|
Ninilchik
Ninilchik ( Dena'ina: ''Niqnalchint'', , Alaskan Russian: ''N'in'íl'chik'') is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 883, up from 772 in 2000. It is considered an Alaska Native village under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act. In the 1970s, villagers formed the Ninilchik Native Association Incorporated. Later the Ninilchik Traditional Council (NTC) was established as the government of Alaska Natives in this area. The Alaska Native people of Ninilchik have ancestors of Aleut and Alutiiq (Sugpiaq) descent, as well as some Dena'ina. Many also include Russian ancestors, from a couple of men who settled here with their Alutiiq wives and children in 1847, and later migrants. Alaskan Russian was widely spoken in the village for almost 200 years. Due to the community's isolation, this Russian dialect continued much in its mid-19th century form. In the 21st century, the dialect has been studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaskan Russian
Alaskan Russian, known locally as Old Russian, is a dialect of Russian, influenced by Eskimo–Aleut languages, spoken in what is now the U.S. state Alaska since the Russian colonial period. Today it is prevalent on Kodiak Island and in Ninilchik (Kenai Peninsula), Alaska; it has been isolated from other varieties of Russian for over a century. Dialects Kodiak Russian was natively spoken on Afognak Strait until the Great Alaskan earthquake and tsunami of 1964. It is now moribund, spoken by only a handful of elderly people, and is virtually undocumented. Ninilchik Russian is better studied and more vibrant; it developed from the Russian colonial settlement of Ninilchik in 1847. ''Russia Bey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
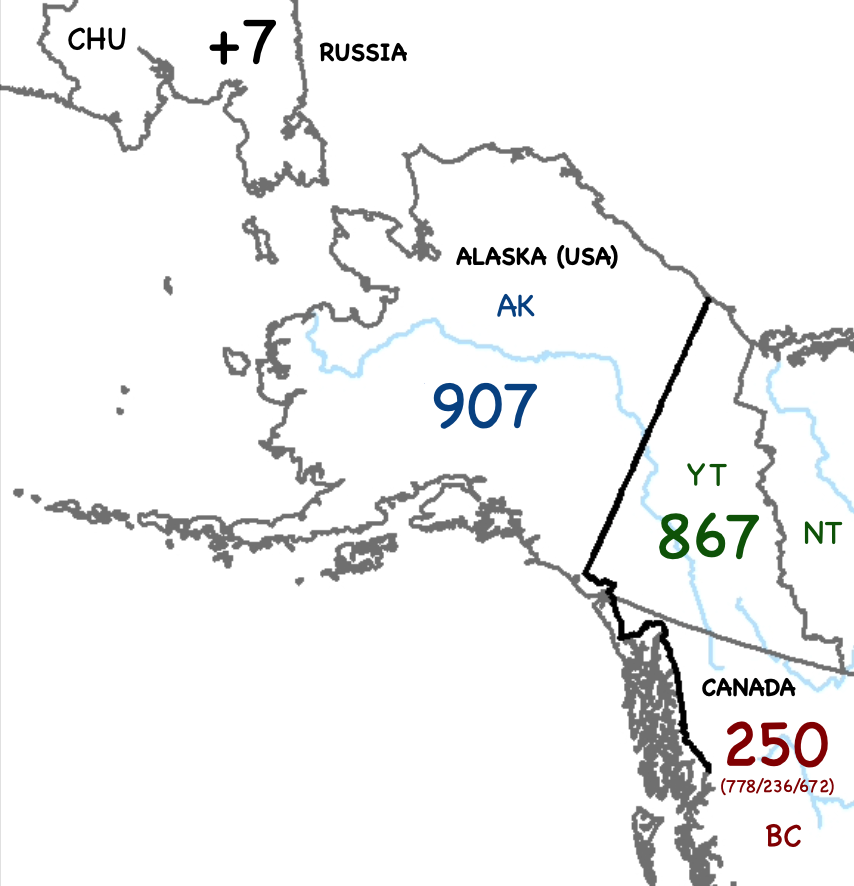
Area Code 907
Area code 907 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for the U.S. state of Alaska, with the exception of the small southeastern community of Hyder, which is served by the Canadian overlay complex 236/250/257/672/778 from the Stewart, British Columbia rate center. Despite having telephone service to the contiguous United States via a terrestrial line via the town of Juneau since 1937,AT&T (1974) ''Events in Telephone History'' Alaska was not assigned an area code until after the Alaska submarine cable was opened for traffic in 1956. The Alaska numbering plan area (NPA) was assigned the area code 907 and entered service in 1957. The Alaska numbering plan area is geographically the largest of any in the United States. It is the second-largest in the NANP, and on the entire North American continent behind 867, which serves Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska
Kenai Peninsula Borough is a borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 census, the population was 58,799, up from 55,400 in 2010. The borough seat is Soldotna, the largest city is Kenai, and the most populated community is the census-designated place of Kalifornsky. The borough includes most of the Kenai Peninsula and a large area of the mainland of Alaska on the opposite side of Cook Inlet. Geography The borough has a total area of , of which is land and (3.4%) is water. Adjacent boroughs and census areas * Bethel Census Area, Alaska - northwest * Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska - north * Municipality of Anchorage, Alaska - north * Chugach Census Area, Alaska - east * Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska - west * Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska - south National protected areas * Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge (part of Gulf of Alaska unit) ** Chiswell Islands ** Tuxedni Wilderness * Chugach National Forest (part) * Katmai National Park and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage, officially the Municipality of Anchorage, is the List of cities in Alaska, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alaska. With a population of 291,247 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it contains nearly 40 percent of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska, Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 398,328 in 2020, accounting for more than half the state's population. At of land area, the city is the List of cities in the United States by area, fourth-largest by area in the U.S. Anchorage is in Southcentral Alaska, at the terminus of the Cook Inlet, on a peninsula formed by the Knik Arm to the north and the Turnagain Arm to the south. First settled as a tent city near the mouth of Ship Creek, Alaska, Ship Creek in 1915 when construction on the Alaska Railroad began, Anchorage was incorporated as a city in November 1920. In September 1975, the City of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutiiq People
The Alutiiq (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a Yupik peoples, one of eight groups of Alaska Natives that inhabit the southern-central coast of the region. Their traditional homelands date back to over 7,500 years ago, and include areas such as Prince William Sound and outer Kenai Peninsula (), the Kodiak Archipelago and the Alaska Peninsula (). In the early 1800s there were more than 60 Alutiiq villages in the Kodiak archipelago, with an estimated population of 13,000 people. Today more than 4,000 Alutiiq live in Alaska. Terminology At present, the most commonly used title is (singular), (dual), (plural). These terms derive from the names (, ) that the '' promyshlenniki'' ( indigenous Siberian and Russian fur traders and settlers) gave to the native people in the region. Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenai Peninsula
The Kenai Peninsula ( Dena'ina: ''Yaghenen'') is a large peninsula jutting from the coast of Southcentral Alaska. The name Kenai (, ) is derived from the word "Kenaitze" or "Kenaitze Indian Tribe", the name of the Native Athabascan Alaskan tribe, the Kahtnuht’ana Dena’ina ("People along the Kahtnu (Kenai River)"), who historically inhabited the area. They called the Kenai Peninsula ''Yaghanen'' ("the good land"). Geography The peninsula extends about southwest from the Chugach Mountains, south of Anchorage. It is separated from the mainland on the west by Cook Inlet and on the east by Prince William Sound. Most of the peninsula is part of the Kenai Peninsula Borough. Athabaskan and Alutiiq Native groups lived on the peninsula for thousands of years prior to colonization during the Russian America era. The glacier-covered Kenai Mountains run along the southeast spine of the peninsula along the coast of the Gulf of Alaska. Much of the range is within Kenai Fjords Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet (; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage. The Cook Inlet and both its arms are bodies of brackish water, containing a turbid mix of ocean salt-water and freshwater runoff from the various rivers and streams. The narrow channel of the inlet funnels the tides creating very fast-moving currents, rip tides, and occasional bore tides. Cook Inlet watershed is the most populated watershed in Alaska. The drainage basin, watershed covers about of southern Alaska, east of the Aleutian Range, south and east of the Alaska Range, receiving water from its tributaries, which include the Knik River, the Little Susitna River, the Susitna River, Susitna and Matanuska River, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) was signed into law by U.S. President, President Richard Nixon on December 18, 1971, constituting what is still the largest land claims settlement in United States history. ANCSA was intended to resolve long-standing issues surrounding aboriginal land claims in Alaska, as well as to stimulate economic development throughout Alaska."Recognition of aboriginal land rights in Alaska was a sharp departure from American Indian policy in other parts of the US. Observers believe this was more a result of slow economic development within Alaska than rejection of Indian policy," citing Cooley, R.A. 1983. "Evolution of Alaska land policy." in Morehouse, T. A. (editor). ''Alaskan Resources Development: Issues of the 1980s''. Boulder: Westview Press, pp. 13-49. The settlement established Alaska Native claims to the land by transferring titles to twelve Alaska Native Regional Corporations, Alaska Native regional corporations and over 200 local vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |