|
Negevite Pottery
Negevite pottery, Negev pottery, Negebite ware, etc. are the names given to a hand-made ware, i.e. without using the potter's wheel, found in Iron Age sites of the Negev desert, southern Jordan, and the Shfela of Israel. However, its use was not limited to the Iron Age, starting instead in the Bronze Age and continuing uninterruptedly until the Early Muslim period. It was produced from coarse clay containing straw and other organic materials. It was discovered by C. Leonard Woolley and T.E. Lawrence in the northeastern Sinai, found again by Nelson Glueck in Tell el-Kheleifeh, and at last identified by Yohanan Aharoni as the wares manufactured and used by the people of the desert. Negevite wares show some similarities with Midianite pottery bowls (in form) and with Edomite pottery (in decoration). Negevite cylindrical vessels found at excavations of Iron Age IIA sites in the Negev Highlands represent the largest and most dominant ceramic assemblage of simple-shaped vessels discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potter's Wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, and for applying incised decoration or rings of colour. Use of the potter's wheel became widespread throughout the Old World but was unknown in the Pre-Columbian New World, where pottery was handmade by methods that included coiling and beating. A potter's wheel may occasionally be referred to as a "potter's lathe". However, that term is better used for another kind of machine that is used for a different shaping process, turning, similar to that used for shaping of metal and wooden articles. The pottery wheel is an important component to create arts and craft products. The techniques of jiggering and jolleying can be seen as extensions of the potter's wheel: in jiggering, a shaped tool is slowly brought down onto the plastic clay bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
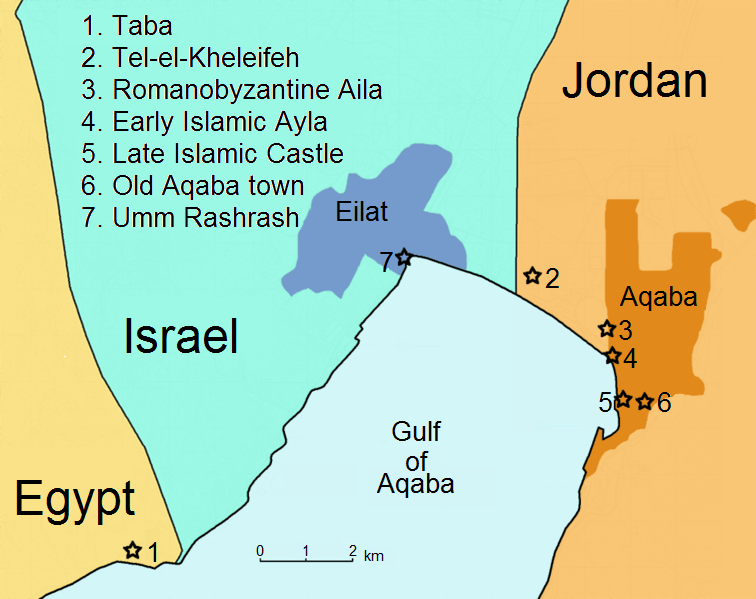
Tell El-Kheleifeh
Tell el-Kheleifeh (also Tell el-Chulefi) is an archaeological site in Jordan at the head of the Gulf of Aqaba immediately northwest of the city of Aqaba. Its older identification with the 10th-century port from the biblical King Solomon narrative does not stand up to newer archaeological assessments, while its identification with biblical Ezion-geber and/or Elath of a later date remains a matter of speculative interpretation.Pratico (1985)Finkelstein (2014) Archaeological field investigation During his excavations in 1933, the researcher Fritz Frank stated that he believed the ruins were those of Ezion-geber.Fritz Frank: ''From the ''Arabah, I: Tell el-ChleTi''. In: Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins (1934) 57, pp. 243–45. During his excavations from 1938 to 1940, American archaeologist Nelson Glueck adopted the same thesis. He distinguished five settlement periods, which he dated to between the 10th and 5th centuries BCE. Periods In 1985, Gary Pratico presented a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Exploration Journal
The ''Israel Exploration Journal'' is a biannual academic journal which has been published by the Israel Exploration Society since 1950. It primarily covers research in archaeology, but also history and geography relating to Israel and the surrounding areas. The editors-in-chief are Shmuel Ahituv, Amihai Mazar, and Z. Weiss. The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Arts & Humanities Citation Index and Current Contents ''Current Contents'' is a rapid alerting service database from Clarivate Analytics, formerly the Institute for Scientific Information and Thomson Reuters. It is published online and in several different printed subject sections. History ''C .../Arts & Humanities. References External links * * Archaeology journals Middle Eastern studies journals Publications established in 1950 English-language journals Biannual journals {{archaeology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal species involved include cattle, camels, goats, yaks, llamas, reindeer, horses and sheep. Pastoralism occurs in many variations throughout the world, generally where environmental characteristics such as aridity, poor soils, cold or hot temperatures, and lack of water make crop-growing difficult or impossible. Operating in more extreme environments with more marginal lands means that pastoral communities are very vulnerable to the effects of global warming. Pastoralism remains a way of life in many geographic areas, including Africa, the Tibetan plateau, the Eurasian steppes, the Andes, Patagonia, the Pampas, Australia and many other places. , between 200 million and 500 million people globally practised pastoralism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potter's Wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, and for applying incised decoration or rings of colour. Use of the potter's wheel became widespread throughout the Old World but was unknown in the Pre-Columbian New World, where pottery was handmade by methods that included coiling and beating. A potter's wheel may occasionally be referred to as a "potter's lathe". However, that term is better used for another kind of machine that is used for a different shaping process, turning, similar to that used for shaping of metal and wooden articles. The pottery wheel is an important component to create arts and craft products. The techniques of jiggering and jolleying can be seen as extensions of the potter's wheel: in jiggering, a shaped tool is slowly brought down onto the plastic clay bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edomite Pottery
Edomite pottery, also known as 'Busayra Painted Ware' and 'Southern Transjordan-Negev Pottery' (STNP), is the name given to several ware types found in archaeological sites in southern Jordan and the Negev dated to the 7th and 6th centuries BCE. It is attributed to the Biblical people of the Edomites. It consists of several ware types, of which the most representative ones are the plain wares, usually kraters and bowls with a denticulated fringe applied around the vessel; bowls with red and black-painted geometric decorations; cooking-pots with a stepped-rim; and vessels, mainly carinated bowls, influenced by “Assyrian ware” pottery. It was first identified by archaeologist Nelson Glueck in the 1930s-1940s.N. Glueck, ''Explorations in Eastern Palestine II''. AASOR 15. New Haven: ASOR, 1935, 123-137. It has been noticed that Negevite pottery Negevite pottery, Negev pottery, Negebite ware, etc. are the names given to a hand-made ware, i.e. without using the potter's wheel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midianite Pottery
Midianite pottery, also known as Qurayya ware is a ware type found in the Hejaz (northwestern Saudi Arabia), southern and central Jordan, southern Palestine and the Sinai, generally dated to the 13th-12th centuries BCE, although later dates are also possible.N. Glueck, 'Some Edomite Pottery from Tell el-Kheleifeh, Parts I and II', ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', 188 (1967), 8-38. Research history Midianite pottery was discovered during the 1930s by Nelson Glueck in his surveys in southern Jordan and his excavations at Tell el-Kheleifeh in the southern Arabah valley. Glueck identified these wares as Iron Age II Edomite pottery. During his surveys and excavations in the Arabah in the late 1950s and 1960s, Beno Rothenberg found similar decorated wares; and after the discovery at Timna valley of the several Egyptian findings belonging to the 19th and 20th Dynasties, Rothenberg dated this pottery to the 13th-12th centuries BCE. Petrographic studies carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yohanan Aharoni
Yohanan Aharoni (Hebrew:יוחנן אהרוני)(7 June 1919 – 9 February 1976) was an Israeli archaeologist and historical geographer, chairman of the Department of Near East Studies and chairman of the Institute of Archaeology at Tel-Aviv University. Life Born to the Aronheim family, in Germany on 7 June 1919, Aharoni immigrated to Mandatory Palestine in 1933. He studied at the Hebrew Reali School in Haifa, and later at the Mikve Yisrael agricultural school. He married Miriam Gross and became a member of kibbutz Alonim. Career Aharoni studied archaeology at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and began to teach there in 1954. By 1966, he became a professor at the university. However, in 1968, he moved to Tel-Aviv University and became chairman of the Department of Near East Studies and chairman of the Institute of Archaeology. Aharoni participated in many excavations, including Ramat Rachel, Tel Arad, Tel Be'er Sheva, Tel Hazor and Lachish. He also studied ancient roadway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Glueck
Nelson Glueck (June 4, 1900 – February 12, 1971) was an American rabbi, academic and archaeologist. He served as president of Hebrew Union College from 1947 until his death, and his pioneering work in biblical archaeology resulted in the discovery of 1,500 ancient sites. Biography Nelson Glueck was born in Cincinnati, Ohio to Lithuanian Jewish parents. He died in Cincinnati in 1971, after announcing plans to step down from the HUC presidency and four months after his final trip to Israel. He was succeeded as president of HUC by Rabbi Alfred Gottschalk. Rabbinic career Glueck developed a passion for religion early in life, and was ordained as a Reform rabbi in 1923. He received his Ph.D from the University of Jena in Germany in 1926. By 1928 he was a member of the Hebrew Union College faculty, teaching at the seminary of the Reform Jewish movement. Archaeology career In the course of his career, he became an expert on ancient pottery, he was able to match small ceramic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Bedouin towns, including Rahat and Tel Sheva and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Trans-Jordan's name". Despite th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about (6 percent of Egypt's total area) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north. In the classical era the region was known as Arabia Petraea. The peninsula acquired the name Sinai in modern times due to the assumption that a mountain near Saint Catherine's Monastery is the Biblical Mount Sinai. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Woolley
Sir Charles Leonard Woolley (17 April 1880 – 20 February 1960) was a British archaeologist best known for his excavations at Ur in Mesopotamia. He is recognized as one of the first "modern" archaeologists who excavated in a methodical way, keeping careful records, and using them to reconstruct ancient life and history. Woolley was knighted in 1935 for his contributions to the discipline of archaeology. He married the British archaeologist Katharine Woolley. Early life Woolley was the son of a clergyman, and was brother to Geoffrey Harold Woolley, VC, and George Cathcart Woolley. He was born at 13 Southwold Road, Upper Clapton, in the modern London Borough of Hackney and educated at St John's School, Leatherhead and New College, Oxford. He was interested in excavations from a young age. Career In 1905, Woolley became assistant of the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford. Volunteered by Arthur Evans to run the excavations on the Roman site at Corbridge (near Hadrian's Wall) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_Q73536.jpg)