|
Nasalis Muscle
The nasalis muscle is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose. It has a transverse part and an alar part. It compresses the nasal cartilages, and can "flare" the nostrils. Some people can use it to close the nostrils to prevent entry of water when underwater. It can be used to test the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it. Structure The nasalis muscle covers the nasal cartilages of the lower surface of the nose. It consists of two parts, ''transverse'' and ''alar'': * The ''transverse part'' (compressor naris muscle) arises from the maxilla, above and lateral to the incisive fossa. Its fibers proceed upward and medially, expanding into a thin aponeurosis which is continuous on the bridge of the nose with that of the muscle of the opposite side, and with the aponeurosis of the procerus muscle. It compresses the nostrils and may completely close them. * The ''alar part'' (dilator naris muscle) arises from the maxilla over the lateral incisor and inserts into the greater alar cartilag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; plural: ''aponeuroses'') is a type or a variant of the deep fascia, in the form of a sheet of pearly-white fibrous tissue that attaches sheet-like muscles needing a wide area of attachment. Their primary function is to join muscles and the body parts they act upon, whether bone or other muscles. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections. The primary regions with thick aponeuroses are in the ventral abdominal region, the dorsal lumbar region, the ventriculus in birds, and the palmar (palms) and plantar (soles) regions. Anatomy Anterior abdominal aponeuroses The anterior abdominal aponeuroses are located just superficial to the rectus abdominis muscle. It has for its borders the external oblique, pectoralis muscles, and the latissimus dorsi. Posterior lumbar aponeuroses The posterior lumbar aponeu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. Although these two meanings of "symmetry" can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article. Mathematical symmetry may be observed with respect to the passage of time; as a spatial relationship; through geometric transformations; through other kinds of functional transformations; and as an aspect of abstract objects, including theoretic models, language, and music. This article describes symmetry from three perspectives: in mathematics, including geometry, the most familiar type of symmetry for many people; in science and natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Septum
The nasal septum () separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils. It is depressed by the depressor septi nasi muscle. Structure The fleshy external end of the nasal septum is called the columella or columella nasi, and is made up of cartilage and soft tissue. The nasal septum contains bone and hyaline cartilage. It is normally about 2 mm thick. The nasal septum is composed of four structures: * Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone * Vomer bone * Septal nasal cartilage * Maxillary bone (the crest) The lowest part of the septum is a narrow strip of bone that projects from the maxilla and the palatine bones, and is the length of the septum. This strip of bone is called the maxillary crest; it articulates in front with the septal nasal cartilage, and at the back with the vomer. The maxillary crest is described in the anatomy of the nasal septum as having a maxillary component and a palatine component. Development At an early perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
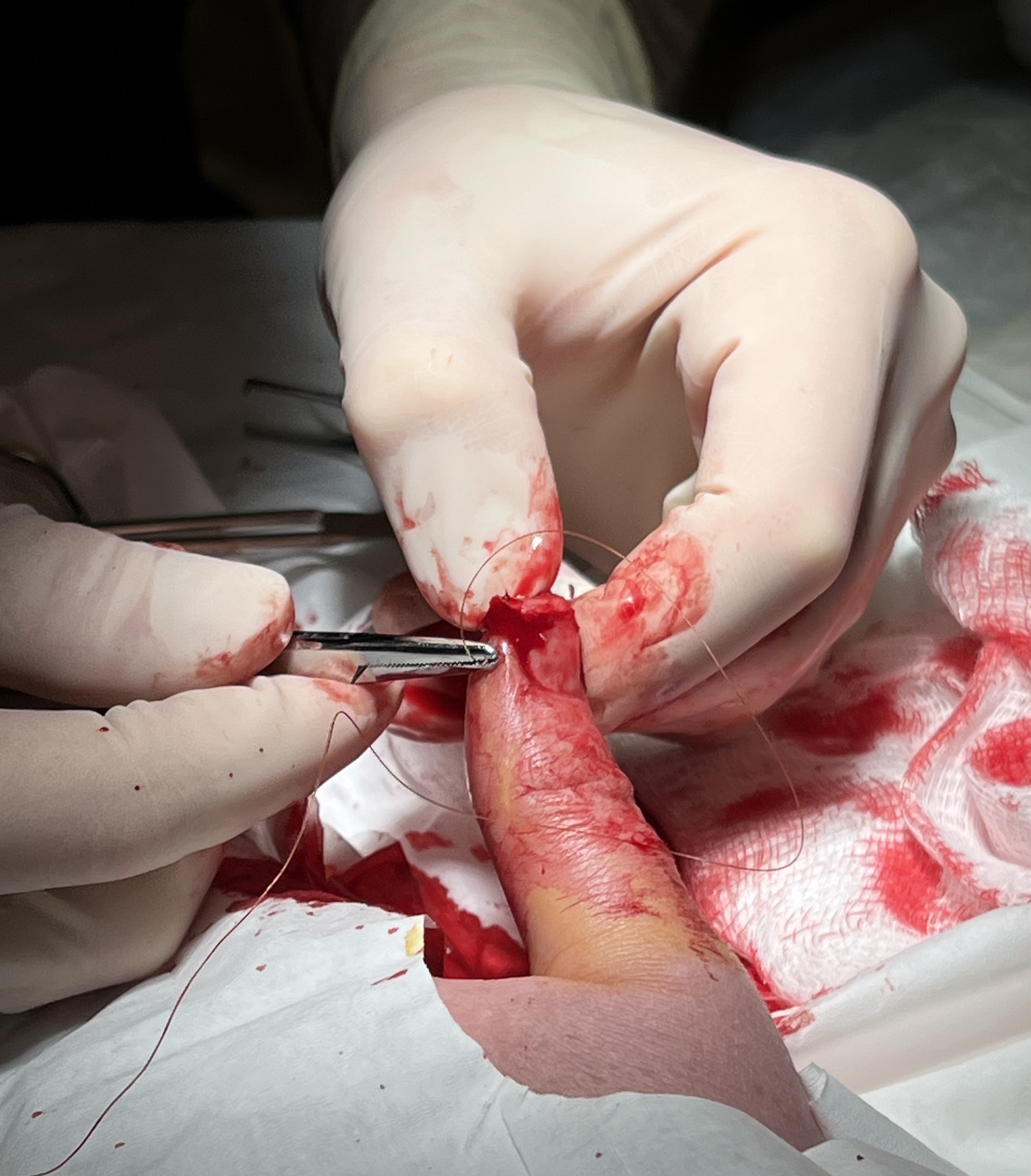
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconstructive Surgery
Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition. Description Reconstructive surgery is a term with training, clinical, and reimbursement implications. It has historically been referred to as synonymous with plastic surgery. In regard to training, Plastic Surgery is a recognized medical specialty and a surgeon can be a "board-certified" plastic surgeon by the American Board of Plastic Surgery. However, reconstructive surgery is not a specialty and there are no board-certified reconstructive surgeons. More accurately, reconstructive surgery should be contrasted with cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery is performed to # Improve/restore to normal function. # Restore to a normal appearance of "abnormal" or "malformed" body parts caused by the disease or condition and/or # Improve the patient's quality of life. Separately, the patient must be healthy enough so that the benefits o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Livingstone
Churchill Livingstone is an academic publisher. It was formed in 1971 from the merger of Longman's medical list, E & S Livingstone (Edinburgh, Scotland) and J & A Churchill (London, England) and was owned by Pearson PLC, Pearson. Harcourt (publisher), Harcourt acquired Churchill Livingstone in 1997. It is now integrated as an imprint (trade name), imprint in Elsevier's health science division after Elsevier acquired Harcourt in 2001. In the past it published a number of classic medical texts, including Sir William Osler's textbook ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine, Gray's Anatomy,'' and ''Margaret Myles, Myles' Textbook for Midwives.'' In the 1980s, in addition to new texts in all areas of clinical medicine, it published an extensive list of medical and nursing textbooks in low-cost editions for low-income countries supported by the UK-funded Educational Low Priced Book Scheme (ELBS). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleft Lip And Cleft Palate
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate (the roof of the mouth) contains an opening into the nose. The term orofacial cleft refers to either condition or to both occurring together. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders. Cleft lip and palate are the result of tissues of the face not joining properly during development. As such, they are a type of birth defect. The cause is unknown in most cases. Risk factors include smoking during pregnancy, diabetes, obesity, an older mother, and certain medications (such as some used to treat seizures). Cleft lip and cleft palate can often be diagnosed during pregnancy with an ultrasound exam. A cleft lip or palate can be successfully treated with surgery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depressor Septi Nasi Muscle
The depressor septi nasi muscle (or depressor alae nasi muscle) is a muscle of the face. It connects the incisive fossa of the maxilla and the orbicularis oris muscle to the nasal septum of the nose. It draws the ala of the nose downwards, reducing the size of the nostrils. Structure The depressor septi nasi muscle arises from the incisive foramen of the maxilla. It may also partially originate from the orbicularis oris muscle. Its fibers ascend to be inserted into the nasal septum and back part of the alar part of nasalis muscle. It lies between the mucous membrane and muscular structure of the lip. Function The depressor septi is a direct antagonist of the other muscles of the nose, drawing the ala of the nose downward, constricting the nostrils. It works like the alar part of the nasalis muscle. Clinical significance During rhinoplasty, repositioning of the head of the depressor septi nasi muscle ensures normal nose position after surgery Surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Alar Cartilage
The major alar cartilage (greater alar cartilage) (lower lateral cartilage) is a thin, flexible plate, situated immediately below the lateral nasal cartilage, and bent upon itself in such a manner as to form the medial wall and lateral wall of the nostril of its own side. The portion which forms the medial wall (crus mediale) is loosely connected with the corresponding portion of the opposite cartilage, the two forming, together with the thickened integument and subjacent tissue, the nasal septum. The part which forms the lateral wall (crus laterale) is curved to correspond with the ala of the nose; it is oval and flattened, narrow behind, where it is connected with the frontal process of the maxilla by a tough fibrous membrane, in which are found three or four small cartilaginous plates, the lesser alar cartilages (cartilagines alares minores; sesamoid cartilages). Above, it is connected by fibrous tissue to the lateral cartilage and front part of the cartilage of the septum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilator Naris Muscle
The dilator naris muscle (or alae nasi muscle) is a part of the nasalis muscle. It has an anterior and a posterior part. It has origins from the nasal notch of the maxilla and the major alar cartilage, and a single insertion near the margin of the nostril. It controls nostril width, including changes during breathing. Its function can be tested as an analogue for the function of the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it. Structure The dilator naris muscle is divided into posterior and anterior parts. * The ''dilator naris posterior'' is placed partly beneath the levator labii superioris muscle. It arises from the margin of the nasal notch of the maxilla, and from the minor alar cartilages. It is inserted into the skin near the margin of the nostril. * The ''dilator naris anterior'' is a delicate fasciculus. It originates from the lateral crus of the major alar cartilage, more laterally. It inserts into the margin of the nostril, the alar groove. It is situated in front of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |