|
No. 140 Wing RAF
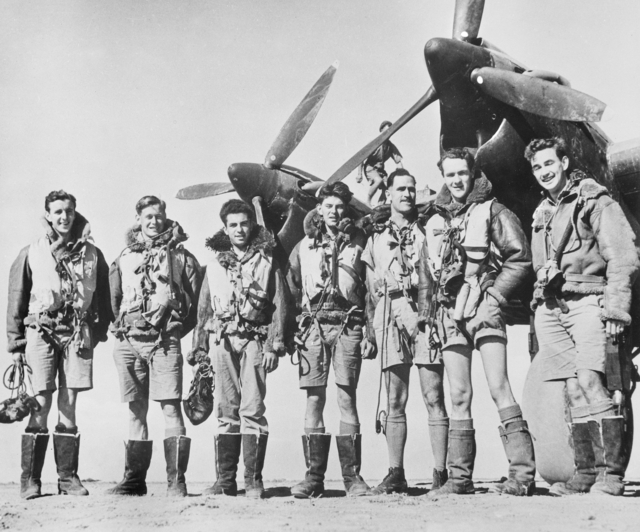
No. 140 Wing RAF was a formation of the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. It comprised No. 21 Squadron RAF, No. 464 (RAAF) Squadron RAF and No. 487 (RNZAF) Squadron RAF. It carried out many notable low-level bombing operations, including Operation Jericho (Amiens prison) and Operation Carthage in Copenhagen. No. 464 and No. 487 Squadrons were Article XV Squadrons, i.e. they were Commonwealth squadrons which operated under the operational control of the Royal Air Force The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ..., which also was responsible e.g. for their pay. References {{RAF Wings Wings of the Royal Air Force in the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many List of islands of the United Kingdom, smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
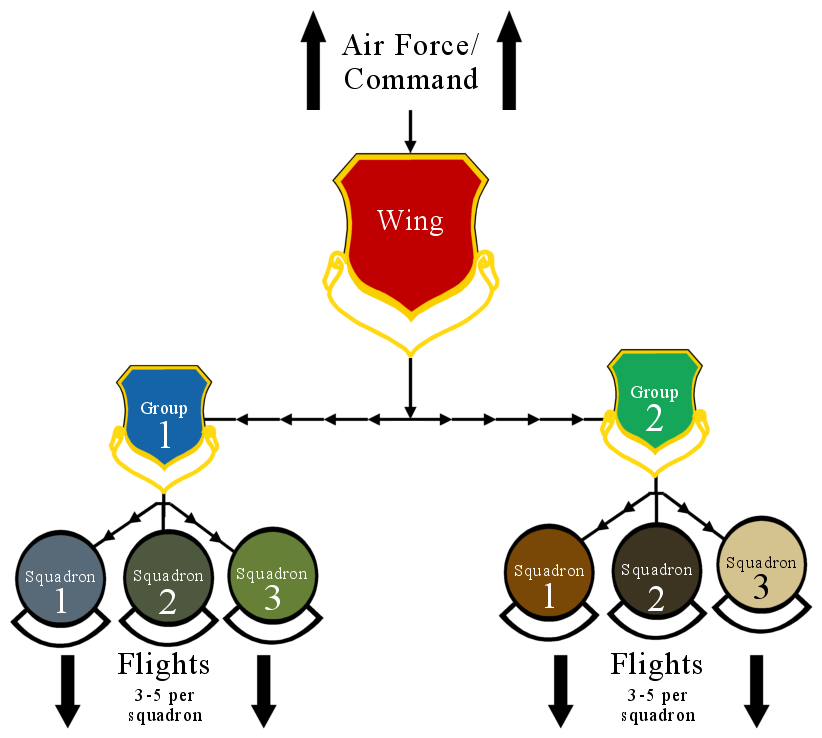
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
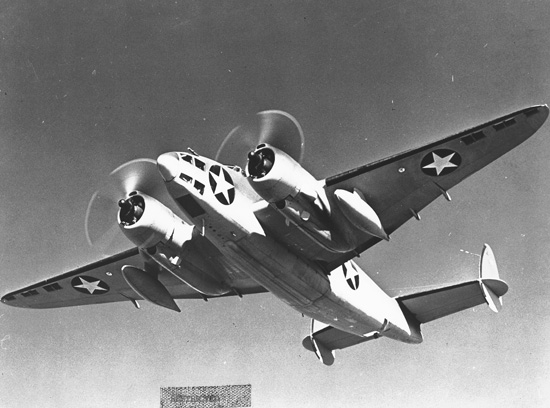
Lockheed Ventura
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II. The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1943 in the Pacific. The bomber was also used by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), which designated it the Lockheed B-34 (''Lexington'') and B-37 as a trainer. Commonwealth of Nations, British Commonwealth forces also used it in several guises, including antishipping and antisubmarine search and attack. The Ventura was developed from the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar transport, as a replacement for the Lockheed Hudson bombers then in service with the Royal Air Force. Used in daylight attacks against occupied Europe, they proved to have weaknesses and were removed from bomber duty and some used for patrols by Coastal Command. After USAAF monopolization of land-based bombers was removed, the US Navy ordered a revised design which enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Mosquito
The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito is a British twin-engined, shoulder-winged, multirole combat aircraft, introduced during the World War II, Second World War. Unusual in that its frame was constructed mostly of wood, it was nicknamed the "Wooden Wonder", or "Mossie". Max Aitken, 1st Baron Beaverbrook, Lord Beaverbrook, Minister of Aircraft Production, nicknamed it "Freeman's Folly", alluding to Air Chief Marshal Sir Wilfrid Freeman, who defended Geoffrey de Havilland and his design concept against orders to scrap the project. In 1941, it was one of the fastest operational aircraft in the world.Bowman 2005, p. 21. Originally conceived as an unarmed fast bomber, the Mosquito's use evolved during the war into many roles, including low- to medium-altitude daytime tactical bomber, high-altitude night bomber, Pathfinder (RAF), pathfinder, Day fighter, day or night fighter, fighter-bomber, intruder (air combat), intruder, maritime strike aircraft, maritime strike, and photo-reconnaissan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Jericho
Operation Jericho (Ramrod 564) took place on 18 February 1944 during the Second World War. Allied aircraft bombed Amiens Prison in German-occupied France at very low altitude to blow holes in the prison walls, kill German guards and use shock waves to spring open cell doors. The French Resistance was waiting on the outside to rescue prisoners and spirit them away. Mosquito fighter-bombers breached the walls, prison buildings and destroyed the guards' barracks. Of the 832 prisoners, 102 were killed by the bombing, 74 were wounded and 258 escaped, including 79 Resistance members and political prisoners; two-thirds of the escapees were recaptured. Two Mosquitos and a Typhoon fighter escort were shot down and another Typhoon was lost at sea. The raid is notable for the precision and daring of the attack, which was filmed by a camera on one of the Mosquitos. There is debate as to who requested the attack and whether it was necessary. Background French resistance During 1943 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Carthage
Operation Carthage, on 21 March 1945, was a British air raid on Copenhagen, Denmark during the Second World War which killed 145 civilians. The target of the raid was the , the Gestapo headquarters in the city centre. It was used for the storage of dossiers and the torture of Danish citizens during interrogations. The Danish Resistance had long requested the British conduct a raid against the site. The building was destroyed, 18 prisoners were freed and Nazi anti-resistance activities were disrupted. Part of the raid was mistakenly directed against a school which was roughly to the west-southwest; the raid caused 125 civilian deaths, including 86 schoolchildren and 18 adults at the school. The Aarhus Air Raid was a similar attack against the Gestapo headquarters in Aarhus on 31 October 1944, which succeeded. Background The raid was requested by members of the Danish resistance movement to free imprisoned members and to destroy the records of the Gestapo, to disrupt their o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan area has 2,057,142 people. Copenhagen is on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital of the Kalmar Union, being the seat of monarchy, governing the majority of the present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Article XV Squadrons
Article XV squadrons were Australian, Canadian, and New Zealand air force squadrons formed from graduates of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (1939) during World War II. These units complemented another feature of the BCATP, under which personnel from the Royal Air Force (RAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) were placed in a common pool, and assigned to Article XV and RAF squadrons – in Europe, the Mediterranean Theatre, Africa and South-East Asia – according to operational needs. The RAAF, RCAF and RNZAF also formed non-Article XV squadrons, which performed home defence duties and saw active service in various parts of the Pacific Theatre. History Negotiations regarding the BCATP, between the four governments concerned, took place in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada during late 1939. The Air Training Agreement (sometimes known as the "Ottawa Agreement" or the "Riverdale Agreement", after the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations amongst member states. Numerous organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


