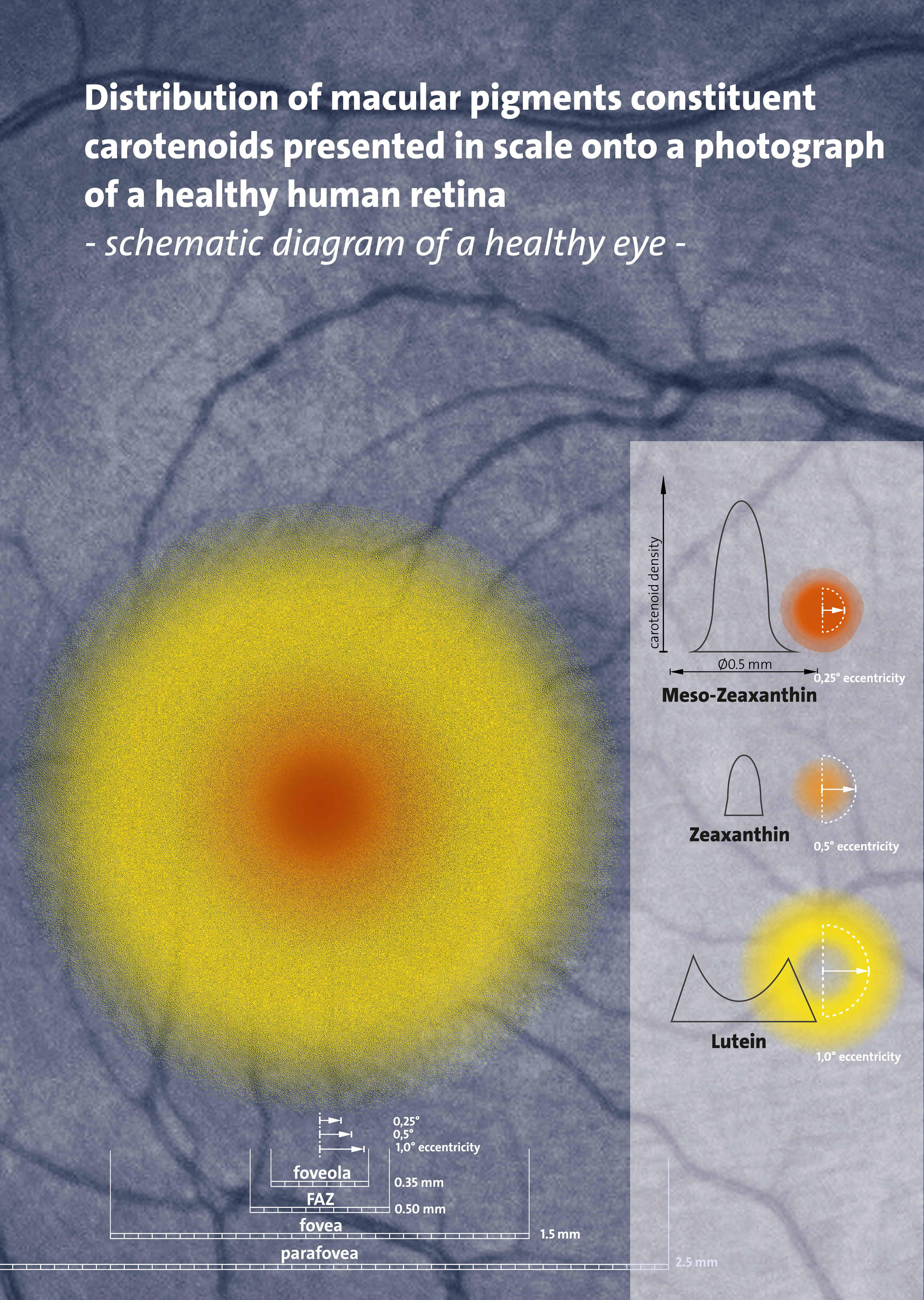
|
Neoxanthin Synthesis
Neoxanthin is a carotenoid and xanthophyll. In plants, it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone abscisic acid. It is often present in two forms: all-trans and 9-cis isomers. It is produced from violaxanthin, but a suspected neoxanthin synthase is still to be confirmed. Two different genes were confirmed to be implied in violaxanthin conversion to neoxanthin in Arabidopsis and tomato. It has a specific role in protection against photooxidative stress. It is a major xanthophyll found in green leafy vegetables such as spinach Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed eit .... References {{Carotenoids Carotenoids Epoxides Cumulated dienes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes xanthophylls (which contain oxygen) and carotenes (which are purely hydrocarbons and contain no oxygen). All are derivatives of tetraterpenes, meaning that they are produced from 8 isoprene units and contain 40 carbon atoms. In general, carotenoids absorb wavelengths ranging from 400 to 550 nanometers (violet to green light). This causes the compounds to be deeply colored yellow, orange, or red. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf coloration of about 15-30% of tree species, but many plant colors, especially reds and purples, are due to polyphenols. Carotenoids serve two key roles in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek: (), meaning "yellow", and (), meaning "leaf"), due to their formation of the yellow band seen in early chromatography of leaf pigments. Molecular structure As both are carotenoids, xanthophylls and carotenes are similar in structure, but xanthophylls contain oxygen atoms while carotenes are ''purely hydrocarbons'', which do not contain oxygen. Their content of oxygen causes xanthophylls to be more polar (in molecular structure) than carotenes, and causes their separation from carotenes in many types of chromatography. (Carotenes are usually more orange in color than xanthophylls.) Xanthophylls present their oxygen either as hydroxyl groups and/or as hydrogen atoms substituted by oxygen atoms when acting as a bridge to form epoxides. Occurrence Like other c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, freezing tolerance, heat stress and heavy metal ion tolerance. Discovery In the 1940s, Torsten Hemberg, while working at the University of Stockholm, found evidence that a positive correlation exists between the rest period and the occurrence of an acidic ether soluble growth inhibitor in potato tubers. In 1963, abscisic acid was first identified and characterized as a plant hormone by Frederick T. Addicott and Larry A. Davis. They were studying compounds that cause abscission (shedding) of cotton fruits (bolls). Two compounds were isolated and called abscisin I and abscisin II. Abscisin II is presently called abscisic acid (ABA). In plants Function ABA was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violaxanthin
Violaxanthin is a xanthophyll pigment with an orange color found in a variety of plants. Violaxanthin is the product of the epoxidation of zeaxanthin where the oxygen atoms are from reactive oxygen species (ROS). Such ROS's arise when a plant is subject to solar radiation so intense that the light cannot all be absorbed by the chlorophyll. Food coloring Violaxanthin is used as a food coloring under the E number E161e and INS number The International Numbering System for Food Additives (INS) is an international naming system for food additives, aimed at providing a short designation of what may be a lengthy actual name."Class Names and the International Numbering System for Fo ... 161e. The coloring is not approved for use in food in the EU or the United States, but is allowed in Australia and New Zealand.Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code Violaxanthin cycle Violaxanthin is a participant in the violaxanthin cycle. : References {{Carotenoids Carotenoids Epoxides Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoxanthin Synthase
In enzymology, a neoxanthin synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: :violaxanthin \rightleftharpoons neoxanthin Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, violaxanthin, and one product, neoxanthin. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically a class of other intramolecular oxidoreductases. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivi ... of this enzyme class is violaxanthin---neoxanthin isomerase (epoxide-opening). This enzyme is also called NSY. This enzyme participates in carotenoid biosynthesis - general. References * * EC 5.3.99 Enzymes of unknown structure {{isomerase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model. Status Currently, the genus ''Arabidopsis'' has nine species and a further eight subspecies recognised. This delimitation is quite recent and is based on morphological and molecular phylogenies by O'Kane and Al-Shehbaz and others. Their findings confirm the species formerly included in ''Arabidopsis'' made it polyphyletic. The most recent reclassification moves two species previously placed in ''Cardaminopsis'' and ''Hylandra'' and three species of '' Arabis'' into ''Arabidopsis'', but excludes 50 that have been moved into the new genera ''Beringia, Crucihimalaya, Ianhedg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originated from and was domesticated in western South America. It was introduced to the Old World by the Spanish in the Columbian exchange in the 16th century. Tomato plants are vines, largely Annual plant, annual and vulnerable to frost, though sometimes living longer in greenhouses. The flowers are able to self-fertilise. Modern varieties have been bred to ripen uniformly red, in a process that has impaired the fruit's sweetness and flavor. There are thousands of cultivars, varying in size, color, shape, and flavor. Tomatoes are attacked by many insect pests and nematodes, and are subject to diseases caused by viruses and by mildew and blight fungi. The tomato has a strong savoury umami flavor, and is an important ingredient in cuisines around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinach
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed either fresh or after storage, using Food preservation, preservation techniques by canning, Freezing (food), freezing, or Dehydrated food, dehydration. It may be eaten cooked or raw, and the taste differs considerably; the high oxalate content may be reduced by steaming. It is an annual plant (rarely biennial plant, biennial), growing as tall as . Spinach may Overwintering, overwinter in temperate regions. The leaf, leaves are alternate, simple, ovate to triangular, and very variable in size: long and broad, with larger leaves at the base of the plant and small leaves higher on the flowering stem. The flowers are inconspicuous, yellow-green, in diameter, and mature into a small, hard, dry, lumpy fruit cluster across containing several see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoids
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, maize, corn, tomatoes, Domestic Canary, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes xanthophylls (which contain oxygen) and carotenes (which are purely hydrocarbons and contain no oxygen). All are derivative (chemistry), derivatives of tetraterpenes, meaning that they are produced from 8 isoprene units and contain 40 carbon atoms. In general, carotenoids absorb wavelengths ranging from 400 to 550 nanometers (violet to green light). This causes the compounds to be deeply colored yellow, orange, or red. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf coloration of about 15-30% of tree species, but many plant colors, especially reds and purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom Ring (chemistry), ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often Volatility (chemistry), volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |