|
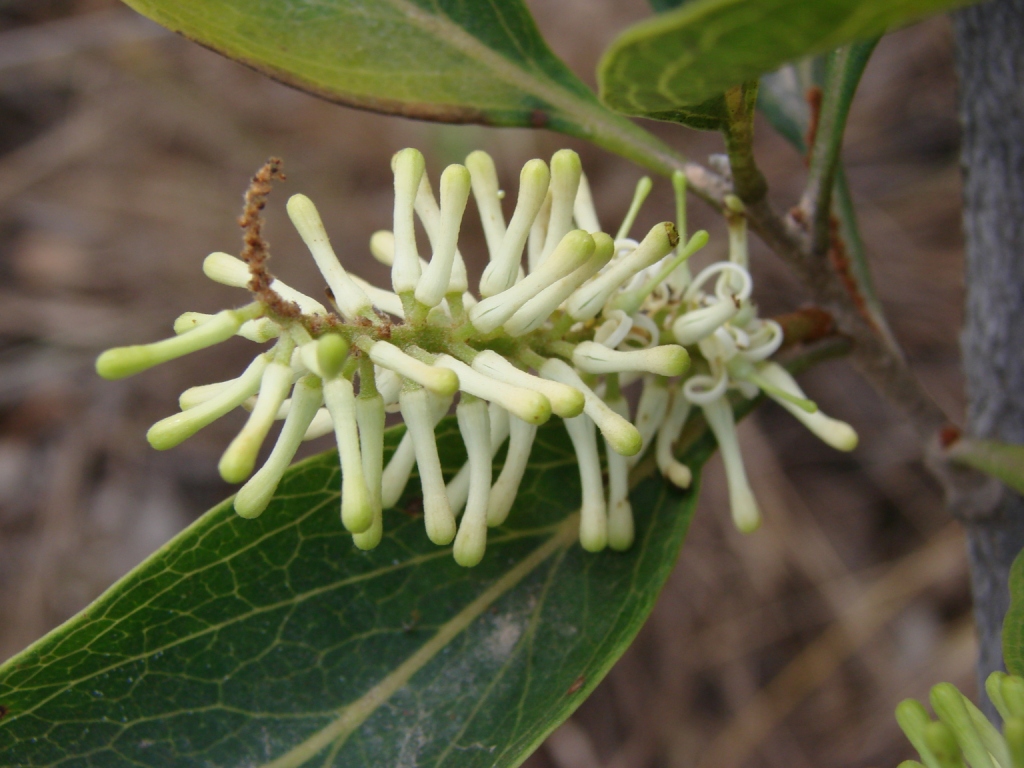
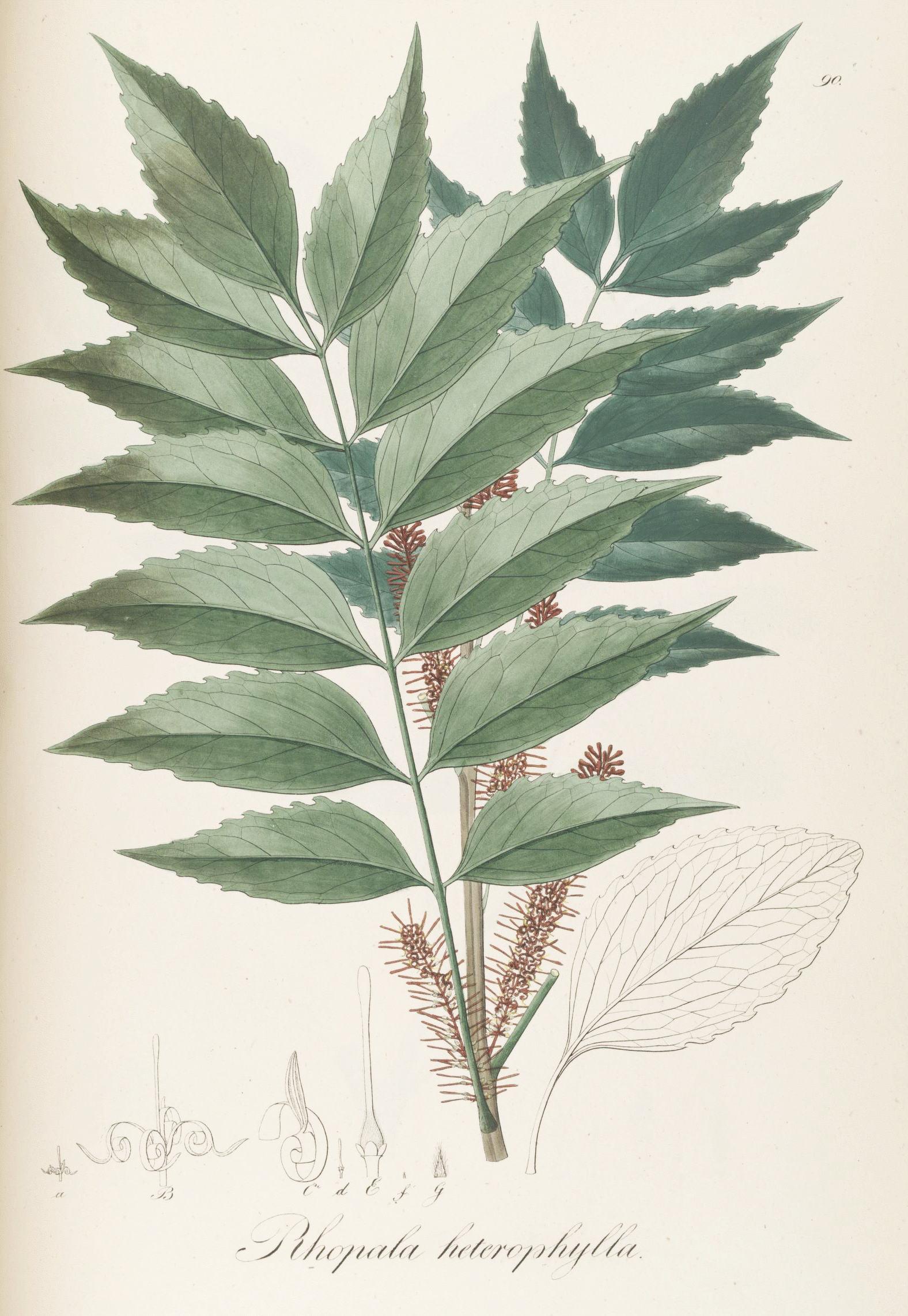
Neorites
''Neorites'' is a monotypic genus of plants in the family Proteaceae. The sole species ''Neorites kevedianus'', commonly called fishtail oak or fishtail silky oak, is a tall tree endemic to the wet tropics rainforests of north eastern Queensland, Australia. Taxonomy and naming Queensland botanist Lindsay Smith named the species in 1969, based on a specimen collected near Kuranda in 1955 by Queensland forestry officers Kevin J. White and H. Edgar Volck. Smith coined the species name from the first names of the finders. Peter H. Weston and Nigel Barker refined the classification of the Proteaceae in 2006, incorporating molecular data. Here, ''Neorites'' emerged as closely related to the genera ''Orites'' and '' Roupala''. They thus placed the three genera in the subtribe ''Roupalinae'', conceding that the next closest relatives of this group is unclear. This group lies within the subfamily Grevilleoideae. Clock dating with molecular and fossil data indicated ancestors of ''Neo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roupala
''Roupala'' is a Neotropical genus of woody shrubs and trees in the plant family Proteaceae. Its 34 species are generally found in forests from sea level to 4000 m altitude from Mexico to Argentina. Taxonomy and naming The genus was described by Jean Baptiste Christophore Fusée Aublet in 1775, its name derived from a local name ''roupale'' in French Guiana. In their 1975 monograph on the Proteaceae, Lawrie Johnson and Barbara Briggs placed it in a subtribe Roupalinae alongside the New Caledonian genus ''Kermadecia'' as the genera had similar floral parts and leaves. Both taxa also have 14 chromosome pairs. In 2006, the family's classification was redefined using molecular data. Here, ''Roupala'' emerged as a sister to the genera ''Orites'' and '' Neorites'', with ''Knightia'' as the next most closely related taxon, while ''Kermadecia'' was not related. They thus placed the first three genera in the subtribe ''Roupalinae'', conceding that the next closest relatives of this gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindsay Stewart Smith
Lindsay Stuart Smith (27 November 1917 – 12 September 1970) was an Australian botanist, naturalist and public servant. Early years Lindsay Smith was born in Bundaberg in Queensland and attended Bundaberg South State School and later Bundaberg State High School. In 1933 he began work as a clerk in the Queensland Department of Agriculture and Stock. Except for war service with the Second Australian Imperial Force in World War II, he remained in that department, rising through the ranks to the position of Senior Botanist. After the war, he studied science in the evenings and in 1948 was awarded the degree of First Class Honours in Botany. Career During World War II, Smith made collections of rainforest species in New Guinea and subsequently studied these species with the help of C.T. White and W.D. Francis and some of his collections become the nucleus of the herbarium at Lae. He made extensive studies of the genus ''Lantana'', a group of invasive species in Australia, collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevilleoideae
The Grevilleoideae are a subfamily of the plant family Proteaceae. Mainly restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, it contains around 46 genera and about 950 species. Genera include ''Banksia'', ''Grevillea'', and '' Macadamia''. Description The Grevilleoideae grow as trees, shrubs, or subshrubs. They are highly variable, making a simple, diagnostic identification key for the subfamily essentially impossible to provide. One common and fairly diagnostic characteristic is the occurrence of flowers in pairs that share a common bract. However, a few Grevilleoideae taxa do not have this property, having solitary flowers or inflorescences of unpaired flowers. In most taxa, the flowers occur in densely packed heads or spikes, and the fruit is a follicle. Distribution and habitat Grevilleoideae are mainly a Southern Hemisphere family. The main centre of diversity is Australia, with around 700 of 950 species occurring there, and South America also contains taxa. However, the Grevilleoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindsay Stuart Smith
Lindsay Stuart Smith (27 November 1917 – 12 September 1970) was an Australian Botany, botanist, Natural history, naturalist and Civil service, public servant. Early years Lindsay Smith was born in Bundaberg in Queensland and attended Bundaberg South State School and later Bundaberg State High School. In 1933 he began work as a clerk in the Queensland Department of Agriculture and Stock. Except for war service with the Second Australian Imperial Force in World War II, he remained in that department, rising through the ranks to the position of Senior Botanist. After the war, he studied science in the evenings and in 1948 was awarded the degree of British undergraduate degree classification, First Class Honours in Botany. Career During World War II, Smith made collections of rainforest species in New Guinea and subsequently studied these species with the help of Cyril Tenison White, C.T. White and William D. Francis, W.D. Francis and some of his collections become the nucleus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include '' Protea'', '' Banksia'', '' Embothrium'', '' Grevillea'', '' Hakea'' and '' Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea ('' Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of '' Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Tropical Rain Forests
The Queensland tropical rain forests ecoregion (WWF ID: AA0117) covers a portion of the coast of Queensland in northeastern Australia and belongs to the Australasian realm. The forest contains the world's best living record of the major stages in the evolutionary history of the world's land plants, including most of the world's relict species of plants from the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana. The history of the evolution of marsupials and songbirds is also well represented. Location and description The ecoregion covers of northeastern coastal Queensland, from the coast up a series of plateaus and tablelands to the mountains behind the coast. The ecoregion comprises three separate sections. The northern area, which includes Cairns, is the largest, from 15°30’ to 19°25’ south latitude. This northern section is also known as the Wet Tropics bioregion, and is just east of the Einasleigh Uplands. The middle section is centered on Mackay, Queensland, and the southern se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk ( ALP) , legislature = Parliament of Queensland , judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants
Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants, also known as RFK, is an identification key giving details—including images, taxonomy, descriptions, range, habitat, and other information—of almost all species of flowering plants (i.e. trees, shrubs, vines, forbs, grasses and sedges, epiphytes, palms and pandans) found in tropical rainforests of Australia, with the exception of most orchids which are treated in a separate key called Australian Tropical Rainforest Orchids (see External links section). A key for ferns is under development. RFK is a project initiated by the Australian botanist Bernie Hyland. History The information system had its beginnings when Hyland started working for the Queensland Department of Forestry in the 1960s. It was during this time that he was tasked with the creation of an identification system for rainforest trees, but given no direction as to its format. Having little belief in single-access keys, he began work on creating a multi-access key (or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia and in France, Chile and the United States, employing about 5,500 people. Federally funded scientific research began in Australia years ago. The Advisory Council of Science and Industry was established in 1916 but was hampered by insufficient available finance. In 1926 the research effort was reinvigorated by establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly and achieved significant early successes. In 1949, further legislated changes included renaming the organisation as CSIRO. Notable developments by CSIRO have included the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, ''Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter H
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (album), a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a 1934 film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather Animals * Peter, the Lord's cat, cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), Chief Mouser between 1929 and 1946 * Peter II (cat), Chief Mouser between 1946 and 1947 * Peter III (cat), Chief Mouser between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


