|
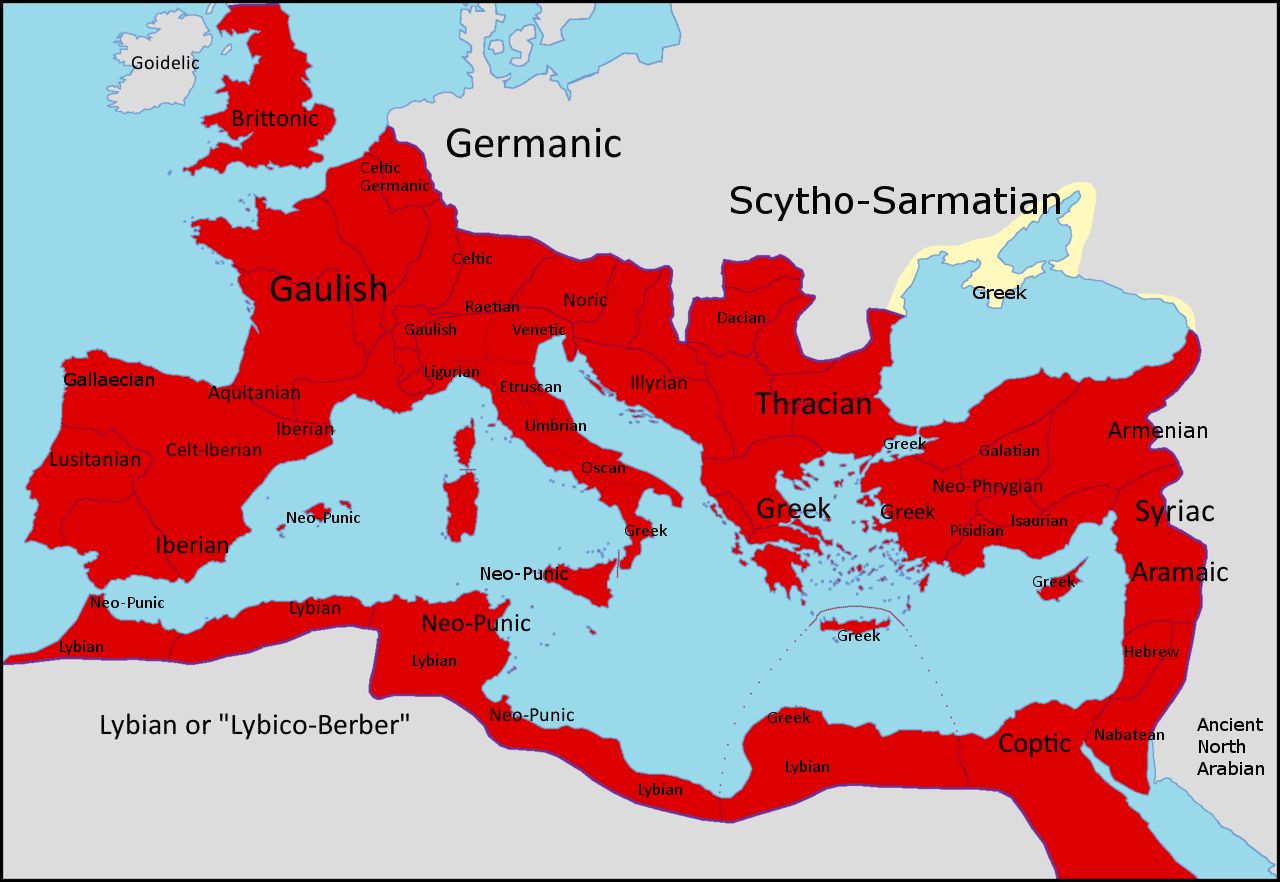
Northwest Semitic Languages
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite in the Middle Bronze Age. The oldest coherent texts are in Ugaritic, dating to the Late Bronze Age, which by the time of the Bronze Age collapse are joined by Old Aramaic, and by the Iron Age by Sutean and the Canaanite languages (Hebrew, Phoenician/ Punic, Edomite and Moabite). The term was coined by Carl Brockelmann in 1908,The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook, Chapter V page 425 who separated Fritz Hommel's 1883 classification of |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aegean, eastern Libya, and the Balkans. The collapse was sudden, violent, and culturally disruptive for many Bronze Age civilizations, creating a sharp material decline for the region's previously existing powers. The palace economy of Mycenaean Greece, the Aegean region, and Anatolia that characterized the Late Bronze Age disintegrated, transforming into the small isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages, which lasted from to , and were followed by the better-known Archaic Age. The Hittite Empire spanning Anatolia and the Levant collapsed, while states such as the Middle Assyrian Empire in Mesopotamia and the New Kingdom of Egypt survived in weakened forms. Other cultures such as the Phoenicians enjoyed increased autonomy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eblaite Language
Eblaite (, also known as Eblan ISO 639-3), or Palaeosyrian, is an extinct East Semitic language used during the 3rd millennium BC in Northern Syria. It was named after the ancient city of Ebla, in modern western Syria. Variants of the language were also spoken in Mari, Syria, Mari and Tell Brak, Nagar. According to Cyrus Gordon, Cyrus H. Gordon, although scribes might have spoken it sometimes, Eblaite was probably not spoken much, being rather a written lingua franca with East and West Semitic features. The language was discovered through cuneiform tablets found in Ebla. Discovery The 1964 discovery at the Ebla, Tell Mardikh site in Northern Syria of an ancient city from the second half of the third millennium BC completely altered archaeological knowledge of the time, as it indicated the existence of a contemporary urban culture during the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia), Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia, within a geographic zone where, at the time, previous excavat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa, Babylonia and perhaps Dilmun) from the mid- third millennium BC until its gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC. Akkadian, which is the earliest documented Semitic language, is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (–2154 BC). It was written using the cuneiform script, originally used for Sumerian, but also used to write multiple languages in the region including Eblaite, Hurrian, Elamite, Old Persian and Hittite. The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian went beyond just the cuneiform script; owing to their close proximity, a lengthy span of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Semitic Languages
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced by the non-Semitic Sumerian language and adopted cuneiform writing. East Semitic languages stand apart from other Semitic languages, which are traditionally called West Semitic, in a number of respects. Historically, it is believed that the linguistic situation came about as speakers of East Semitic languages wandered further east, settling in Mesopotamia during the 3rd millennium BC, as attested by Akkadian texts from this period. By the early 2nd millennium BC, East Semitic languages, in particular Akkadian, had come to dominate the region. Phonology Modern understanding of the phonology of East Semitic languages can be derived only from careful study of written texts and comparison with the reconstructed Proto-Semitic. Most striking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Hommel
Fritz Hommel (31 July 1854 – 17 April 1936) was a German Orientalist. Biography Hommel was born on 31 July 1854 in Ansbach. He studied in Leipzig and was habilitated in 1877 in Munich, where in 1885, he became an extraordinary professor of Semitic languages. He became a full professor in 1892, and after his retirement in 1925, continued to give lectures at the University of Munich. He was the doctoral supervisor of Islamic philosopher and poet Muhammad Iqbal, who wrote the thesis ''The Development of Metaphysics in Persia'' under his supervision. He was intrigued by linguistical problems, and also interested in the history of the Middle East and its connection with culture and intellectual life. He excelled in studies of cuneiform literature, ancient Arabic poetry, old Turkic inscriptions and Egyptian pyramid texts. He died on 17 April 1936 aged 81 in Munich. Works Among his better written efforts were a history of Babylonia and Assyria, ''Geschichte Babyloniens und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Brockelmann
Carl Brockelmann (17 September 1868 – 6 May 1956) German Semitic studies, Semiticist, was the foremost Orientalism, orientalist of his generation. He was a professor at the universities in University of Wrocław, Breslau, Berlin and, from 1903, University of Königsberg, Königsberg. He is best known for his multi-volume ''Geschichte der arabischen Litteratur'' (first published 1898–1902) ('History of Arabic literature') which included all writers in Arabic to 1937, and remains the fundamental reference volume for all Arabic literature, apart from the Christian Arabic texts (covered by Georg Graf). He also published ''Syrische Grammatik mit Litteratur, Chrestomathie und Glossar'' (1899), ''Semitische Sprachwissenschaft'' (1906), ''Lexicon syriacum'' (1928), and ''Arabische Grammatik'' (under his own name 1941, but this was the eleventh edition of the grammar of Albert Socin, previously revised by Brockelmann several times). Career Brockelmann pursued Oriental studies, class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moabite Language
The Moabite language, also known as the Moabite dialect, is an extinct sub-language or dialect of the Canaanite languages, themselves a branch of Northwest Semitic languages, formerly spoken in the region described in the Bible as Moab (modern day central-western Jordan) in the early 1st millennium BC. The body of Canaanite epigraphy found in the region is described as Moabite; this is a very small corpus limited primarily to the Mesha Stele and a few seals. Moabite, together with the similarly poorly-attested Ammonite and Edomite, belonged to the dialect continuum of the Canaanite group of northwest Semitic languages, together with Hebrew and Phoenician. History An altar inscription written in Moabite and dated to 800 BC was revealed in an excavation in Khirbat Ataruz. It was written using a variant of the Phoenician alphabet. Most knowledge about Moabite comes from the Mesha Stele, which is the only known extensive text in the language. In addition, there is the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edomite Language
Edomite is a Northwest Semitic Canaanite language, very similar to Biblical Hebrew, Ekronite, Ammonite, Phoenician, Amorite and Sutean, spoken by the Edomites in Idumea (modern-day southwestern Jordan and parts of Israel) in the 2nd and 1st millennium BCE. It is extinct and known only from an extremely small corpus, attested in a scant number of impression seals, ostraca, and a single late 7th or early 6th century BCE letter, discovered in Horvat Uza. Like Moabite, but unlike Hebrew, it retained the feminine ending ''-t'' in the singular absolute state. In early times, it seems to have been written with a Phoenician alphabet. However, by the 6th century BCE, it adopted the Aramaic alphabet. Meanwhile, Aramaic or Arabic features such as ''whb'' ("gave") and ''tgr/tcr'' ("merchant") entered the language, with ''whb'' becoming especially common in proper names. Like many other Canaanite languages, Edomite features a prefixed definite article derived from the presentative partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Language
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, is an extinct variety of the Phoenician language, a Canaanite languages, Canaanite language of the Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic branch of the Semitic languages. An offshoot of the Phoenician language of coastal West Asia (modern Lebanon and north western Syria), it was principally spoken on the Mediterranean coast of Northwest Africa, the Iberian Peninsula and several List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean islands, such as Malta, Sicily, and Sardinia by the Punic people, or western Phoenicians, throughout classical antiquity, from the 8th century BC to the 6th century AD. History Early history Punic is considered to have gradually separated from its Phoenician parent around the time that Carthage became the leading Phoenician city under Mago I of Carthage, Mago I, but scholarly attempts to delineate the dialects lack precision and generally disagree on the classification. The Punics s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Language
Phoenician ( ; ) is an extinct language, extinct Canaanite languages, Canaanite Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet History of the Greek alphabet, spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern Alphabet#European alphabets, European scripts. Phoenician belongs to the Canaanite languages and as such is quite similar to Biblical Hebrew and other languages of the group, at least in its early stages, and is therefore mutually intelligible with them. The area in which Phoenician was spoken, which the Phoenicians called ''Pūt'', includes the northern Levant, specifically the areas now including Syria, Lebanon, the Galilee, Western Galilee, parts of Cyprus, some adjacent areas of Anatolia, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |