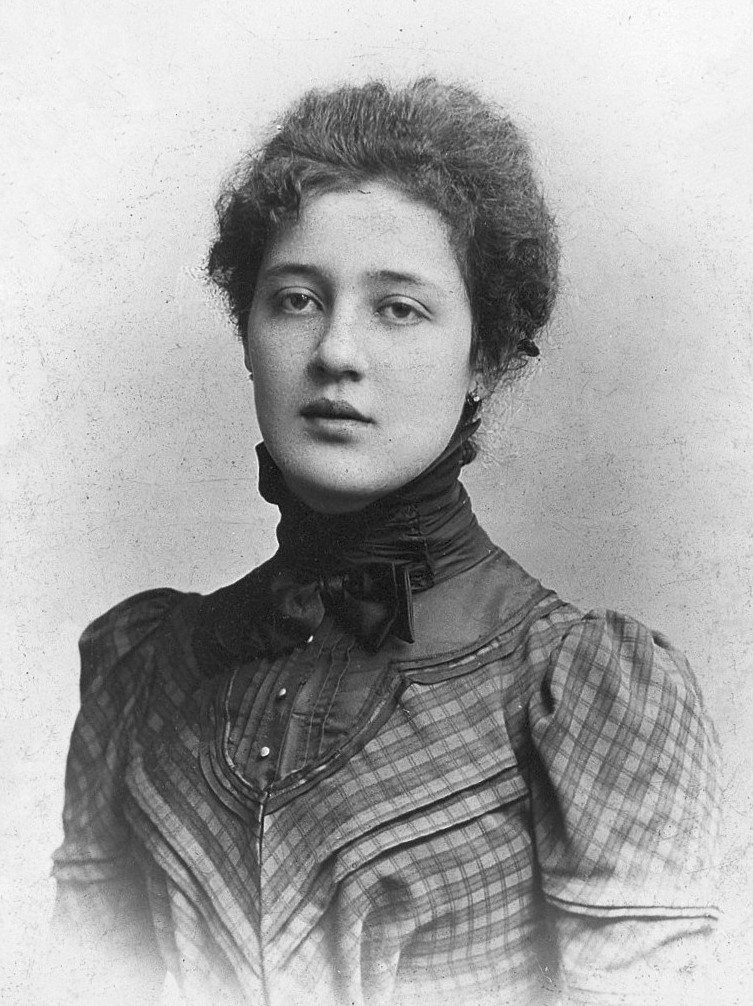|
Neville Symington
Neville Symington (3 July 1937 - 3 December 2019) was a member of the Middle Group of British Psychoanalysts which argues that the primary motivation of the child is object-seeking rather than drive gratification. He published a number of books on psychoanalytic topics, and was President of the Australian Psychoanalytical Society from 1999 to 2002. Life and career Neville Symington was born in Portugal, and was a Catholic priest before becoming a psychoanalyst. He worked in England at the Tavistock Clinic, and the British Institute of Psycho-Analysis, before emigrating to Australia in 1986. On narcissism Symington was perhaps best known for his work on narcissism, which he considered to be the central psychopathology underlying all others. Symington introduced the concept of the 'lifegiver' as a kind of transitional object A comfort object, more formally a transitional object or attachment object, is an item used to provide psychological comfort, especially in unusual o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Group
The Independent or Middle Group of British analysts represents one of the three distinct sub-schools of the British Psychoanalytical Society, and 'developed what is known as the ''British independent'' perspective, which argued that the primary motivation of the child is object-seeking rather than drive gratification'. The 'Independent group...is strongly associated with the concept of countertransference as well as with a seemingly pragmatic, anti-theoretical attitude to psychoanalysis'. Origins In the wake of the wartime Controversial Discussions, 'the British Psycho-Analytical Society divided into several sets of followers – eventually three sets in one'. On the one side, were the followers of Melanie Klein, on the other those of Anna Freud, and 'in between, as a kind of buffer zone, were the British group who came to be known as "Independents" – Sylvia Payne, Marjorie Brierley, Ronald Fairbairn and Ella Freeman Sharpe, and eventually Donald Winnicott and Paula Heimann, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nina Coltart
Nina Coltart (21 November 1927 – 24 June 1997), a British psychoanalyst, psychotherapist, and essayist. Family She was born in Shortlands, Kent, England. Her father was a medical doctor and her mother, a housewife. In 1940 she and her younger sister Gill were evacuated to Cornwall, where they lived with their maternal grandmother and a nanny who, years before, had cared for Coltart's mother. Coltart's parents died in a train wreck under blackout conditions that year on their way to visit their daughters. Education Coltart attended Sherborne School for Girls and from there went to Somerville College, Oxford, where she read English and Modern Languages. She applied to St. Bartholomew's Hospital's Medical College, where she was the first female editor of the Barts Journal. She earned a medical degree there and began work as a psychiatrist. Psychoanalysis Soon after Coltart began training in psychoanalysis. In her training analysis she was analyzed by Eva Rosenfeld. Coltart bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Psychotherapists
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Psychoanalysts
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Psychology
Self psychology, a modern psychoanalytic theory and its clinical applications, was conceived by Heinz Kohut in Chicago in the 1960s, 70s, and 80s, and is still developing as a contemporary form of psychoanalytic treatment. In self psychology, the effort is made to understand individuals from within their subjective experience via vicarious introspection, basing interpretations on the understanding of the self as the central agency of the human psyche. Essential to understanding self psychology are the concepts of empathy, selfobject, mirroring, idealising, alter ego/twinship and the tripolar self. Though self psychology also recognizes certain drives, conflicts, and complexes present in Freudian psychodynamic theory, these are understood within a different framework. Self psychology was seen as a major break from traditional psychoanalysis and is considered the beginnings of the relational approach to psychoanalysis. Origins Kohut came to psychoanalysis by way of neurology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanie Klein
Melanie Klein (; ; Reizes; 30 March 1882 – 22 September 1960) was an Austrian-British author and psychoanalysis, psychoanalyst known for her work in child analysis. She was the primary figure in the development of object relations theory. Klein's work primarily focused on the role of ambivalence and moral ambiguity in human development. Klein suggested that pre-verbal existentialism, existential anxiety in infancy catalyzed the formation of the unconscious, which resulted in the unconscious splitting of the world into good and bad fantasy (psychology), idealizations. In her theory, how the child resolves that split depends on the constitution of the child and the character of nurturing the child experiences. The quality of resolution can inform the presence, absence, and/or type of distresses a person experiences later in life. Life Melanie Klein was born into a History of the Jews in Austria, Jewish family and spent most of her early life in Vienna, Austria, Vienna. She was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph J
Joseph is a common male name, derived from the Hebrew (). "Joseph" is used, along with " Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese and Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled , . In Kurdish (''Kurdî''), the name is , Persian, the name is , and in Turkish it is . In Pashto the name is spelled ''Esaf'' (ايسپ) and in Malayalam it is spelled ''Ousep'' (ഔസേപ്പ്). In Tamil, it is spelled as ''Yosepu'' (யோசேப்பு). The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with ''Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especially common in contemporary Israel, as either "Yossi" or "Yossef", and in Italy, where the name "Giuseppe" was the most com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeanette Winterson
Jeanette Winterson (born 27 August 1959) is an English author. Her first book, '' Oranges Are Not the Only Fruit'', was a semi-autobiographical novel about a lesbian growing up in an English Pentecostal community. Other novels explore gender polarities and sexual identity and later ones the relations between humans and technology. She broadcasts and teaches creative writing. She has won a Whitbread Prize for a First Novel, a BAFTA Award for Best Drama, the John Llewellyn Rhys Prize, the E. M. Forster Award and the St. Louis Literary Award, and the Lambda Literary Award twice. She has received an Officer of the Order of the British Empire (OBE) and a Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) for services to literature, and is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature. Her novels have been translated to almost 20 languages. Early life and education Winterson was born in Manchester and adopted by Constance and John William Winterson on 21 January 1960. She grew up in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert M
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Psychoanalytical Society
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (other) * Australia (other) * * * Austrian (other) Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen * Austrian German dialect * Something associated with the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Phillips (psychologist)
Adam Phillips (19 September 1954"Phillips, Adam", ''Who's Who 2012'', A & C Black, 2012; online edn, Oxford University Press, Dec 2011; online edn, Nov 201accessed 9 July 2012/ref>) is a British psychoanalytic psychotherapist and essayist. Since 2003, he has been the general editor of the new Penguin Modern Classics translations of Sigmund Freud. He is also a regular contributor to the ''London Review of Books''. Joan Acocella, writing in ''The New Yorker'', described Phillips as "Britain's foremost psychoanalytic writer", an opinion echoed by historian Élisabeth Roudinesco in ''Le Monde''. Life Phillips was born in Cardiff, Wales, in 1954, the child of second-generation Polish Jews. He grew up as part of an extended family of aunts, uncles and cousins and describes his parents as "very consciously Jewish but not believing". As a child, his first interest was the study of tropical birds and it was not until adolescence that he developed an interest in literature. He was edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |