|
Negative Thermal Expansion
Negative thermal expansion (NTE) is an unusual physicochemical process in which some materials contract upon heating, rather than expand as most other materials do. The most well-known material with NTE is water at 0 to 3.98 °C. Also, the density of solid water (ice) is lower than the density of liquid water at standard pressure. Water's NTE is the reason why water ice floats, rather than sinks, in liquid water. Materials which undergo NTE have a range of potential engineering, photonic, electronic, and structural applications. For example, if one were to mix a negative thermal expansion material with a "normal" material which expands on heating, it could be possible to use it as a thermal expansion compensator that might allow for forming composites with tailored or even close to zero thermal expansion. Origin of negative thermal expansion There are a number of physical processes which may cause contraction with increasing temperature, including transverse vibrational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria. Physical chemistry, in contrast to chemical physics, is predominantly (but not always) a supra-molecular science, as the majority of the principles on which it was founded relate to the bulk rather than the molecular or atomic structure alone (for example, chemical equilibrium and colloids). Some of the relationships that physical chemistry strives to understand include the effects of: # Intermolecular forces that act upon the physical properties of materials ( plasticity, tensile strength, surface tension in liquids). # Reaction kinetics on the rate of a reaction. # The identity of ions and the electrical conductivity of materials. # Surface science and electrochemistry of cell m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandium Trifluoride
Scandium(III) fluoride, ScF3, is an ionic compound. This salt is slightly soluble in water but dissolves in the presence of excess fluoride to form the ScF63− anion. Production ScF3 can be produced by reacting scandium and fluorine.S.A.Cotton, Scandium, Yttrium and the Lanthanides: Inorganic and Coordination Chemistry, Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry, 1994, John Wiley & Sons, . It is also formed during the extraction from the ore thortveitite by the reaction of Sc2O3 with ammonium bifluoride at high temperature:Pradyot Patnaik, 2003, ''Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals'', McGraw-Hill Professional, . : Sc2O3 + 6 NH4HF2 → 2 ScF3 + 6 NH4F + 3 H2O The resulting mixture contains a number of metal fluorides and this is reduced by reaction with calcium metal at high temperature. Further purification steps are required to produce usable metallic scandium. Properties Scandium trifluoride exhibits the unusual property of negative thermal expansion, meaning it shrinks when heated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
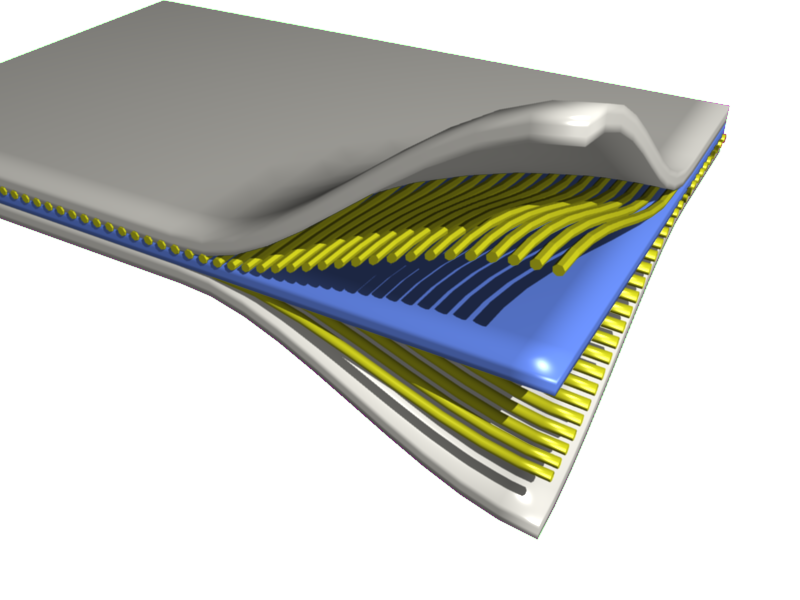
Composite Material
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called ''composite laminates''. Typical engineered composite materials are made up of a binding agent forming the ''matrix'' and a Filler (materials), filler material (particulates or fibres) giving ''substance'', e.g.: * Concrete, reinforced concrete and masonry with cement, lime or Mortar (masonry), mortar (which is itself a composite material) as a binder * Composite wood such as glulam and plywood with wood glue as a binder * Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and fibre-rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
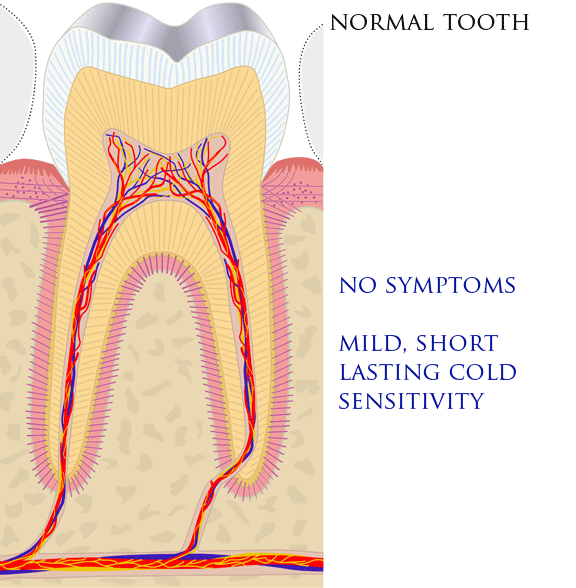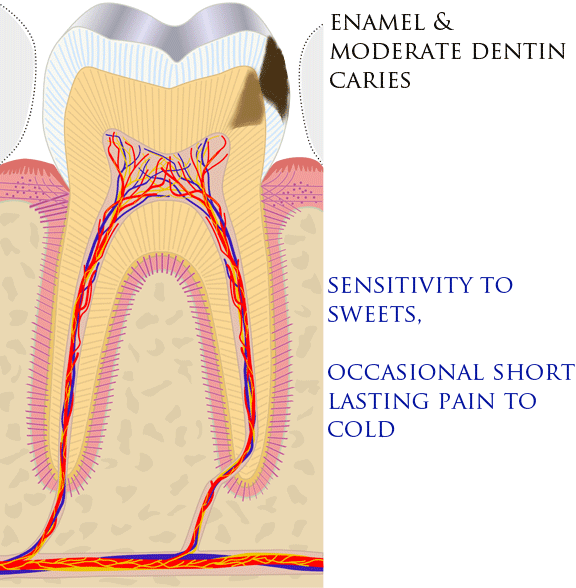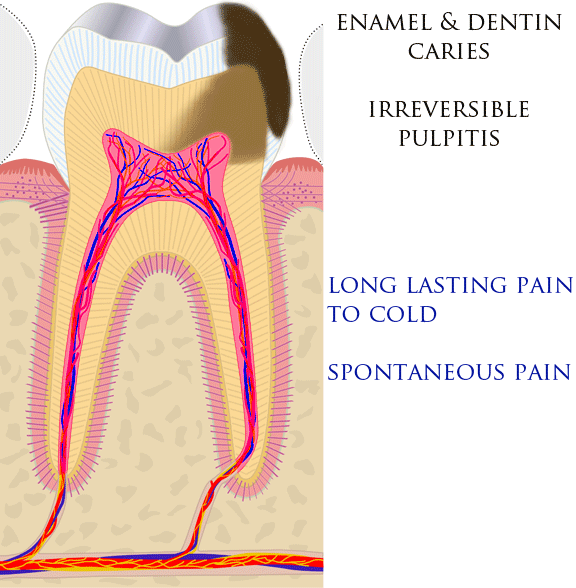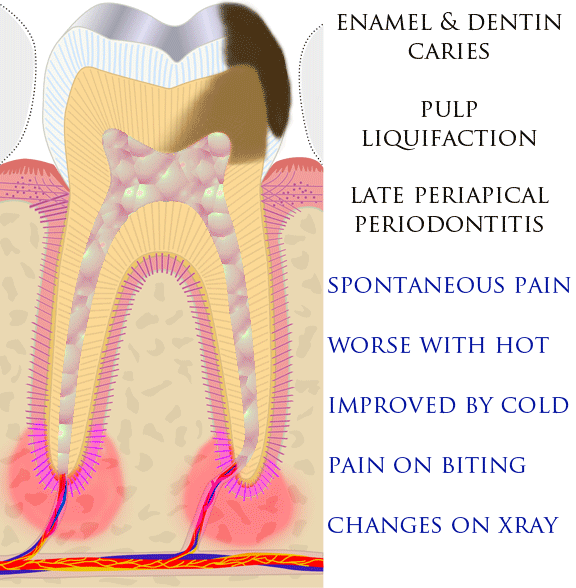
Toothache
Toothaches, also known as dental pain or tooth pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or referred pain, pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities. Common causes include pulpitis, inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to dental caries, tooth decay, dental trauma, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity, apical periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone around the Root apex (dental), root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis ("dry socket", a possible complication of dental extraction, tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder. Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Restoration
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—''direct'' and ''indirect''—and are further classified by location and size. Root canal therapy, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides and are more hectic than a normal filling. History In Italy evidence dated to the Paleolithic, around 13,000 years ago, points to bitumen used to fill a tooth and in Neolithic Slovenia, 6500 years ago, beeswax was used to close a fracture in a tooth. Graeco-Roman literature, such as Pliny the Elder's Naturalis Historia (AD 23–79), contains references to filling materials for hollow teeth. Tooth preparation Restoring a tooth to good form and function requires two steps: # prepari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittleness
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress (physics), stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength of materials, strength. Breaking is often accompanied by a sharp snapping sound. When used in materials science, it is generally applied to materials that fail when there is little or no plasticity (physics), plastic deformation before failure. One proof is to match the broken halves, which should fit exactly since no plastic deformation has occurred. Brittleness in different materials Polymers Mechanical characteristics of polymers can be sensitive to temperature changes near room temperatures. For example, poly(methyl methacrylate) is extremely brittle at temperature 4˚C, but experiences increased ductility with increased temperature. Amorphous polymers are polymers that can behave differently at different temperatures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room Temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and other factors. In certain fields, like science and engineering, and within a particular context, room temperature can mean different agreed-upon ranges. In contrast, ambient temperature is the actual temperature, as measured by a thermometer, of the air (or other medium and surroundings) in any particular place. The ambient temperature (e.g. an unheated room in winter) may be very different from an ideal ''room temperature''. Food and beverages may be served at "room temperature", meaning neither heated nor cooled. Comfort temperatures Comfort temperature is interchangeable with neutral temperature in the scientific literature, which can be calculated through regression analysis between thermal sensation votes and indoor temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric stoves, to baking in various types of ovens, reflecting local conditions. Types of cooking also depend on the skill levels and training of the Cook (profession), cooks. Cooking is done both by people in their own dwellings and by professional cooks and chefs in restaurants and other food establishments. Preparing food with heat or fire is an activity unique to humans. Archeological evidence of cooking fires from at least 300,000 years ago exists, but some estimate that humans started cooking up to 2 million years ago. The expansion of agriculture, commerce, trade, and transportation between civilizations in different regions offered cooks many new ingredients. New inventions and technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of f. If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point p, the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from p, and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function f(\mathbf) may be defined by: df=\nabla f \cdot d\mathbf where df is the total infinitesimal change in f for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooktop
A cooktop (American English), stovetop (Canadian and American English) or hob (British English), is a device commonly used for cooking that is commonly found in kitchens and used to apply heat to the base of cookware, pans or pots. Cooktops are often found integrated with an oven into a kitchen stove but may also be standalone devices. Cooktops are commonly powered by gas or electricity, although oil or other fuels are sometimes used. Gas Gas cooktops consist of one or more gas burners with arrangements to control the rate of flow. They often have integral lighters or (in older models) pilot lights, and may have safety interlocks designed to reduce the risk of hazardous gas leaks. Gas cooking has been associated with negative health effects, such as reduced pulmonary function and a higher rate of respiratory symptoms in children. Electric Coil An electric coil cooktop uses electric elements that directly heat pots placed on them. They are inexpensive to buy and maintain, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass-ceramic
Glass-ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass, producing a fine uniform dispersion of crystals throughout the bulk material. Crystallization is accomplished by subjecting suitable glasses to a carefully regulated heat treatment schedule, resulting in the nucleation and growth of crystal phases. In many cases, the crystallization process can proceed to near completion, but in a small proportion of processes, the residual glass phase often remains. Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics. Glass-ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so-called "controlled crystallization" in contrast to a spontaneous crystallization, which is usually not wanted in glass manufacturing. Glass-ceramics have the fabrication advantage of glass, as well as special properties of ceramics. When used for sealing, some glass-ceramics do not require brazing but can w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |