|
Newgrange
Newgrange () is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, placed on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of the town of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3100 BC, making it older than Stonehenge and the Egyptian pyramids. Newgrange is the main monument in the Brú na Bóinne complex, a World Heritage Site that also includes the passage tombs of Knowth and Dowth, as well as other henges, burial mounds and standing stones. Newgrange consists of a large circular mound with an inner stone passageway and cruciform chamber. Burnt and unburnt human bones, and possible grave goods or votive offerings, were found in this chamber. The monument has a striking façade made mostly of white quartz cobblestones, and it is ringed by engraved kerbstones. Many of the larger stones of Newgrange are covered in megalithic art. The mound is also ringed by a stone circle. Some of the material that makes up the monument ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brú Na Bóinne
(, "mansion or palace of the Boyne"), also called the Boyne Valley tombs, is an ancient monument complex and ritual landscape in County Meath, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It is one of the world's most important Neolithic landscapes, comprising at least ninety monuments including passage tombs, burial mounds, standing stones and Enclosure (archaeology), enclosures. The site is dominated by the passage tombs of Newgrange (), Knowth () and Dowth (), built during the 32nd century BC. Together these have the largest assemblage of megalithic art in Europe. The associated archaeological culture is called the "Boyne culture". ''Brú na Bóinne'' is also an important archaeoastronomical site; several of the passage tombs are aligned with the winter solstice and equinoxes. The area continued to be a site of ritual and ceremonial activity in the later Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. In Irish mythology, the tombs are said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowth
Dowth () is the site of Neolithic passage tombs near the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It is one of the three main tombs of the ''Brú na Bóinne'' World Heritage Site, along with Newgrange and Knowth. Its features align it with the other passage tombs, which date from around 3200 BC. Unlike its bigger neighbours, Dowth has mostly been left as a ruin, although its smaller inner chambers are largely intact. The Royal Irish Academy carried out a botched excavation in 1847, leaving a large crater in the mound that has never been repaired. Description The cairn or tumulus is about in diameter and high, and surrounded by large kerbstones, some of which are decorated. Quartz was found fallen outside the kerbing, suggesting that the entrance to this tomb was surrounded by glittering white stone, as at Newgrange. Three stone-lined passages lead into the mound from the west. These comprise two passage tombs (known as Dowth North and Dowth South) and a souterrain. The longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowth
Knowth (; ) is a prehistoric tomb overlooking the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland. It comprises a large passage tomb surrounded by 17 smaller tombs, built during the Neolithic era around 3200 BC. It contains the largest assemblage of megalithic art in Europe. Knowth is part of the Brú na Bóinne complex, a World Heritage Site that also includes the similar passage tombs of Newgrange and Dowth. After its initial period of use, Knowth gradually became a ruin, although the area continued to be a site of ritual activity in the Bronze Age. During the early Middle Ages, a royal residence was built on top of the great mound, which became the seat of the Kings of Knowth or Northern Brega. Archaeologist George Eogan led an extensive investigation of the site from the 1960s to 1980s, and parts of the monument were reconstructed. Description The large mound has been estimated to date from c. 3200 BC. The mound is about high and in diameter, covering roughly a hectare. It contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County Louth, Louth to the northeast, County Kildare, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the southwest, Westmeath to the west, County Cavan, Cavan to the northwest, and County Monaghan, Monaghan to the north. To the east, Meath also borders the Irish Sea along a narrow strip between the rivers River Boyne, Boyne and Delvin River, Delvin, giving it the List of Irish counties by coastline, second shortest coastline of any county. Meath County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. Meath is the List of Irish counties by area, 14th-largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties by land area, and the List of Irish counties by population, 8th-most populous, with a total population of 220,826 according to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern). For that hemisphere, the winter solstice is the day with the shortest daytime, period of daylight and longest night of the year, and when the Sun is at its lowest culmination, daily maximum elevation in the sky. Each Polar Circle, polar region experiences polar night, continuous darkness or twilight around its winter solstice. The opposite event is the summer solstice. The winter solstice occurs during the hemisphere's winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, this is the December solstice (December 21 or 22) and in the Southern Hemisphere, this is the June solstice (June 20 or 21). Although the winter solstice itself lasts only a moment, the term also refers to the day on which it occurs. Traditionally, in many Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
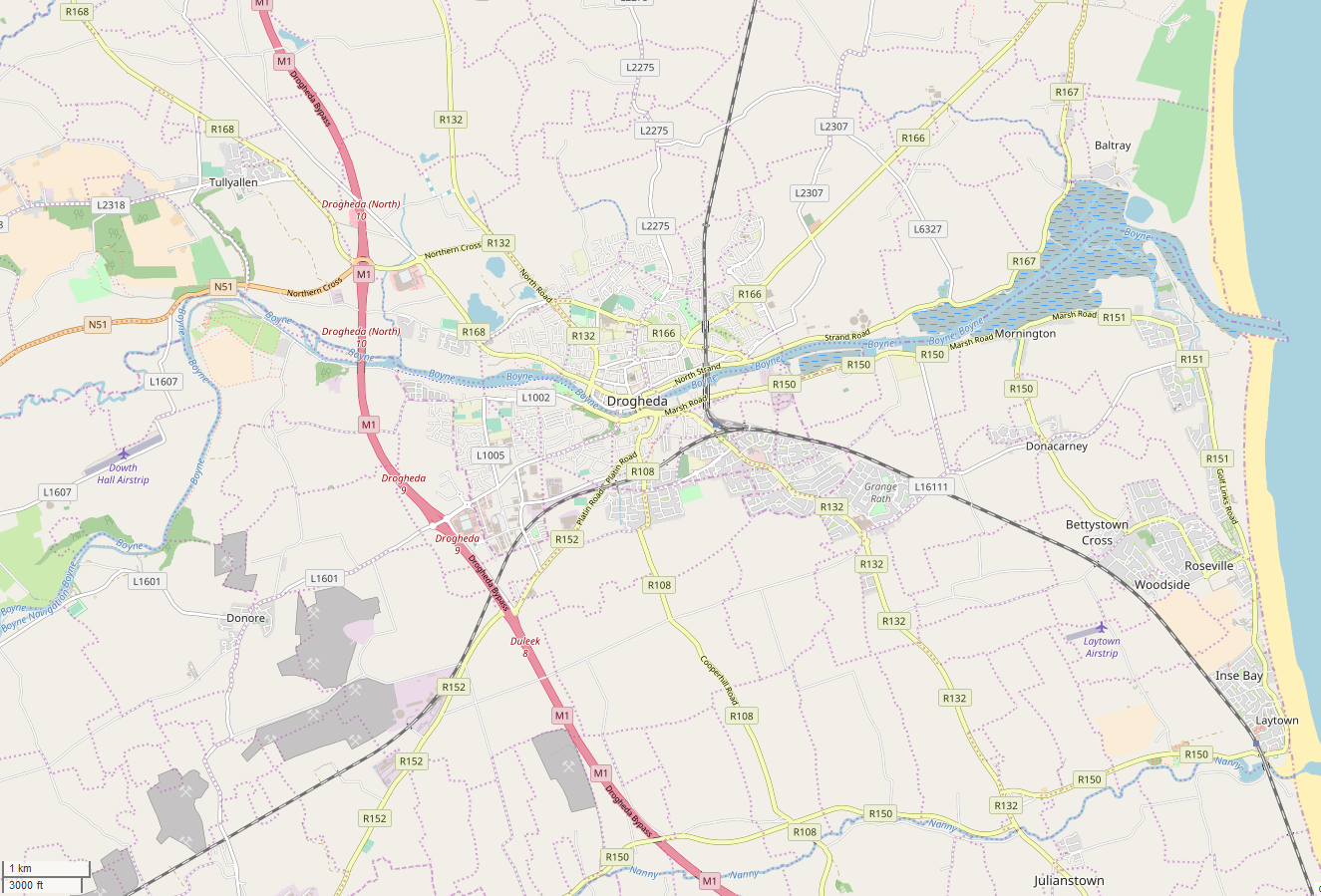
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin city centre. Drogheda had a population of 44,135 inhabitants in 2022, making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in Ireland, by both population and area. It is the second largest in County Louth with 35,990 and sixth largest in County Meath with 8,145. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Area Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roofbox
{{Short description, Archaeological feature In archaeology, a roofbox is a term for a specially contrived opening above a doorway, that is constructed in such way that at particular times of the year e.g. the winter or summer solstices, the Sun would be directly in view from the chamber or passage within. The term was coined by Professor Michael O’Kelly during his excavation of the Newgrange passage cairn, at Brú Na Bóinne, Ireland. The roofbox was built directly above the entrance door to the passage. The passage and chamber were specifically aligned with the rising sun of the mornings around the winter solstice in December. The 17 metre passage rises in elevation as it leads to the chamber. The chamber floor, the roofbox and the local horizon are on a single plane and so as the sun's morning rays penetrate the roofbox, they illuminate the chamber floor for a maximum of 17 minutes (weather depending). A roofbox is also found in Cairn G of the Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemeter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavrinis
Gavrinis () is a small island in the Gulf of Morbihan in Brittany, France. It contains the Gavrinis tomb, a Neolithic passage tomb built around 4200–4000 BC, making it one of the world's oldest surviving buildings. Stones inside the passage and chamber are covered in megalithic art. It is likened to other Neolithic passage tombs such as Barnenez in Brittany and Newgrange in Ireland. Geography Reachable by boat from the town of Larmor-Baden near the opening of Morbihan Gulf to the Atlantic Ocean, Gavrinis is an uninhabited granite rock outcrop of 750 × 400m. Its highest point dominates much of the surrounding area. Name The name ''Gavrinis'' is popularly believed to be derived from the Breton words ''gavr'' (goat) and ''enez'' (island), suggesting a meaning of "goat island". This is probably a false etymology. In documents dating from 1184 and 1202, the island is named ''Guirv Enes'' and ''Guerg Enes'', respectively. The old Breton word ''Guerg'' is not related to ''gavr' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalithic Art
Megalithic art refers to art either painted or carved onto megaliths in prehistoric Europe and found on the structural elements, like the kerbstones, orthostats, or capstones of megalithic tombs, but recent investigations have included decorations on stelae and menhirs. Megalithic art is found in many places in Western Europe although the main concentrations are in England, Malta, Ireland, Brittany and Iberia. Megalithic art started in the Neolithic and continued into the Bronze Age. Although many monument types received this form of art the majority is carved on Neolithic passage graves. Megalithic art tends to be highly abstract and contains relatively few representations of recognizable real objects. Megalithic art is often similar to prehistoric rock art and contains many similar motifs such as the ' cup and ring mark', although the two forms of rock carving also have large stylistic differences. The meaning of megalithic art is the subject of much debate. Weathering an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Europe
The European Neolithic is the period from the arrival of Neolithic (New Stone Age) technology and the associated population of Early European Farmers in Europe, (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) until –1700 BC (the beginning of Bronze Age Europe with the Nordic Bronze Age). The Neolithic overlaps the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe as cultural changes moved from the southeast to northwest at about 1 km/year – this is called the Neolithic Expansion. The duration of the Neolithic varies from place to place, its end marked by the introduction of bronze tools: in southeast Europe it is approximately 4,000 years (i.e. 7000 BC–3000 BC) while in parts of Northwest Europe it is just under 3,000 years (–1700 BC). In parts of Europe, notably the Balkans, the period after is known as the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) due to the invention of copper smelting and the prevalence of copper tools, weapons and other artifacts. The spread of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal lintel stones, held in place with mortise and tenon joints, a feature unique among contemporary monuments. Inside is a ring of smaller bluestones. Inside these are free-standing trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the summer solstice and sunset on the winter solstice. The stones are set within Earthwork (archaeology), earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of Neolithic British Isles, Neolithic and Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred ''tumuli'' (burial mounds). Stonehenge was constructed in several phases beginning about 3100 BC and continuing until about 1600 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |