|
Nikephoros I
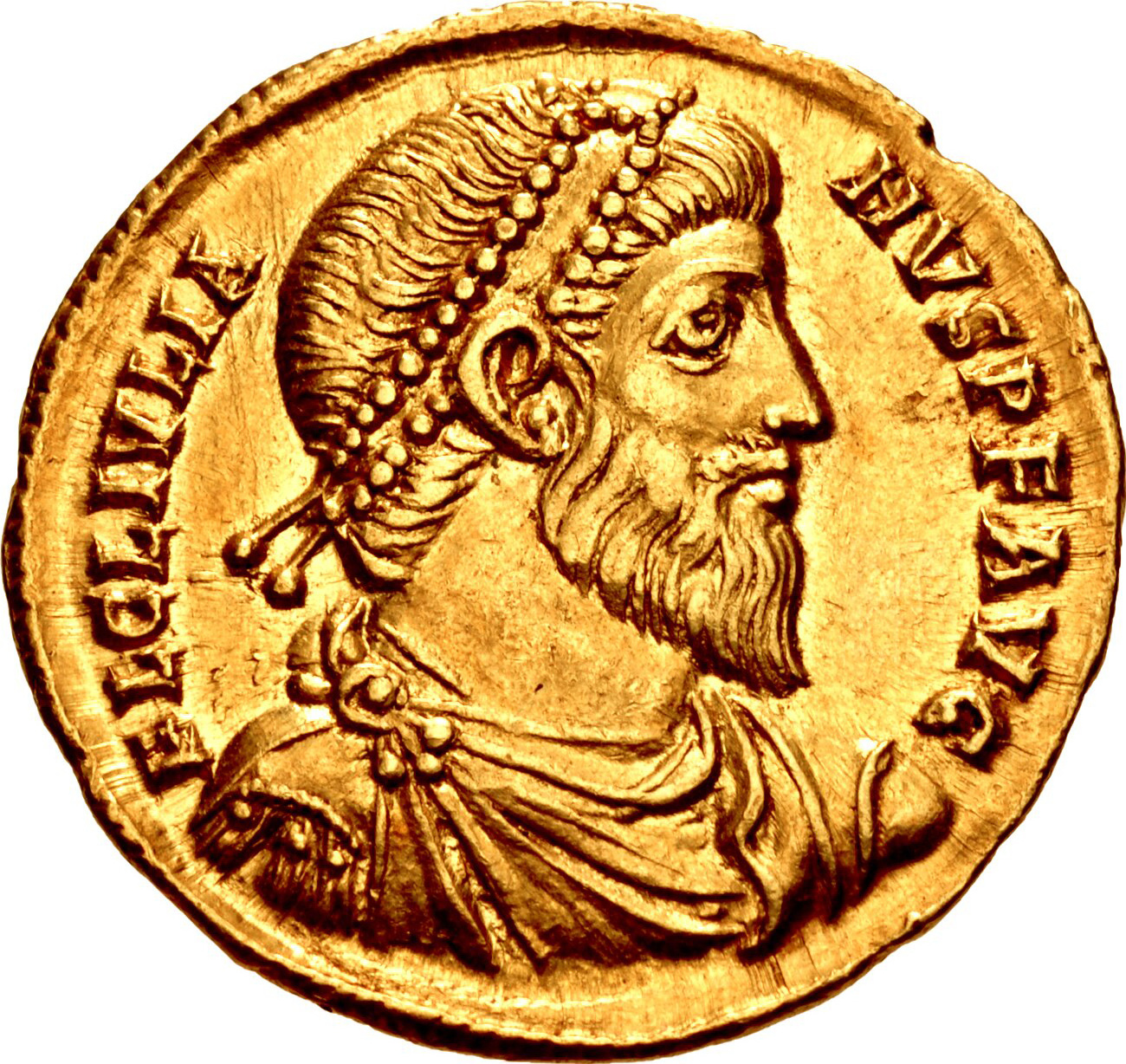
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becoming emperor, he was sometimes referred to as "the Logothete" () and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (), in recognition of his previous role as General Logothete. During his reign, Nikephoros engaged in military campaigns against both the Arabs and the Bulgarians, although the outcomes were varied. While leading an invasion into Bulgaria, he suffered a defeat and was killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background According to several sources outside the Byzantine context, such as Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, there is a tradition that suggests Nikephoros had Ghassanid Arab origins and that he descended from the final Ghassanid ruler Jabala ibn al-Ayham. Al-Tabari assets that he obtained this information from Byzantine sources, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Byzantine Emperors
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the List of Byzantine usurpers, various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. Modern historians distinguish this later phase of the Roman Empire as Byzantine due to the imperial seat moving from Rome to Byzantium, the Empire's integration of Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin. The Byzantine Empire was the direct legal continuation of the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabala Ibn Al-Ayham
Jabala ibn al-Ayham () was the last ruler, or phylarch, of the Ghassanid dynasty in Syria in the 7th century. He commanded Arab Christian tribal contingents on behalf of the Byzantine Empire against Arab Muslim forces during the Muslim conquest of Syria in the 630s. In the battles of Dumat al-Jandal in northern Arabia and the decisive battle of Yarmuk in southern Syria in 636, his forces were defeated. He supposedly converted to Islam, before breaking ties with the faith in protest to indignities he consequently suffered related to Islamic egalitarian principles. Afterward, he left Syria permanently, taking refuge with his tribesmen in Byzantine Anatolia. Historians are divided on the historicity of Jabala due the lack of contemporary source material, with some arguing his personality was essentially a literary device of later Islamic writers. Sources There are no contemporary sources about Jabala, with the narratives of his life derived from Abbasid-era (post-750 CE) literatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarantapechos
Sarantapechos (, ''Sarantápēchos''),; also found as 'Sarantapechys' () or 'Tessarakontapechys' (), . feminine form Sarantapechaena (, ''Sarantapḗchaina''), was a Byzantine Greek noble family originating from Athens. The family is attested in the second half of the eighth century, as well as in the early ninth century and is thought to have been of political influence in central Greece at the time. Very few members are known of the family, the first and most prominent being Irene of Athens, who, after her marriage to emperor Leo IV, became empress consort, later regent, and finally the first empress regnant of the Byzantine Empire in 797. History Name and early accounts The name ''Sarantapēchos'', from Greek ''saránta'' ('forty') and ''pḗchys'' ('cubit'), was probably a reference to one particularly tall member who gave the epithet to his family and reflected a common Byzantine tradition of name-giving based on physical attributes, geographical origins or a partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niketas Triphyllios
Niketas Triphyllios (; died 30 April 803) was one of the highest officials of the Roman Empire during the reign of empress Irene of Athens (797–802), holding the position of Domestic of the Schools. Niketas first appears in Irene's unique triumphal procession on Easter Monday, 1 April 799. At the time, he was already Domestic of the Schools (commander of the elite '' Scholai'' regiment) and holder of the supreme dignity of ''patrikios''. Niketas was one of the four ''patrikioi'' (along with Bardanes Tourkos, Constantine Boilas, and Niketas' brother Sisinnios) leading the four white horses which drew the imperial carriage, a role that marks him out as one of the most prominent of Irene's supporters among the high dignitaries of the state.Guilland (1967), p. 436 A few weeks later, in May, Irene's health worsened considerably and the issue of her succession became opened. At this point Niketas (and possibly his brother too) allied himself with the eunuch Aetios to curb the influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Of The Schools
The office of the Domestic of the Schools () was a senior military post of the Byzantine Empire, extant from the 8th century until at least the early 14th century. Originally simply the commander of the '' Scholai'', the senior of the elite '' tagmata'' regiments, the Domestic quickly rose in prominence: by the mid-9th century, its holders essentially occupied the position of commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army, next to the Emperor. The office was eclipsed in the 12th century by that of the Grand Domestic, and in the Palaiologan period (13th–15th centuries), it was reduced to a purely honorary, mid-level court dignity. History The first holder of the office of Domestic of the Schools first appears in the sources (the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor) for the year 767, shortly after the creation of the . These were elite cavalry regiments stationed in or around the capital Constantinople, commanded by officers titled " Domestics" (δομέστικοι, ) and distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
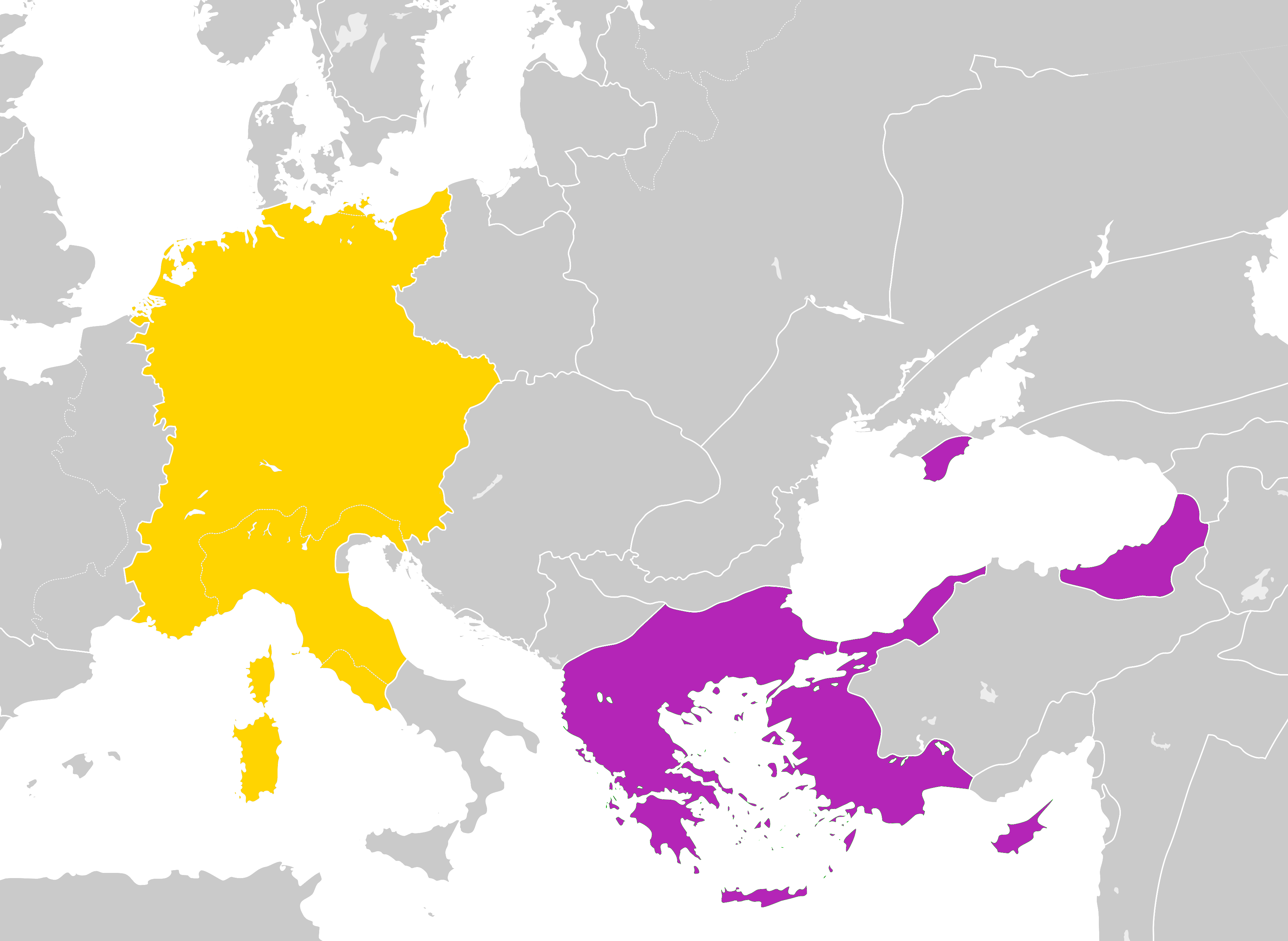
Problem Of Two Emperors
The problem of two emperors or two-emperor problem (deriving from the German term ''Zweikaiserproblem'', ) is the historiographical term for the historical contradiction between the idea of the universal empire, that there was only ever one true emperor at any one given time, and the truth that there were often multiple individuals who claimed the position simultaneously. The term is primarily used in regards to medieval European history and often refers to in particular the long-lasting dispute between the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople and the Holy Roman emperors in modern-day Germany and Austria as to which monarch represented the legitimate Roman emperor. In the view of medieval Christians, the Roman Empire was indivisible and its emperor held a somewhat hegemonic position even over Christians who did not live within the formal borders of the empire. Since the collapse of the Western Roman Empire during late antiquity, the Byzantine Empire (which represented its survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages. A member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. With his brother, Carloman I, he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene (empress)
Irene of Athens (, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaena (, ), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally empress regnant and sole ruler of the Eastern Roman Empire from 797 to 802. A member of the politically prominent Sarantapechos family, she was selected as Leo IV's bride for unknown reasons in 768. Even though her husband was an iconoclast, she harbored iconophile sympathies. During her rule as regent, she called the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, which condemned iconoclasm as heretical and brought an end to the first iconoclast period (730–787). During her 5 year sole reign, her public figure was polarizing, due to the setbacks faced by the Empire and her iconophilic stances, often attributed to her gender and the influence of her retinue. Her reign as sole ruler made her the first ever empress regnant, ruling in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logothetes Tou Genikou
The (, often called or simply (, 'the general ogothete), and usually rendered in English as the General Logothete, was in charge of the 'general financial ministry', the of the middle Byzantine Empire.. History and functions The was responsible for general taxation and revenue, and also served as a court for financial cases. As such, it broadly fulfilled the tasks of the earlier , although it was mostly derived from the "general department" of the praetorian prefecture. The first attested , the monk Theodotos, is mentioned in 692, but the post may have been instituted as early as 626. The bureau of the and its logothete remained one of the chief ministries for the entire middle Byzantine period (7th–12th centuries), with the 899 ''Klētorologion'' of Philotheos recording the position as ranking 33rd in the imperial hierarchy. During the Komnenian period, its importance declined, but recovered under the Angeloi. Following the sack of Constantinople in 1204 and the disso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
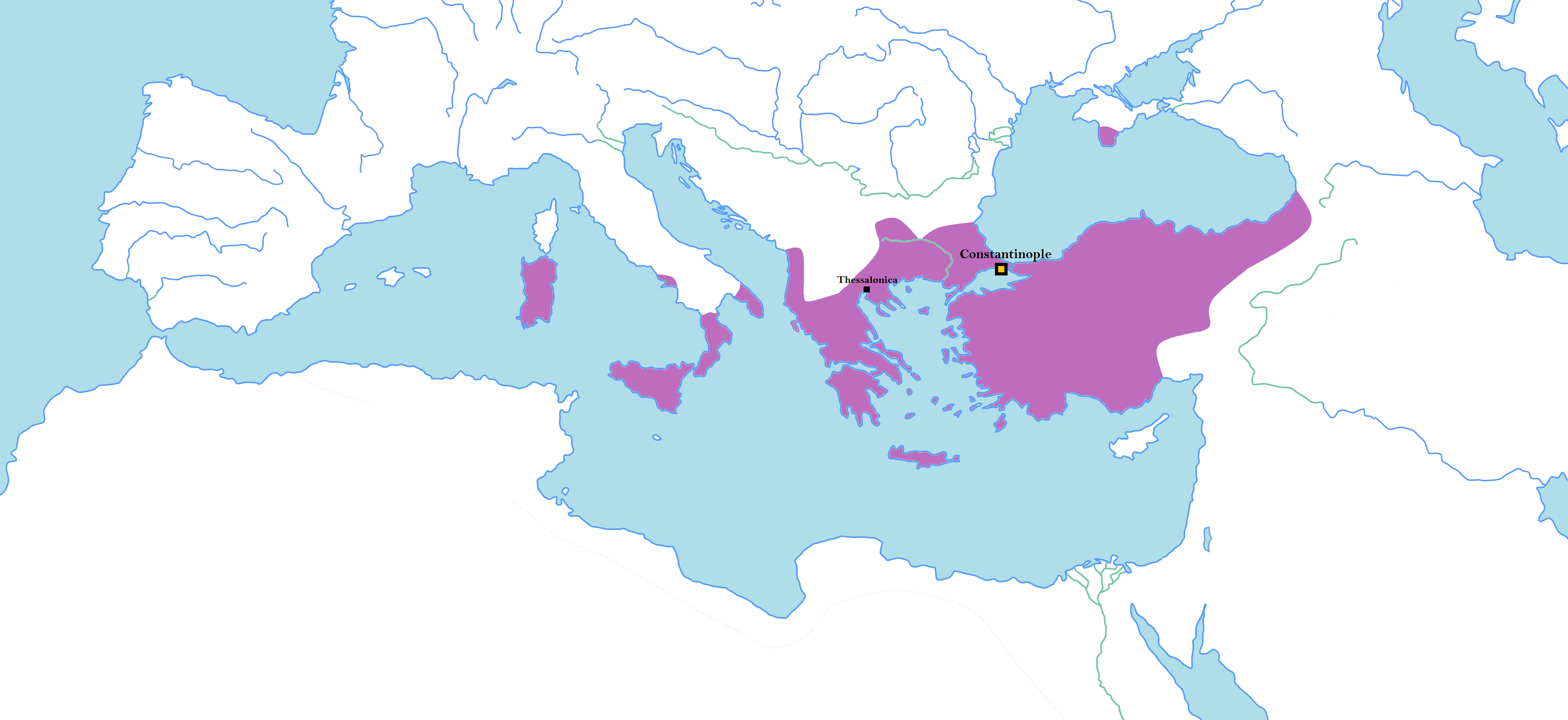
Byzantine Empire 802 AD
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |