|
Navahrudak
Novogrudok or Navahrudak (; ; , ; ) is a town in Grodno Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Novogrudok District. As of 2025, it has a population of 27,624. In the Middle Ages, the city was ruled by King Mindaugas' son Vaišvilkas. During and after Mindaugas' rule, Novogrudok was part of the Kingdom of Lithuania, and later the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which was later part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In the 14th century, it was an episcopal see of the Metropolitanate of Lithuania. From 1795 to 1915, the Russian Empire ruled over the lands, with brief periods of intercession, e.g. Napoleon's ''Grande Armée'' in 1812 and the Uprisings of 1831 and 1863. After 1915, Novogrudok was occupied by the Imperial German Army for three years in World War I, by the Second Polish Republic until the Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939. Thereafter, the Soviet Union annexed the area to the Byelorussian SSR. From 1941 to 1944, Novogrudok was occupied by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navahrudak Castle
The former castle in Navahrudak, Belarus (, , ) was one of the strongholds of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, cited by Maciej Stryjkowski as the location of Mindaugas's coronation as King of Lithuania as well as his likely burial place.Tomas Baranauskas. On the opinion of Lithuanian historians (Tomas Baranauskas, T.Baranauskas etc.), there is no information that King Mindaugas lived or visited Navahrudak at all - it is Maciej Stryjkowski, Maciej Stryjkowski's 16th century written conjecture in the interpretation of legends. As early as the 14th century, Navahrudak is known to have possessed a stone tower along the lines of Tower of Kamyanyets. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. He also largely influenced Ukrainian literature. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's " Three Bards" () and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama '' Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Grażyna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindaugas
Mindaugas (, , , , ; c. 1203 – 12 September 1263) was the first known grand duke of Lithuania, Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only crowned King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or rise to power; he is mentioned in a 1219 treaty as an elder duke, and in 1236 as the leader of all the Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians. The contemporary and modern sources discussing his ascent mention strategic marriages along with banishment or murder of his rivals. He extended his domain into regions southeast of Lithuania proper during the 1230s and 1240s. In 1250 or 1251, during the course of internal power struggles, he was baptised as a Roman Catholic; this action enabled him to establish an alliance with the Livonian Order, a long-standing antagonist of the Lithuanians. By 1245, Mindaugas was already being referred to as "the highest king" in certain documents. During the summer of 1253, he was crowned king, ruling between 300,000 and 400,000 subjects, and got nickn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
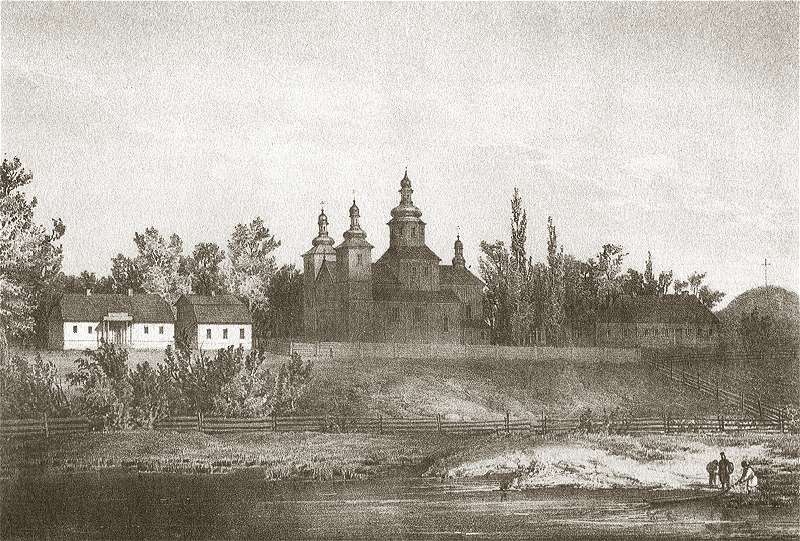
Transfiguration Church, Navahrudak
The Transfiguration Roman Catholic Church () in Novogrudok, Belarus, is a Baroque church erected in 1712–1723, replacing an earlier Gothic building from the late 14th century, and originally consecrated under the title of Corpus Christi. Two Gothic chapels survive and are included in the Baroque building. In 1799, the poet Adam Mickiewicz was baptized in this church. Closed in 1857, re-opened in 1906. Currently active. History Vytautas the Great founded the church in 1395 on the site of a former pagan temple. In 1422 Władysław II Jagiełło married here his fourth wife Sophia of Halshany, establishing the Jagiellonian dynasty. In 1643 local castellan Jan Rudamina added a marble bas-relief in commemoration of the Navahrudaks knights fallen in the Battle of Khotyn in 1621. In 1712-1740 the church was rebuilt. The local masons Jakub Boksza, Jerzy Urłowski, Andrzej Szarecki, Jerzy Stepkowski headed the construction. The keystone was consecrated on July 14, 1714, by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novogrudok District
Novogrudok district or Navahrudak district (; ) is a district (raion) of Grodno region in Belarus. The administrative center is Novogrudok. As of 2024, it has a population of 40,761. Notable residents * Fabijan Abrantovič (1884, Vieraskava village – 1946), religious and civic leader of the first half of the 20th century, victim of the Soviet repressions * Uladzimir Konan (1934, Vieraskava village - 2011), Belarusian philosopher * Michaś Naŭmovič (1922, Kašaliova village - 2004), French artist, member of the Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic * Paval Navara (1927, Kupisk village - 1983), Belarusian émigré public figure and a co-founder of the Anglo-Belarusian Society * Jazep Sažyč (1917, Haradzečna village – 2007), political figure, President of the Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic The Rada of the Belarusian People's Republic (, ) was the governing body of the Belarusian Democratic Republic. Since 1919, the Rada BNR has been in exile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Largest Towns In Belarus
This is a list of cities and towns in Belarus. Neither the Belarusian nor the Russian language makes a distinction between "city" and "town" as English does; the word ''horad'' ( ) or ''gorod'' ( ) is used for both. Overview Belarusian legislation uses a three-level hierarchy of town classifications. According to the Law under May 5, 1998, the categories of the most developed urban localities in Belarus are as follows: * ''capital'' — Minsk; * ''city of regional subordinance'' (; ) — urban locality with a population of not less than 50,000 people; it has its own body of self-government, known as ''Council of Deputies'' (; ) and an executive committee (; ), which stand on the level with these of a ''raion'' (). * ''city of district subordinance'' (; ) — urban locality with a population of more than 6,000 people; it may have its own body of self-government (; ) and an executive committee (; ), which belong to the same level as these of rural councils and of s.c. ''haradski p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six regions and one capital city. The six regions are oblasts (also known as ''voblastsi''), while the city of Minsk has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk also serves as the administrative center of Minsk Region. At the second level, the regions are divided into districts (raions). The layout and extent of the regions were set in 1960 when Belarus (then the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic) was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union. History At the start of the 20th century, the boundaries of the Belarusian lands within the Russian Empire were still being defined. In 1900 it was contained within all of the Minsk and Mogilev governorates, most of Grodno Governorate, parts of Vitebsk Governorate, and parts of Vilna Governorate. World War I, the independence of Poland, as well as the 1920–1921 Polish–Soviet War affected the boundaries. In 1921, Belarus had what is now all of Minsk Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitanate Of Lithuania
The Metropolis of Lithuania was a metropolis of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in the Eastern Orthodox Church. It was erected on the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania between 1315 and 1317. It was disestablished in 1371. The seat (''cathedra'') of the metropolis was initially in Navahrudak. It had only two metropolitan bishops. The establishment took place in the aftermath of the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus' which was exploited by the rulers of Lithuania to greatly expand their territory. To help legitimize their annexations and to bind their new subjects more closely to the state, the royal powers favoured the erection of a metropolis for the inhabitants of the Grand Principality. To avert the possibility of the state going over to the Holy See, the hierarchs based in Moscow latterly supported the erection of the metropolis as the lesser of two evils. Throughout the existence of the metropolis, the metropolitans struggled for religious control of the Rus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaišvilkas
Vaišvilkas or Vaišelga (also spelled ''Vaišvila'', ''Vojszalak'', ''Vojšalk'', ''Vaišalgas''; died 18 April 1267) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1264 until his death in 1267. He was a son of Mindaugas, the first and only Christian King of Lithuania. Name The original Lithuanian name of this Grand Duke has puzzled many linguists and historians. Their reconstructions resulted in two credible variants ''Vaišvilkas'', based on ''Woyszwiłk'' and ''Vaišelga'', based on ''Vojšalk''. The name ''Vaišvilkas'' was first reconstructed by Kazimieras Būga. In fact, the first part of the double-stemmed name ''vaiš-'' causes no dispute and is attested in many similar names. However, the second part ''-vilkas'', meaning "wolf" is very rare to non existent in Lithuanian names. This led to the hypothesis that the initial form of the name should have been ''Vaišvilas''. The variant ''Vaišelga''/''Vaišalga'' has gained more popularity in historical writings even though the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande Armée
The (; ) was the primary field army of the French Imperial Army (1804–1815), French Imperial Army during the Napoleonic Wars. Commanded by Napoleon, from 1804 to 1808 it won a series of military victories that allowed the First French Empire to exercise unprecedented control over most of Europe. Widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest fighting forces ever assembled, it suffered catastrophic losses during the disastrous French invasion of Russia, after which it never recovered its strategic superiority and ended its military career with a total defeat during the Hundred Days in 1815. The ''Grande Armée'' was formed in 1804 from the Army of the Coasts of the Ocean (1804), Army of the Coasts of the Ocean, a field army of over 100,000 men assembled for Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom. He subsequently led the field army to Central Europe and defeated Austrian Empire, Austrian and Russian Empire, Russian forces as part of the War of the Third Coalition. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |