage of cargo rather than passengers. Such aircraft usually do not incorporate passenger amenities and generally feature one or more large doors for loading cargo. Freighters may be operated by civil passenger or cargo airlines, by private individuals or by the armed forces of individual countries. Aircraft designed for cargo flight usually have features that distinguish them from conventional passenger aircraft: a wide/tall fuselage cross-section, a high-wing to allow the cargo area to sit near the ground, numerous wheels to allow it to land at unprepared locations, and a high-mounted tail to allow cargo to be driven directly into and off the aircraft. By 2015, dedicated freighters represent 43% of the 700 billion ATK (available tonne-kilometer) capacity, while 57% is carried in airliner's cargo holds. Also in 2015, Boeing f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
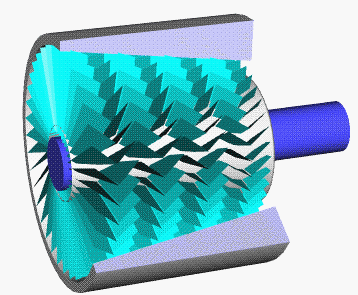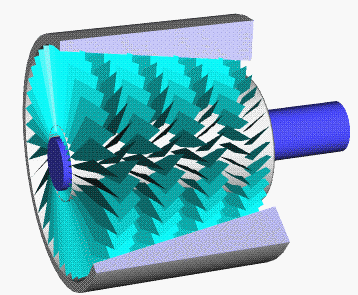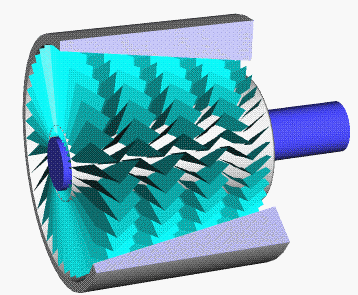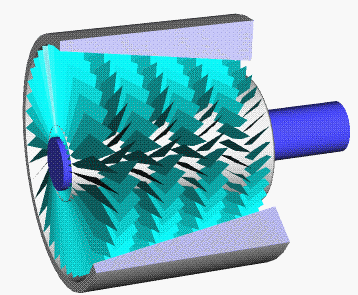
Axial Compressor
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine. Axial flow compressors produce a continuous flow of compressed gas, and have the benefits of high efficiency and large mass flow rate, particularly in relation to their size and cross-section. They do, however, require sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JP-4
JP-4, or JP4 (for "Jet Propellant") was a jet fuel, specified in 1951 by the U.S. government (MIL-DTL-5624). Its NATO code is F-40. It is also known as avtag. Usage JP-4 was a 50-50 kerosene-gasoline blend. It had a lower flash point than JP-1, but was preferred because of its greater availability. It was the primary U.S. Air Force jet fuel between 1951 and 1995. MC-77 is the Swedish military equivalent of JP-4. Mixture JP-4 was a mixture of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons. It was a flammable transparent liquid with clear or straw color, and a kerosene-like smell. It evaporated easily and floated on water. Although it had a low flash point (), a lit match dropped into JP-4 would not ignite the mixture. JP-4 froze at , and its maximum burning temperature was . JP-4 was a non-conductive liquid, prone to build up static electricity when being moved through pipes and tanks. As it is volatile and has a low flash point, the static discharge could cause a fire. Beginning in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |