|
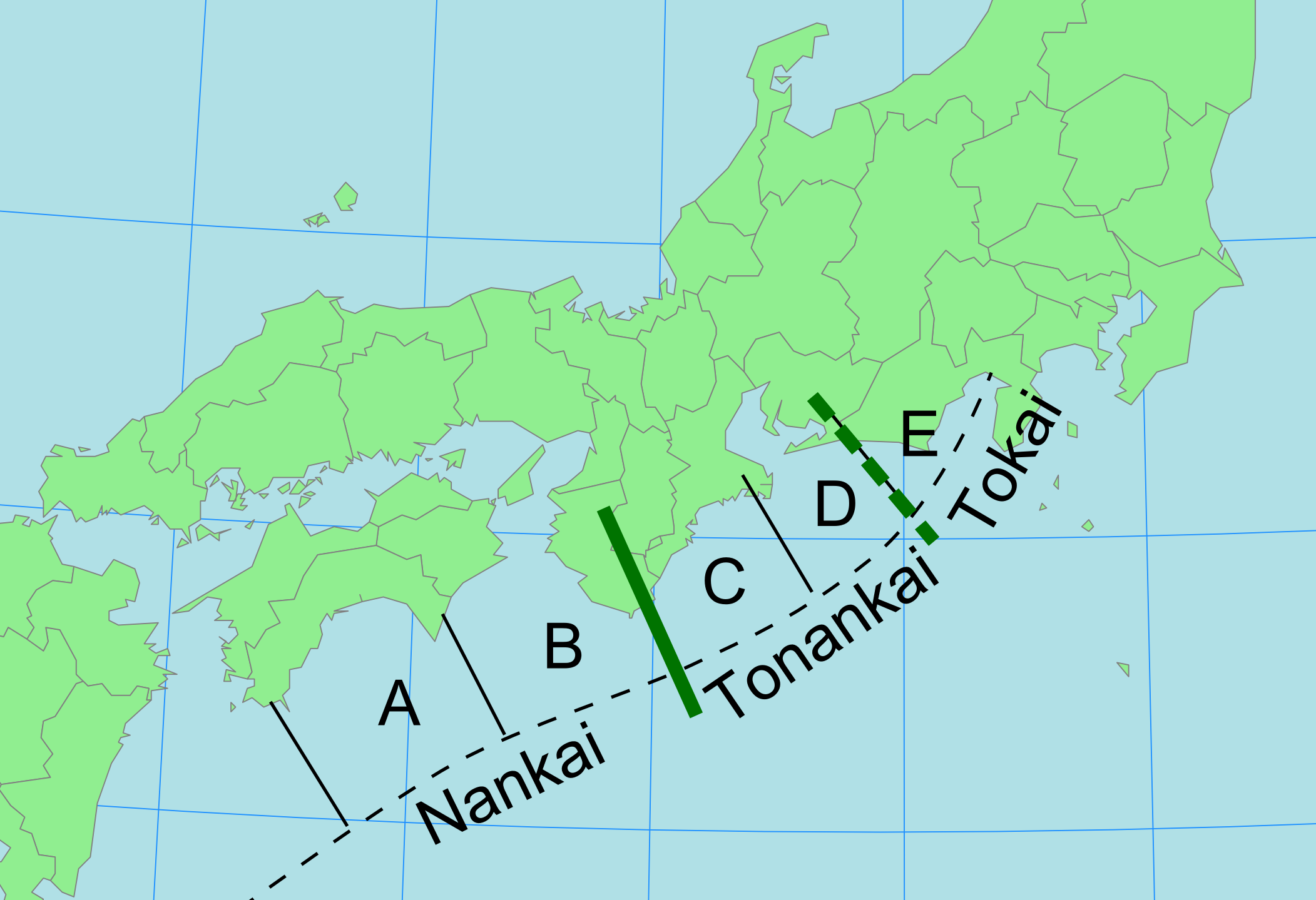
Nankai Megathrust Earthquakes
Nankai megathrust earthquakes are great megathrust earthquakes that occur along the ''Nankai megathrust'' – the fault under the Nankai Trough – which forms the plate interface between the subducting Philippine Sea Plate and the overriding Amurian Plate (part of the Eurasian Plate), which dips beneath southwestern Honshu, Japan. The fault is divided into five segments in three zones, which rupture separately or in combination, and depending on location, the resulting earthquakes are subdivided by zone from west to east into Nankai earthquakes, Tōnankai earthquakes, and Tōkai earthquakes. The earthquakes occur with a return period of about 90–200 years, and often occur in pairs, where a rupture along one part of the fault is followed by a rupture elsewhere on the fault, notably the 1854 Ansei-Tōkai earthquake and the 1854 Ansei-Nankai earthquake the next day, and the 1944 Tōnankai earthquake, followed by the 1946 Nankaidō earthquake. In one recorded case (the 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megathrust Earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (''Mw'') that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. The thrust faults responsible for megathrust earthquakes often lie at the bottom of oceanic trenches; in such cases, the earthquakes can abruptly displace the sea floor over a large area. As a result, megathrust earthquakes often generate tsunamis that are considerably more destructive than the earthquakes themselves. Teletsunamis can cross ocean basins to devastate areas far from the original earthquake. Terminology and mechanism The term ''megathrust'' refers to an extremely large thrust fault, typically formed at the plate interface along a subduction zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1707 HĹŤei Earthquake
The struck south-central Japan at 14:00 local time on 28 October. It was the largest earthquake in Japanese history until it was surpassed by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake. It caused moderate to severe damage throughout southwestern Honshu, Shikoku and southeastern Kyūshū. The earthquake, and the resulting destructive tsunami, caused more than 5,000 casualties. This event ruptured all of the segments of the Nankai megathrust simultaneously, the only earthquake known to have done this, with an estimated magnitude of 8.6 or 8.7 . It possibly also triggered the last eruption of Mount Fuji 49 days later. Hōei (宝永) was the era spanning the years from March 1704 through April 1711. Tectonic setting The southern coast of Honshu runs parallel to the Nankai Trough, which marks the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate. Movement on this convergent plate boundary leads to many earthquakes, some of them of megathrust type. The Nankai megathrust has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TĹŤkai Region
The is a subregion of the Chūbu region and Kansai region in Japan that runs along the Pacific Ocean. The name comes from the Tōkaidō, one of the Edo Five Routes. Because Tōkai is a sub-region and is not officially classified, there is some disagreement about where exactly the region begins and ends, however Japanese maps widely conclude that the region includes Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu and Mie prefectures. The largest major city in the region is Nagoya and the Chūkyō Metropolitan Area (Nagoya Metropolitan Area) makes up a large portion of the region and has Japan's third strongest economy. The business influence of this urban area sometimes extends out into the outlying areas of the three prefectures centered on Nagoya which are Aichi, Gifu, and Mie; this area is sometimes referred to as the Chūkyō region. Tōkai is a heavy manufacturing area and is one of the most industrial regions in Japan. Its coast is lined with densely populated cities with economies tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splay Fault
Splay may refer to: *Splay, a verb meaning slant, slope or spread outwards *Splay (physiology), the difference between urine threshold and saturation *Splay (Japanese band), a J-pop band from Osaka *Splay Networks, a Sweden-headquartered group of multi-channel networks for Sweden, Finland, Norway, Denmark, and Germany * In architecture **chamfer, a beveled edge connecting two surfaces **talus (fortification), a sloping face at the base of a fortified wall *Splay (plastics) Splay is a term used in the manufacture of injection molded plastics to refer to off-colored streaking along the surface of a molded part. A cosmetic defect, it is often silvery in color and is sometimes called 'silver streak's. The most common cau ..., off-colored streaking that occurs in injection molded plastics * Splay tree, a type of search tree * Splay fault, geology * Splay leg, a condition in birds and poultry * ''Splay'' (Shiner album), 1996 * ''Splay'' (Jim Black album), 2002 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized air gun or a seismic vibrator. Reflection seismology is similar to sonar and echolocation. This article is about surface seismic surveys; for vertical seismic profiles, see VSP. History Reflections and refractions of seismic waves at geologic interfaces within the Earth were first observed on recordings of earthquake-generated seismic waves. The basic model of the Earth's deep interior is based on observations of earthquake-generated seismic waves transmitted through the Earth's interior (e.g., Mohorovičić, 1910). The use of human-generated seismic waves to map in detail the geology of the upper few kilometers of the Earth's crust followed shortly thereafter and ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okinawa Plate
The Okinawa Plate, or Okinawa Platelet, is a minor continental tectonic plate in the northern and eastern hemispheres stretching from the northern end of Taiwan to the southern tip of the island of Kyūshū. The Okinawa Plate hosts typical earthquakes, like the 1911 Kikai Island earthquake, and various types of slow earthquakes, including low frequency earthquakes, very low frequency earthquakes, tremor, and slow slip events. Boundaries The eastern side of the Okinawa Plate forms a convergent boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate, forming the Ryukyu Trench and the island arc that forms the Ryukyu Islands. The Okinawa Plate is bounded on the western side by the Okinawa Trough, a back arc basin and divergent boundary with the Yangtze Plate. A section of the southern boundary between the Okinawa Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate is a former subduction zone that now accommodates oblique slip and was the location of the 1771 Great Yaeyama Tsunami The 1771 Great Yaeyama Tsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth. Mount Fuji is an active stratovolcano that last erupted from 1707 to 1708. The mountain is located about southwest of Tokyo and is visible from there on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is covered in snow for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers. Mount Fuji is one of Japan's along with Mount Tate and Mount Haku. It is a Special Place of Scenic Beauty and one of Japan's Historic Sites. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okhotsk Plate
The Okhotsk Plate is a minor tectonic plate covering the Kamchatka Peninsula, Magadan Oblast, and Sakhalin Island of Russia; Hokkaido, Kantō and Tōhoku regions of Japan; the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the disputed Kuril Islands. It was formerly considered a part of the North American Plate, but recent studies indicate that it is an independent plate, bounded on the north by the North American Plate. The boundary is a left-lateral moving transform fault, the Ulakhan Fault originating from a triple junction in the Chersky Range. On the east, the plate is bounded by the Pacific Plate at the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench and the Japan Trench, on the south by the Philippine Sea Plate at the Nankai Trough, on the west by the Eurasian Plate, and on the southwest by the Amurian Plate. Geology The boundary between Okhotsk Plate and Amurian Plate might be responsible for many strong earthquakes that occurred in the Sea of Japan as well as in Sakhalin Island, such as the MW7.1 ( M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of islands which contains older volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. The curved shape of many v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2.7 million in the 2020 census, it is also the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, which is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan and the 10th largest urban area in the world with more than 19 million inhabitants. Osaka was traditionally considered Japan's economic hub. By the Kofun period (300–538) it had developed into an important regional port, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it served briefly as the imperial capital. Osaka continued to flourish during the Edo period (1603–1867) and became known as a center of Japanese culture. Following the Meiji Restoration, Osaka greatly expanded in size and underwent rapid industrialization. In 1889, Osaka was officially established as a municipality. The cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |