|
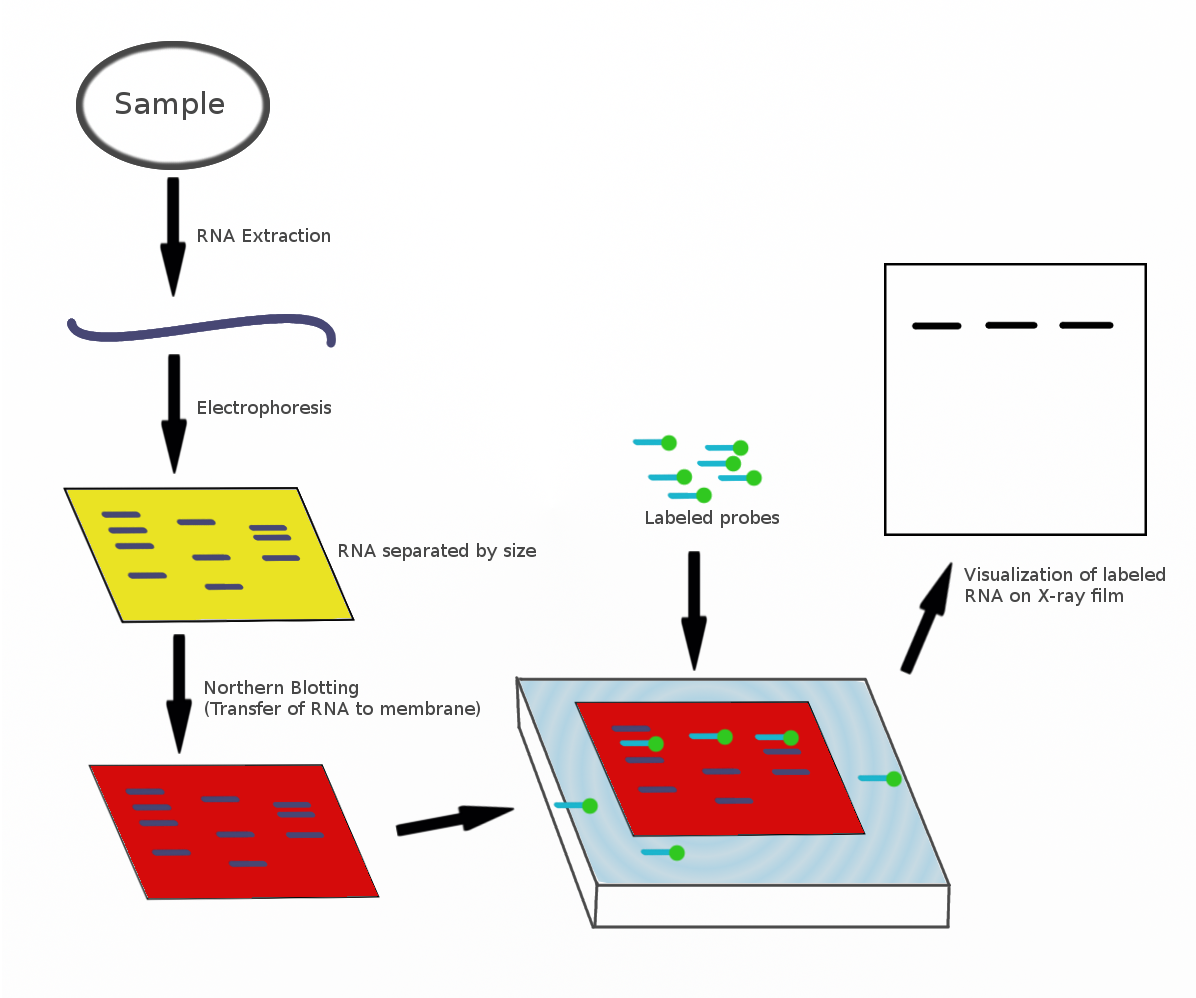
Northern Blot
The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.Kevil, C. G., Walsh, L., Laroux, F. S., Kalogeris, T., Grisham, M. B., Alexander, J. S. (1997) An Improved, Rapid Northern Protocol. Biochem. and Biophys. Research Comm. 238:277–279. With northern blotting it is possible to observe cellular control over structure and function by determining the particular gene expression rates during differentiation and morphogenesis, as well as in abnormal or diseased conditions. Northern blotting involves the use of electrophoresis to separate RNA samples by size, and detection with a hybridization probe complementary to part of or the entire target sequence. Strictly speaking, the term 'northern blot' refers specifically to the capillary transfer of RNA from the electrophoresis gel to the blotting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Blot Diagram
Northern may refer to the following: Geography * North, a point in direction * Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe * Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States * Northern Province, Sri Lanka * Northern Range, a range of hills in Trinidad * Northern State (Sudan), one of the 18 wilayat (states) of Sudan Schools * Northern Collegiate Institute and Vocational School (NCIVS), a school in Sarnia, Canada * Northern Secondary School, Toronto, Canada * Northern Secondary School (Sturgeon Falls), Ontario, Canada * Northern University (other), various institutions * Northern Guilford High School, a public high school in Greensboro, North Carolina Companies * Arriva Rail North, a former train operating company in northern England * Chemins de fer du Nord (Northern Railway Company), a former rail transport company in northern France * Nord Aviation, Nord-Aviation (Northern Aviation), a former state-owned France, French aircraft manufacturer. * Compa� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Confusion can arise because some authors use the acronym RT-PCR to denote real-time PCR. In this article, RT-PCR will denote Reverse Transcription PCR. Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings. The close association between RT-PCR and qPCR has led to metonymic use of the term qPCR to mean RT-PCR. Such use may be confusing, as RT-PCR can be used without qPCR, for example to enable molecular cloning, sequencing or simple detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-Seq
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a technique that uses next-generation sequencing to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA molecules in a biological sample, providing a snapshot of gene expression in the sample, also known as transcriptome. RNA-Seq facilitates the ability to look at alternative gene spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusion, mutations/ SNPs and changes in gene expression over time, or differences in gene expression in different groups or treatments. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-Seq can look at different populations of RNA to include total RNA, small RNA, such as miRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal profiling. RNA-Seq can also be used to determine exon/intron boundaries and verify or amend previously annotated 5' and 3' gene boundaries. Recent advances in RNA-Seq include single cell sequencing, bulk RNA sequencing, 3' mRNA-sequencing, in situ sequencing of fixed tissue, and native RNA molecule sequencin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptavidin
Streptavidin is a 52 Atomic mass unit, kDa protein (tetramer) purified from the bacterium ''Streptomyces avidinii''. Streptavidin Homotetramer, homo-tetramers have an extraordinarily high affinity for biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H). With a dissociation constant (Kd) on the order of ≈10−14 mol/L, the binding of biotin to streptavidin is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions known in nature. Streptavidin is used extensively in molecular biology and bionanotechnology due to the streptavidin-biotin complex's resistance to organic solvents, denaturants (e.g. guanidinium chloride), detergents (e.g. Sodium dodecyl sulfate, SDS, Triton X-100), proteolytic enzymes, and extremes of temperature and pH. Structure The crystal structure of streptavidin with biotin bound was reported by two groups in 1989. The structure was solved using multi wavelength anomalous diffraction by Hendrickson et al. at Columbia University and using multiple isomorphous replacemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avidin
Avidin is a tetrameric biotin-binding protein produced in the oviducts of birds, reptiles and amphibians and deposited in the whites of their eggs. Dimeric members of the avidin family are also found in some bacteria. In chicken egg white, avidin makes up approximately 0.05% of total protein (approximately 1800 μg per egg). The tetrameric protein contains four identical subunits (homotetramer), each of which can bind to biotin (Vitamin B7, vitamin H) with a high degree of affinity and specificity. The dissociation constant of the avidin-biotin complex is measured to be ''K''D ≈ 10−15 M, making it one of the strongest known non-covalent bonds. In its tetrameric form, avidin is estimated to be 66–69 k Da in size. 10% of the molecular weight is contributed by carbohydrate, composed of four to five mannose and three N-acetylglucosamine residues The carbohydrate moieties of avidin contain at least three unique oligosaccharide structural types that are similar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotin
Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', borrowed from the German , derives from the Ancient Greek word (; 'life') and the suffix "-in" (a suffix used in chemistry usually to indicate 'forming'). Biotin appears as a white, needle-like crystalline solid. Chemical description Biotin is classified as a heterocyclic compound, with a sulfur-containing tetrahydrothiophene ring fused to a ureido group. A C5-carboxylic acid side chain is appended to the former ring. The ureido ring, containing the −N−CO−N− group, serves as the carbon dioxide carrier in carboxylation reactions. Biotin is a coenzyme for five carboxylase enzymes, which are involved in the catabolism of amino acids and fatty acids, synthesis of fatty acids, and gluconeogenesis. Biotinylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseradish Peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various organic substrates by hydrogen peroxide. Structure The structure of the enzyme was first solved by X-ray crystallography in 1997; and has since been solved several times with various substrates. It is a large alpha-helix, alpha-helical glycoprotein which binds heme as a redox Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor. Substrates Alone, the HRP enzyme, or conjugates thereof, is of little value; its presence must be made visible using a Substrate (biochemistry), substrate that, when Redox, oxidized by HRP using hydrogen peroxide as the oxidizing agent, yields a characteristic color change that is detectable by spectrophotometric methods. Numerous substrates for horseradish peroxidase have been described and commercialized to exploit the desir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function, but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of '' E. coli'' bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia. The level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is checked through the ALP test, which is often par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescence (also chemoluminescence) is the emission of light (luminescence) as the result of a chemical reaction, i.e. a chemical reaction results in a flash or glow of light. A standard example of chemiluminescence in the laboratory setting is the luminol test. Here, blood is indicated by luminescence upon contact with iron in hemoglobin. When chemiluminescence takes place in living organisms, the phenomenon is called bioluminescence. A light stick emits light by chemiluminescence. Physical description As in many chemical reactions, chemiluminescence starts with the combining of two compounds, say A and B, to give a product C. Unlike most chemical reactions, the product C converts to a further product, which is produced in an electronically excited state often indicated with an asterisk: : A + B → C : C → D* D* then emits a photon (''h''ν), to give the ground state of D: I : D* → D + ''h''ν In theory, one photon of light should be given off for each mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide (abbreviated as PAM or pAAM) is a polymer with the formula (-CH2CHCONH2-). It has a linear-chain structure. PAM is highly water-absorbent, forming a soft gel when hydrated. In 2008, an estimated 750,000,000 kg were produced, mainly for water treatment and the paper and mineral industries. Physicochemical properties Polyacrylamide is a polyolefin. It can be viewed as polyethylene with amide substituents on alternating carbons. Unlike various nylons, polyacrylamide is not a polyamide because the amide groups are not in the polymer backbone. Owing to the presence of the amide (CONH2) groups, alternating carbon atoms in the backbone are stereogenic (colloquially: chiral). For this reason, polyacrylamide exists in atactic, syndiotactic, and isotactic forms, although this aspect is rarely discussed. The polymerization is initiated with radicals and is assumed to be stereorandom. Copolymers and modified polymers Linear polyacrylamide is a water-soluble polymer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethidium Bromide
Ethidium bromide (or homidium bromide, chloride salt homidium chloride) is an intercalating agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag (nucleic acid stain) in molecular biology laboratories for techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis. It is commonly abbreviated as EtBr, which is also an abbreviation for bromoethane. To avoid confusion, some laboratories have used the abbreviation EthBr for this salt. When exposed to ultraviolet light, it will fluoresce with an orange colour, intensifying almost 20-fold after binding to DNA. Under the name homidium, it has been commonly used since the 1950s in veterinary medicine to treat trypanosomiasis in cattle. The high incidence of antimicrobial resistance makes this treatment impractical in some areas, where the related isometamidium chloride is used instead. Despite its reputation as a mutagen, tests have shown it to have low mutagenicity without metabolic activation. Structure, chemistry, and fluorescence As with most fluoresc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |