|
Nana (echos)
Phthora nana (Medieval Greek ) is one of the ten modes of the Hagiopolitan Octoechos consisting of 8 diatonic echoi and two additional phthorai. It is used in different traditions of Orthodox chant until today (→ Neobyzantine Octoechos). The name "nana" is taken from the syllables (written in ligatures "ʅʅ") sung during the intonation which precedes a melody composed in this mode. The name "phthora" derived from the verb and means "destroy" or "corrupt". It was usually referred to the diatonic genus of the eight mode system and as a sign used in Byzantine chant notation it indicated a "change to another genus" (), in the particular case of phthora nana a change to the enharmonic genus. Today the "nana" intonation has become the standard name of the third authentic mode which is called "echos tritos" () in Greek and "third glas" () in Old Church Slavonic. The different functions of phthora nana In the theory and notation of Byzantine and Orthodox chant nana is the name of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Fall of Constantinople, Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division of the empire. However, this approach is rather arbitrary as it is more an assumption of political, as opposed to cultural and linguistic, development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heirmologion
Irmologion ( grc-gre, τὸ εἱρμολόγιον ) is a liturgical book of the Eastern Orthodox Church and those Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite. It contains ''irmoi'' () organised in sequences of odes (, sg. ) and such a sequence was called ''canon'' ( 'law'). These canons of nine, eight, four or three odes are supposed to be chanted during the morning service (Orthros). The book ''Irmologion'' derives from ''heirmos'' () which means 'link'. The is a melodic model which preceded the composition of the odes. According to the etymology, the book 'collects' ( ) the . The melodic irmos and the odes of the canon and its use during the morning service An important portion of Matins and other services in the Orthodox Church is the canon, a long liturgical poem divided into nine strophes with a sophisticated meter called ode. Each ode and its prosodic meter is made according to a certain irmos, and concerning its celebration during Orthros it is followe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyeleos
The Polyeleos is a festive portion of the Matins or All-Night Vigil service as observed on higher-ranking feast days in the Eastern Orthodox, Eastern Lutheran, and Byzantine Rite Catholic Churches. The Polyeleos is considered to be the high point of the service, and contains the reading of the Matins Gospel. Because of its liturgical importance, settings for the Polyeleos have been composed by Sergei Rachmaninoff and others. The name derives from Greek Πολυέλεος (pl. Πολυέλεοι), meaning "of much mercy", because of the repetition in one of the Polyeleoi of the phrase "ὅτι εἰς τὸν αἰῶνα τὸ ἔλεος αὐτοῦ" (''hoti eis ton aiōna to eleos autou''), meaning "because forever astsHis mercy"), Psalms Specifically, the Polyeleos consists of Psalms 134 and 135 (Septuagint numbering; King James Version: Psalms and ), which are solemnly chanted in a festive melody, with refrains Alleluia chanted between each verse. The refrain for Psalm 134 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
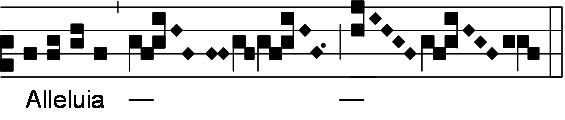
Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of scripture, usually from the Psalms. This chant is commonly used before the proclamation of the Gospel. In Western Christianity, congregations commonly cease using the word "Alleluia" during the period of Lent but restore it into their services at Easter. The form of praise "Alleluia" is used by Christians to thank and glorify God; it finds itself present in many prayers and hymns, especially those related to Eastertide, such as ''Jesus Christ Is Risen Today''. History The Hebrew word ''Hallelujah'' as an expression of praise to God was preserved, untranslated, by the Early Christians as a superlative expression of thanksgiving, joy, and triumph. Thus it appears in the ancient Greek Liturgy of St. James, which is still used to this day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticheron
A sticheron ( Greek: "set in verses"; plural: stichera; Greek: ) is a hymn of a particular genre sung during the daily evening (Hesperinos/Vespers) and morning ( Orthros) offices, and some other services, of the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic churches. ''Stichera'' are usually sung in alternation with or immediately after psalm or other scriptural verses. These verses are known as ''stichoi'' (sing: ''stichos''), but ''sticheraric'' poetry usually follows the hexameter and is collected in a book called sticherarion ( Greek: ). A sticherarion is a book containing the stichera for the morning and evening services throughout the year, but chant compositions in the ''sticheraric melos'' can also be found in other liturgical books like the Octoechos or the ''Anastasimatarion'', or in the Anthology for the Divine Liturgy. The sticheraric melos and the troparion In the current traditions of Orthodox Chant, the ''sticherarion'' as a hymn book was also used to call a chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiomelon
(Medieval Greek: from , 'unique' and , 'melody'; Church Slavonic: , )—pl. ''idiomela''—is a type of sticheron found in the liturgical books used in the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite, and many other Orthodox communities like Old Believers. are unique compositions, while or —sing. , or (Medieval Greek: , Church Slavonic: , )—were used to create other hymns by a composition over the 's melody and following the poetic meter provided by the musical rhythm. The genre composed over these was characterised as or (Medieval Greek: 'similar to', Church Slavonic: , ). Definition of ''idiomelon'', ''avtomelon'' and ''prosomoion'' The hymn category can only be understood in comparison with and . Already in the older book Tropologion each melody of a certain hymn was classified by a modal signature of the Byzantine octoechos—the eight-mode system as it had developed in Constantinople, Damascus, Jerusalem, and in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irmos
The irmos (or heirmos from grc-x-koine, εἱρμός) in the Byzantine liturgical tradition is the initial troparion of an ode of a canon. The meter and melody of an irmos is followed by the remaining troparia of the ode; when more than one canon is used (as is typical at matins), only the first canon's irmos is sung, but the irmoi of the subsequent canons must be known in order to determine an ode's melody and so, even in canons where it is known that the irmos is never sung, the irmos is nonetheless specified. Note that in the Russian tradition, often only the irmos is sung, the rest of the ode simply being read; in Greek parishes, often the remaining troparia are simply eliminated, but in non-Russian traditions, all troparia of a canon are sung The term comes from the Greek verb "to tie, link" meaning that it poetically connects the Biblical ode to the subject of the canon. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ManCo
Manco is a male given name, and may refer to: *Manco Capac, also known as Manco Inca and Ayar Manco, according to some historians, founder and first governor of the Inca civilization in Cuzco (KOOZ-Koh), possibly in the early 13th century *Manco Inca Yupanqui (1516–1544), founder and monarch of the independent Neo-Inca State in Vilcabamba, originally a puppet Inca Emperor installed by the Spaniards *Manco, the nickname of the Man with No Name The Man with No Name ( it, Uomo senza nome) is the antihero character portrayed by Clint Eastwood in Sergio Leone's "''Dollars Trilogy''" of Italian Spaghetti Western films: ''A Fistful of Dollars'' (1964), ''For a Few Dollars More'' (1965), ..., a character in the film '' For a Few Dollars More'' Manco may also refer to: *Manco Inc., manufacturer of Duck Tape brand products, now a part of Shurtape Technologies {{disambiguation, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampadarios
A lampadarius, plural ''Lampadarii'', from the Latin ''lampada'', from Ancient Greek "lampas" λαμπάς (candle), was a slave who carried torches before consuls, emperors and other officials of high dignity both during the later Roman Republic and under the Empire. ''Lampadarios'' in the post-Byzantine period designates the leader of the second (left) choir of singers in the Eastern Orthodox church practice. Lampadarius in Christianity There seems no special reason to attribute to the lampadarii any ecclesiastical character, though their functions were imitated by the acolytes and other clerics who preceded the bishop or celebrant, carrying torches in their hands, in the solemn procession to the altar and in other processions. There is very little evidence that any strictly liturgical use was made of lamps in the early centuries of Christianity. The fact that many of the services took place at night, and that after the lapse of a generation or two the meetings of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Chrysaphes
Manuel Doukas Chrysaphes ( el, , ) was the most prominent Byzantine musician of the 15th century. Life and works A singer, composer, and musical theoretician, Manuel Chrysaphes was called "the New Koukouzeles" by his admirer, the Cretan composer John Plousiadinos. He is the author of at least 300 compositions, including nearly full modal cycles of liturgical ordinaries (alleluiaria, cheroubika, and koinonika), kalophonic stichera for various movable and fixed feasts throughout the year, kratemata (wordless compositions), and both simple and kalophonic psalmody for Vespers and Matins. Little is known of his life, except that he held the office of '' lampadarios'' at the Constantinopolitan Court,Not at the Hagia Sophia cathedral, as Chrysanthos of Madytos and others who quoted him, wrote. The "Lampadarios" was a prestigious office of a soloist who replaced or directed the left choir. and received commissions from the last two Byzantine emperors, John VIII Palaiologos and Constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |