|
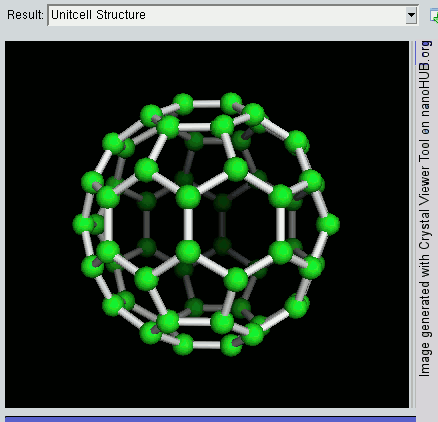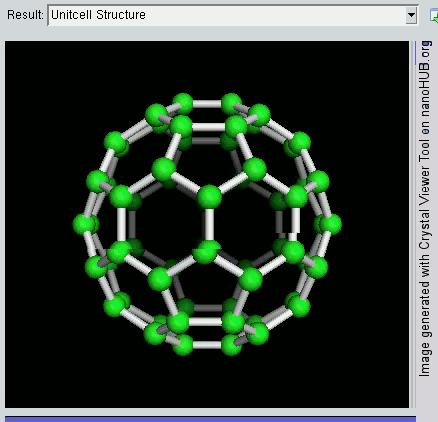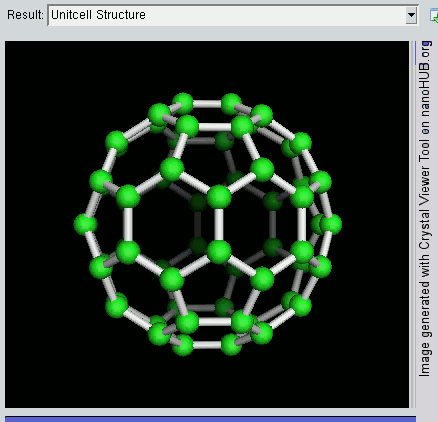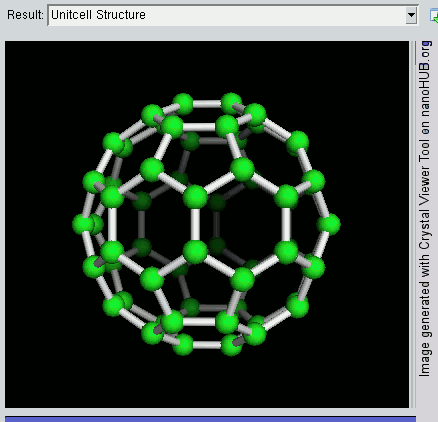
Nanolattices
A nanolattice is a synthetic porous material consisting of nanometer-size members patterned into an ordered lattice structure, like a space frame. The nanolattice is a newly emerged material class that has been rapidly developed over the last decade. Nanolattices redefine the limits of the material property space. Despite being composed of 50-99% of air, nanolattices are very mechanically robust because they take advantage of size-dependent properties that we generally see in nanoparticles, nanowires, and thin films. The most typical mechanical properties of nanolattices include ultrahigh strength, damage tolerance, and high stiffness. Thus, nanolattices have a wide range of applications. Driven by the evolution of 3D printing techniques, nanolattices aiming to exploit beneficial material size effects through miniaturized lattice designs were first developed in the mid-2010s,. Nanolattices are the smallest man-made lattice truss structures and a class of metamaterials that derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Microlattice
A metallic microlattice is a synthetic porous metallic material consisting of an ultra-light metal foam. With a density as low as 0.99 mg/cm3 (0.00561 lb/ft3), it is one of the lightest structural materials known to science. It was developed by a team of scientists from California-based HRL Laboratories, in collaboration with researchers at University of California, Irvine and Caltech, and was first announced in November 2011. The prototype samples were made from a nickel-phosphorus alloy. In 2012, the microlattice prototype was declared one of 10 World-Changing Innovations by ''Popular Mechanics''. Metallic microlattice technology has numerous potential applications in automotive and aeronautical engineering. A detailed comparative review study among other types of metallic lattice structures showed them to be beneficial for light-weighting purposes but expensive to manufacture. Synthesis To produce their metallic microlattice, the HRL/UCI/Caltech team first prepared a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Layer Deposition
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a thin-film deposition technique based on the sequential use of a gas-phase chemical process; it is a subclass of chemical vapour deposition. The majority of ALD reactions use two chemicals called precursors (also called "reactants"). These precursors react with the surface of a material one at a time in a sequential, self-limiting, manner. A thin film is slowly deposited through repeated exposure to separate precursors. ALD is a key process in fabricating semiconductor devices, and part of the set of tools for synthesising nanomaterials. Introduction During atomic layer deposition a film is grown on a substrate by exposing its surface to alternate gaseous species (typically referred to as precursors or reactants). In contrast to chemical vapor deposition, the precursors are never present simultaneously in the reactor, but they are inserted as a series of sequential, non-overlapping pulses. In each of these pulses the precursor molecules react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomaterials
* Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructured materials'', which have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |