|
Ngawang Namgyal (Rinpungpa)
Ngawang Namgyal () (died 1544 or somewhat later) was a prince of the Rinpungpa Dynasty that dominated Tsang in West Central Tibet between 1435 and 1565. He reigned from 1512 to 1544. The succession Ngawang Namgyal was the son of Tsokye Dorje and the grandson of the founder of the dynasty's fortune, Norzang. According to the ''Rinpung durab'' he was born in a Year of the Tiger (1470, 1482, 1494). He is first mentioned in 1510, when his father died. At this time the Rinpungpa had a dominating role in the politics of Central Tibet and also held suzerainty over Guge in western Tibet. The leader of the family was Ngawang Namgyal's cousin Donyo Dorje. The Phagmodrupa dynasty, the actual monarchs (''gongmas'') of Tibet, had been reduced to relative insignificance. However, since 1509 a conflict had arisen between the Rinpungpa and the young and able Phagmodrupa ''gongma'' Ngawang Tashi Drakpa. When the funeral for Tsokye Dorje were still going on in 1510, Donyo Dorje ordered Ngawang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinpungpa
Rinpungpa (; ) was a Tibetan dynastic regime that dominated much of Western Tibet and part of Ü-Tsang between 1435 and 1565. During one period around 1500 the Rinpungpa lords came close to assemble the Tibetan lands around the Yarlung Tsangpo River under one authority, but their powers receded after 1512. Rise to power The Rinpungpa belonged to the Ger () clan, which is traced back to the days of the Tibetan Empire. One of their line, Namkha Gyaltsen, served as ''nanglon'' (minister of internal affairs) under the Phagmodrupa ruler Jamyang Shakya Gyaltsen, who held power over Ü-Tsang. He was appointed ''dzongpon'' (governor) of the fief Rinpung in Rong, a region in Tsang in an unknown year before 1373. His political position was strengthened by the marriage with the Phagmodrupa princess Sönam Palmö. Their daughter in turn was given in marriage to Sangye Gyaltsen, a Phagmodrupa prince, and gave birth to the later ruler Drakpa Jungne (r. 1432–1445). The son of Namkha Gyalt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monlam
Monlam also known as The Great Prayer Festival, falls on 4th–11th day of the 1st Tibetan month in Tibetan Buddhism. History The event of Monlam in Tibet was established in 1409 by Tsong Khapa, the founder of the Geluk tradition. As the greatest religious festival in Tibet, thousands of monks (of the three main monasteries of Drepung, Sera and Ganden) gathered for chanting prayers and performing religious rituals at the Jokhang Temple in Lhasa. In 1517, Gedun Gyatso became the abbot of Drepung monastery and in the following year, he revived the Monlam Chenmo, the Great Prayer Festival and presided over the events with monks from Sera, Drepung and Ganden, the three great monastic universities of the Gelugpa Sect. "The main purpose of the Great Prayer Festival is to pray for the long life of all the holy Gurus of all traditions, for the survival and spreading of the Dharma in the minds of all sentient beings, and for world peace. The communal prayers, offered with strong fait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhasa City is equivalent to the administrative borders of Chengguan District (), which is part of the wider prefectural Lhasa City. Lhasa is the second most populous urban area on the Tibetan Plateau after Xining and, at an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world. The city has been the religious and administrative capital of Tibet since the mid-17th century. It contains many culturally significant Tibetan Buddhist sites such as the Potala Palace, Jokhang Temple and Norbulingka Palaces. Toponymy Lhasa literally translates to "place of gods" ( , god; , place) in the Tibetan language. Chengguan literally translates to "urban gateway" () in the Chinese language. Ancient Tibetan documents and inscriptions demonstrate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ... and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; Topographically, it is dominated by the Indian subcontinent and defined largely by the Indian Ocean on the south, and the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountains on the north. The Amu Darya, which rises north of the Hindu Kush, forms part of the northwestern border. On land (clockwise), South Asia is bounded by Western Asia, Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia. The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an economic cooperation organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir Valley
The Kashmir Valley, also known as the ''Vale of Kashmir'', is an intermontane valley concentrated in the Kashmir Division of the Indian- union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The valley is bounded on the southwest by the Pir Panjal Range and on the northeast by the main Himalayas range. It is approximately long and wide, and drained by the Jhelum River. Geography The Kashmir Valley lies between latitude 33° and 35°N, and longitude 73° and 76°E. The valley is wide and covers in area. It is bounded by sub-ranges of the Western Himalayas: the Great Himalayas bound it in the northeast and separate it from the Tibetan plateau, whereas the Pir Panjal Range in the Lesser Himalayas bounds it on the west and the south, and separates it from the Punjab Plain. The valley has an average elevation of above sea-level, but the surrounding Pir Panjal range has an average elevation of . The Jhelum River is the main river of the Valley. It originates at Verinag; its most im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkand County
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China, located on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin. It is one of 11 counties administered under Kashgar Prefecture. The county, usually referred to as Yarkand in English, was the seat of an ancient Buddhist kingdom on the southern branch of the Silk Road and the Yarkand Khanate. The county sits at an altitude of and had a population of . The fertile oasis is fed by the Yarkand River, which flows north down from the Karakorum mountains and passes through the Kunlun Mountains, known historically as the Congling mountains (lit. 'Onion Mountains' - from the abundance of wild onions found there). The oasis now covers , but was likely far more extensive before a period of desiccation affected the region fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompasses a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir, state of India, located in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the vicinity of the Karakoram and westernmost Himalayan mountain ranges. From 1947 to 2019, Ladakh was part of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since the partition of the subcontinent in 1947." Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China." Ladakh is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, both the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and the Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. With a population of over 500,000, Kashgar has served as a trading post and strategically important city on the Silk Road between China, the Middle East and Europe for over 2,000 years, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the World. At the convergence point of widely varying cultures and empires, Kashgar has been under the rule of the Chinese, Turkic, Mongol and Tibetan empires. The city has also been the site of a number of battles between various groups of people on the steppes. Now administered as a county-level unit, Kashgar is the administrative center of Kashgar Prefecture, which has an area of and a population of approximately 4 million as of 2010. The city itself has a population of 506,640, and its urb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat
Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat Beg ( Persian: میرزا محمد حیدر دولت بیگ c. 1499/1500 – 1551) was a Chagatai Turco-Mongol military general, governor of Kashmir, and a historical writer, He was a Turkic speaking Dughlat prince who wrote in the Persian and Chagatai languages, Haidar and Babur were cousins on their mother's side. Campaigns He first campaigned in Kashmir in 1533, on behalf of Sultan Said Khan, of Kashgar. However, he did not stay long in Kashmir, leaving after making a treaty with the local sultan and striking coins in the name of Said Khan. He had also attacked Tibet through Ladakh but failed to conquer Lhasa. He returned in 1540, fighting for the Mughal Emperor Humayun, first son of Babur, this time for a military takeover at the invitation of one of the two rival factions that continually vied for power in Kashmir. This was shortly after Humayun's 1540 defeat at the Battle of Kanauj, where Dughlat was also on the losing side. Arriving i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bainang County
Bainang County (; ) is a county of Xigazê in the Tibet Autonomous Region The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions .... Towns and townships * Norbu Khyungtse Town (, ) * Gadong Town (, ) * Pältsel Township (, ) * Mak Township (, ) * Wangden Township (, ) * Qunub Township (, ) * Düjung Township (, ) * Jangtö Township (, ) * Gabug Township (, ) * Tashar Township (, ) * Tongshé Township (, ) Counties of Tibet Shigatse {{Shigatse-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
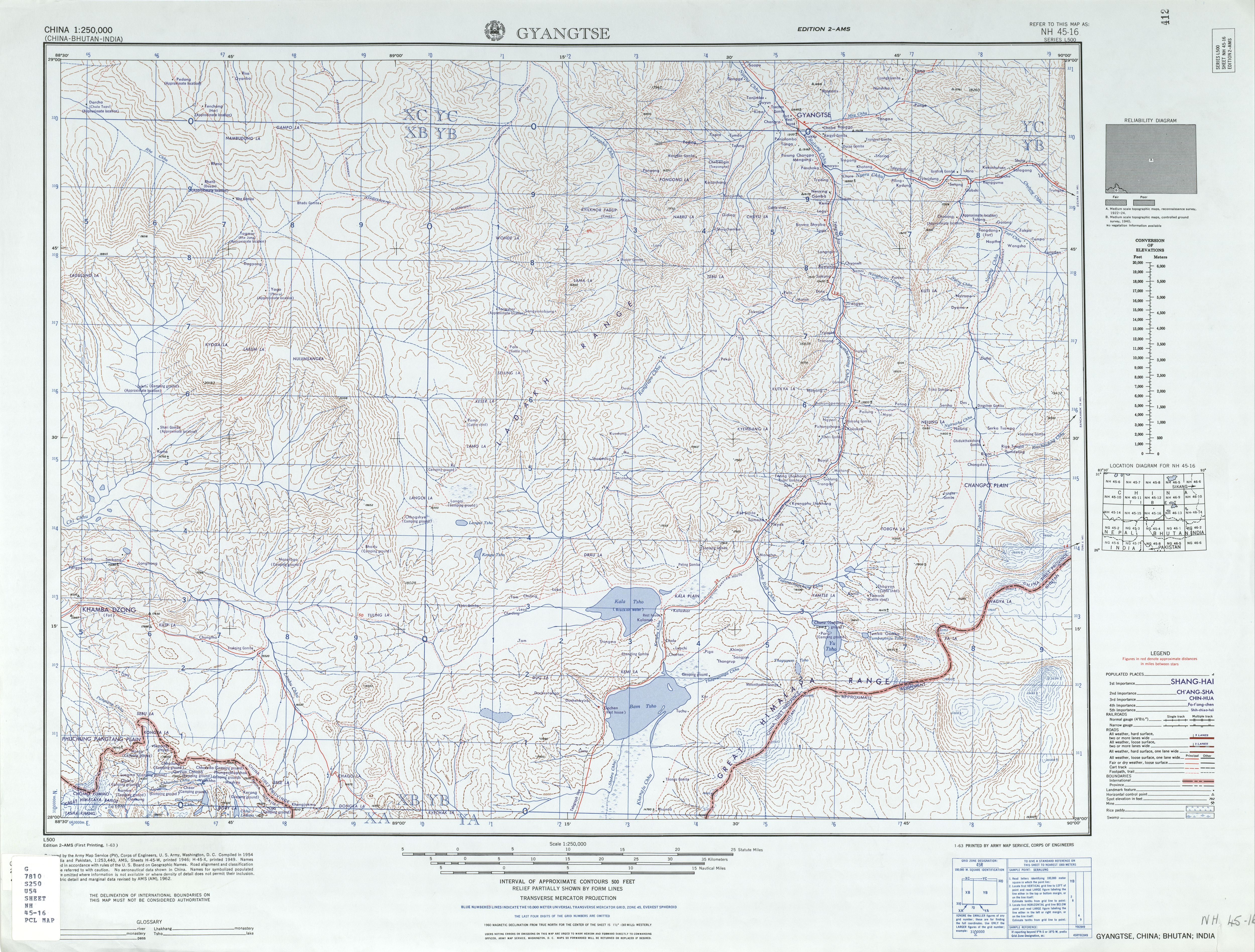
Gyantse
Gyantse, officially Gyangzê Town (also spelled Gyangtse; ; ), is a town located in Gyantse County, Shigatse Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It was historically considered the third largest and most prominent town in the Tibet region (after Lhasa, and Shigatse), but there are now at least ten larger Tibetan cities. Location The town is strategically located in the Nyang Chu valley on the ancient trade routes from the Chumbi Valley, Yatung and Sikkim, which met here. From Gyantse, routes led to Shigatse downstream and also over the Kora La (Pass) to Central Tibet. The fortress (constructed in 1390) guarded the southern approaches to the Yarlung Tsangpo Valley and Lhasa. The town was surrounded by a wall 3 km long.Buckley, Michael and Strauss, Robert (1986), p. 158. Demographics In 1952, Gyantse had a population of perhaps 8,000 people, about the same as in 2008. It is 3,977 meters (13,050 ft) above sea level, and is located 254 km southwest of Lhasa in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_of_Kashgar%2C_73_CE.jpg)