|
Neuronal Migration Disorders
Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblast In vertebrates, a neuroblast or primitive nerve cell is a postmitotic cell that does not divide further, and which will develop into a neuron after a migration phase. In invertebrates such as ''Drosophila,'' neuroblasts are neural progenitor cell ...s during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed dysgenesis (embryology), cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning "smooth brain") is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain appear smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves ( sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and '' pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Symptoms and signs Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; Implantation (embryology), implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An ''embryo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachygyria
Pachygyria (from the Greek "pachy" meaning "thick" or "fat" gyri) is a congenital malformation of the cerebral hemisphere. It results in unusually thick convolutions of the cerebral cortex. Typically, children have developmental delay and seizures, the onset and severity depending on the severity of the cortical malformation. Infantile spasms are common in affected children, as is intractable epilepsy. Presentation The term 'pachygyria' does not directly relate to a specific malformation but rather is used to generally describe physical characteristics of the brain in association with several neuronal migration disorders; most commonly disorders relating to varied degrees of lissencephaly. Lissencephaly is present in 1 of 85,470 births and the life span of those affected is short as only a few survive past the age of 20. Pachygyria is a condition identified by a type of cortical genetic malformation. Clinicians will subjectively determine the malformation based on the degree of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
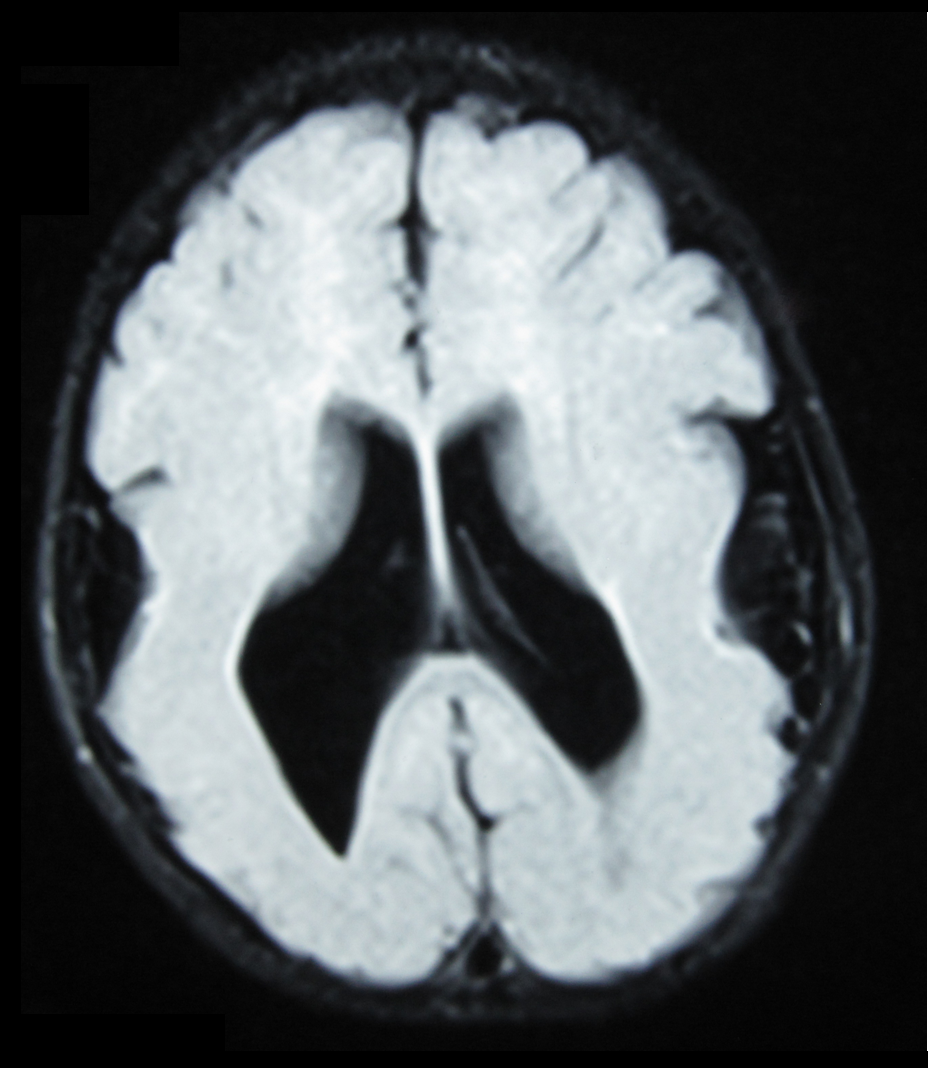
Porencephaly
Porencephaly is an extremely rare cephalic disorder involving encephalomalacia. It is a neurological disorder of the central nervous system characterized by cysts or Body cavity, cavities within the cerebral hemisphere.Parker, J. (2004). The official parent's sourcebook on porencephaly: A revised and updated directory for the internet age. ICON Health Publications. Porencephaly was termed by Heschl in 1859 to describe a cavity in the human brain. Derived from Greek language, Greek roots, the word ''porencephaly'' means 'holes in the brain'. The cysts and cavities (cystic brain lesions) are more likely to be the result of destructive (encephaloclastic) cause, but can also be from abnormal development (malformative), direct damage, inflammation, or hemorrhage. The cysts and cavities cause a wide range of physiological, physical, and neurological symptoms. Depending on the patient, this disorder may cause only minor neurological problems, without any disruption of intelligence, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizencephaly
Schizencephaly () is a rare birth defect characterized by abnormal clefts lined with grey matter that form the ependyma of the cerebral ventricles to the pia mater. These clefts can occur bilaterally or unilaterally. Common clinical features of this malformation include epilepsy, motor deficits, and psychomotor retardation. Presentation Schizencephaly can be distinguished from porencephaly by the fact that in schizencephaly, the fluid-filled component is entirely lined by heterotopic grey matter, while a porencephalic cyst is lined mostly by white matter. Individuals with clefts in both hemispheres, or bilateral clefts, are often developmentally delayed and have delayed speech and language skills and corticospinal dysfunction. Individuals with smaller, unilateral clefts (clefts in one hemisphere) may be weak or paralyzed on one side of the body and may have average or near-average intelligence. Patients with schizencephaly may also have varying degrees of microcephaly, Cognit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlissencephaly
Microlissencephaly (MLIS) is a rare congenital brain disorder that combines severe microcephaly (small head) with lissencephaly (smooth brain surface due to absent sulci and gyri). Microlissencephaly is a heterogeneous disorder, i.e. it has many different causes and a variable clinical course. Microlissencephaly is a malformation of cortical development (MCD) that occurs due to failure of neuronal migration between the third and fifth month of gestation as well as stem cell population abnormalities. Numerous genes have been found to be associated with microlissencephaly, however, the pathophysiology is still not completely understood. The combination of lissencephaly with severe congenital microcephaly is designated as microlissencephaly only when the cortex is abnormally thick. If such combination exists with a normal cortical thickness (2.5 to 3 mm), it is known as " microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern" (MSGP). Both MLIS and MSGP have a much more severe clinical cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning "smooth brain") is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain appear smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves ( sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and '' pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Symptoms and signs Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease; this field is considered necessary for the implementation of genomic medicine. The process integrates: * Interpretation of family and medical histories to assess the chance of disease occurrence or recurrence * Education about inheritance, testing, management, prevention, resources * Counseling to promote informed choices, adaptation to the risk or condition and support in reaching out to relatives that are also at risk History The practice of advising people about inherited traits began around the turn of the 20th century, shortly after William Bateson suggested that the new medical and biological study of heredity be called "genetics". Heredity became intertwined with social reforms when the field of modern eugenics took form. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
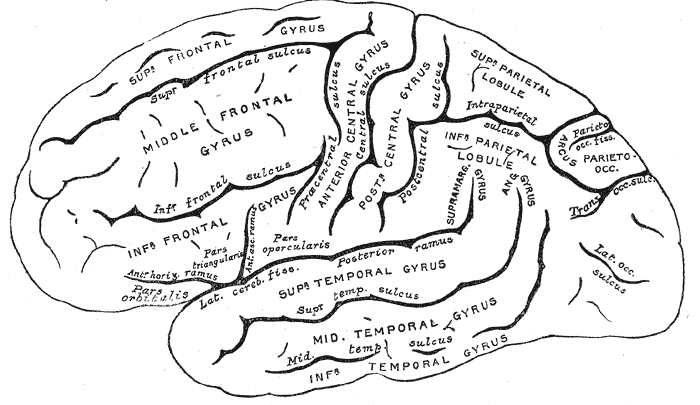
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Space
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to protect the central nervous system. Structure Dura mater The dura mater ( la, tough mother) (also rarely called ''meninx fibrosa'' or ''pachymeninx'') is a thick, durable membrane, closest to the skull and vertebrae. The dura mater, the outermost part, is a loosely arranged, fibroelastic layer of cells, characterized by multiple interdigitating cell processes, no extracellular collagen, and significant extracellular spaces. The middle region is a mostly fibrous portion. It consists of two layers: the endosteal layer, which lies closest to the skull, and the inner meningeal layer, which lies closer to the brain. It contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Layer
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for the brain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricles Of Brain
The ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal fluid can flow. Ventri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)