|
NeXTstation @ Google Office NY
NeXTstation is a high-end workstation computer developed, manufactured, and sold by NeXT from 1990 until 1993. It runs the NeXTSTEP operating system. The system was designed to be a lower-cost option compared to the company's upscale product, the NeXTcube. Compared to the cube, it removed a number of features and had limited expandability, allowing it to fit in a much smaller pizza-box form factor case. There were two major series of the system released during its production run. The initial models were the NeXTstation and NeXTstation Color. Both were based on the Motorola 68040 processor running at 25 MHz. The Color units supported 12-bit color graphics (4,096 colors) stored in a separate 1.5 MB VRAM memory. Turbo versions were released in April 1992, which increased the speed of the processor to 33 MHz and increased the maximum amount of main memory from 32 to 128 MB of RAM. Both the station and the cube initially used the same displays, the original Mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstation'' has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a Personal computer, PC connected to a Computer network, network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC, HP Inc., HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s. Workstations formerly offered higher performance than mainstream personal computers, especially in Central processing unit, CPU, Graphics processing unit, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the Visualization (graphics), visualization and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NeXT MegaPixel Display
The NeXT MegaPixel Display is a range of CRT-based computer monitors manufactured and sold by NeXT for the NeXTcube and NeXTstation workstations, designed by Hartmut Esslinger/ Frog Design Inc. Description The original MegaPixel Display released in 1990 was a monochrome 17" monitor displaying four brightness levels (black, dark gray, light gray, and white) in a fixed resolution of 1120 × 832 at 92 DPI (just shy of a true megapixel at 931,840 total pixels) at 68 Hz. It integrated a mono microphone, mono speaker, stereo RCA sockets, a 3.5 mm headphone socket and a socket for the keyboard (which in turn provided a socket for the mouse). A unique feature was that the monitor was connected to the computer by a single 6 foot cable which provided power, video signals and the aforementioned signals. A severe problem with this setup was that the monitor could not be switched off completely while the computer was powered on. The screen could be switched black but the cathode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced in the 1980s and has seen widespread use on servers and high-end workstations, with new SCSI standards being published as recently as SAS-4 in 2017. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and optical disc drives, although not all controllers can handle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Speaker
Computer speakers, or multimedia speakers, are speakers marketed for use with computers, although usually capable of other audio uses, e.g. for a shelf stereo or television. Most such speakers have an internal amplifier and consequently require a power source, which may be by a mains power supply often via an AC adapter, batteries, or a USB port. The signal input connector is often an analog 3.5 mm jack plug (usually color-coded lime green per the PC 99 standard); RCA connectors are sometimes used, and a USB port or Bluetooth antenna may supply a digital signal to an onboard DAC (some of which work only on computers with an appropriate device driver). Battery-powered wireless speakers require no cables at all. Most computers have speakers of low power and quality built in; when external speakers are connected they disable the built-in speakers by default. Altec Lansing claims to have created the computer speaker market in 1990. Computer speakers range widely in quality a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereo
Stereophonic sound, commonly shortened to stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration of two loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Because the multi-dimensional perspective is the crucial aspect, the term ''stereophonic'' also applies to systems with more than two channels or speakers such as quadraphonic and surround sound. Binaural sound systems are also ''stereophonic''. Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment media such as broadcast radio, recorded music, television, video cameras, cinema, computer audio, and the Internet. Etymology The word ''stereophonic'' derives from the Greek (''stereós'', "firm, solid") + (''phōnḗ'', "sound, tone, voice") and it was coined in 1927 by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 56000
The Motorola DSP56000 (also known as 56K) is a family of digital signal processor (DSP) chips produced by Motorola Semiconductor (later Freescale Semiconductor and then NXP) starting in 1986 with later models still being produced in the 2020s. The 56k series was intended mainly for signal processing in embedded systems, but was also used in a number of early computers, including the NeXT, Atari Falcon030 and SGI Indigo workstations, all using the 56001. Upgraded 56k versions are still used in audio equipment, radar systems, communications devices (like mobile phones) and various other embedded DSP applications. The 56000 was also used as the basis for the updated 96000, which was not commercially successful. Technical description The DSP56000 uses fixed-point arithmetic, with 24- bit program words and 24-bit data words. It includes two 24-bit registers, which can also be referred to as a single 48-bit register. It also includes two 56-bit accumulators, each with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal Processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products. The goal of a DSP is usually to measure, filter or compress continuous real-world analog signals. Most general-purpose microprocessors can also execute digital signal processing algorithms successfully, but may not be able to keep up with such processing continuously in real-time. Also, dedicated DSPs usually have better power efficiency, thus they are more suitable in portable devices such as mobile phones because of power consumption constraints. DSPs often use special m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
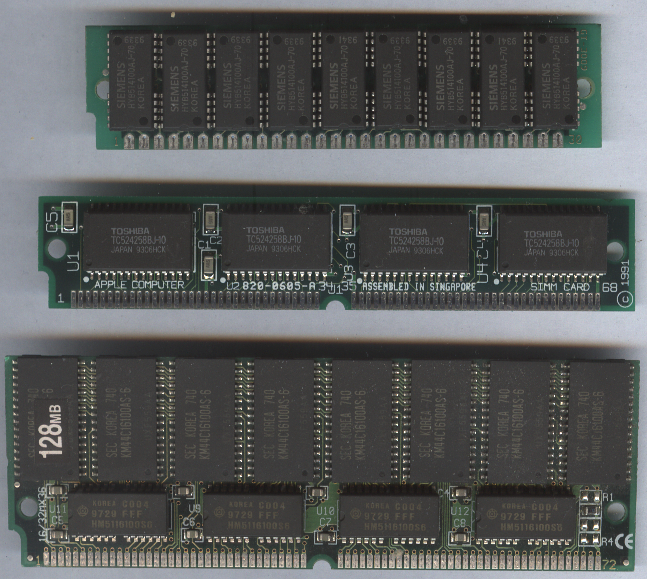
SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or both sides. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards ( 8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1983 by James E. ClaytonClayton, James E. (1983)Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Inc
Canon Inc. (; Hepburn: ) is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo, specializing in optical, imaging, and industrial products, such as lenses, cameras, medical equipment, scanners, printers, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment. Canon has a primary listing on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the TOPIX Core 30 and Nikkei 225 indexes. It used to have a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange. Name The company was originally named (). In 1934, it produced the ''Kwanon'', a prototype for Japan's first-ever 35mm camera with a focal-plane-based shutter. In 1947, the company name was changed to ''Canon Camera Co., Inc.'', shortened to ''Canon Inc.'' in 1969. The name Canon comes from Buddhist bodhisattva (), previously transliterated as Kuanyin, Kwannon, or Kwanon in English. History 1933–1970 The origins of Canon date back to the founding of Precision Optical Instruments Laboratory in Japan in 1933 by Takeshi Mitarai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Computer Systems
Canon Computer Systems, Inc. (CCSI), sometimes shortened to Canon Computer, was an American subsidiary of Canon Inc. formed in 1992 to develop and market the parent company's personal computers and workstations. The subsidiary also assumed the responsibility of marketing Canon's printers and photocopiers, which were formerly sold by other Canon divisions. It went defunct in January 2001. History Canon entered the computer industry in the 1970s, starting with the AX-1 in October 1978. It sported the form factor of a desktop calculator and was fully programmable. Excerpt in This was followed up with the AS-100 in 1982, which was a more-traditional albeit heavier personal computer that ran a Intel 8088 and ran MS-DOS. Canon entered the home computer market in 1984 with the V-20 and V-10 in 1984 and 1985 respectively. In 1987, the company released the Canon Cat—the brainchild of Jef Raskin who pioneered Apple's original Macintosh. In 1989, the company took a large stake in NeXT, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doom (video Game)
''Doom'' is an American media franchise created by John Carmack, John Romero, Adrian Carmack, Kevin Cloud, and Tom Hall. The series usually focuses on the exploits of an unnamed space marine (often referred to as Doomguy, Doom Marine, or Doom Slayer) operating under the auspices of the Union Aerospace Corporation (UAC), who fights hordes of demons and the undead to save Earth from an apocalyptic invasion. The original ''Doom'' is considered one of the first pioneering first-person shooter games, introducing IBM-compatible computers to features such as 3D graphics, third-dimension spatiality, networked multiplayer gameplay, and support for player-created modifications with the ''Doom'' WAD format. Over ten million copies of games in the ''Doom'' series have been sold; the series has spawned numerous sequels, novels, comic books, board games, and film adaptations. Overview The ''Doom'' video games consist of first-person shooters in which the player controls an unnamed space m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Carmack
John D. Carmack II (born August 21, 1970) is an American computer programmer and video game developer. He co-founded the video game company id Software and was the lead programmer of its 1990s games ''Commander Keen'', ''Wolfenstein 3D'', ''Doom (1993 video game), Doom'', ''Quake (video game), Quake'', and their sequels. Carmack made innovations in 3D computer graphics, such as his Carmack's Reverse algorithm for shadow volumes. In 2013, he resigned from id Software to work full-time at Reality Labs, Oculus VR as their Chief technology officer, CTO. In 2019, he reduced his role to Consulting CTO so he could allocate more time toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). In 2022, he left Oculus to work on his AGI startup, Keen Technologies. Biography Early life Carmack was born in Shawnee Mission, Kansas, the son of local television news reporter Stan Carmack. He grew up in the Kansas City metropolitan area, where he became interested in computers at an early age. He attende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |