|
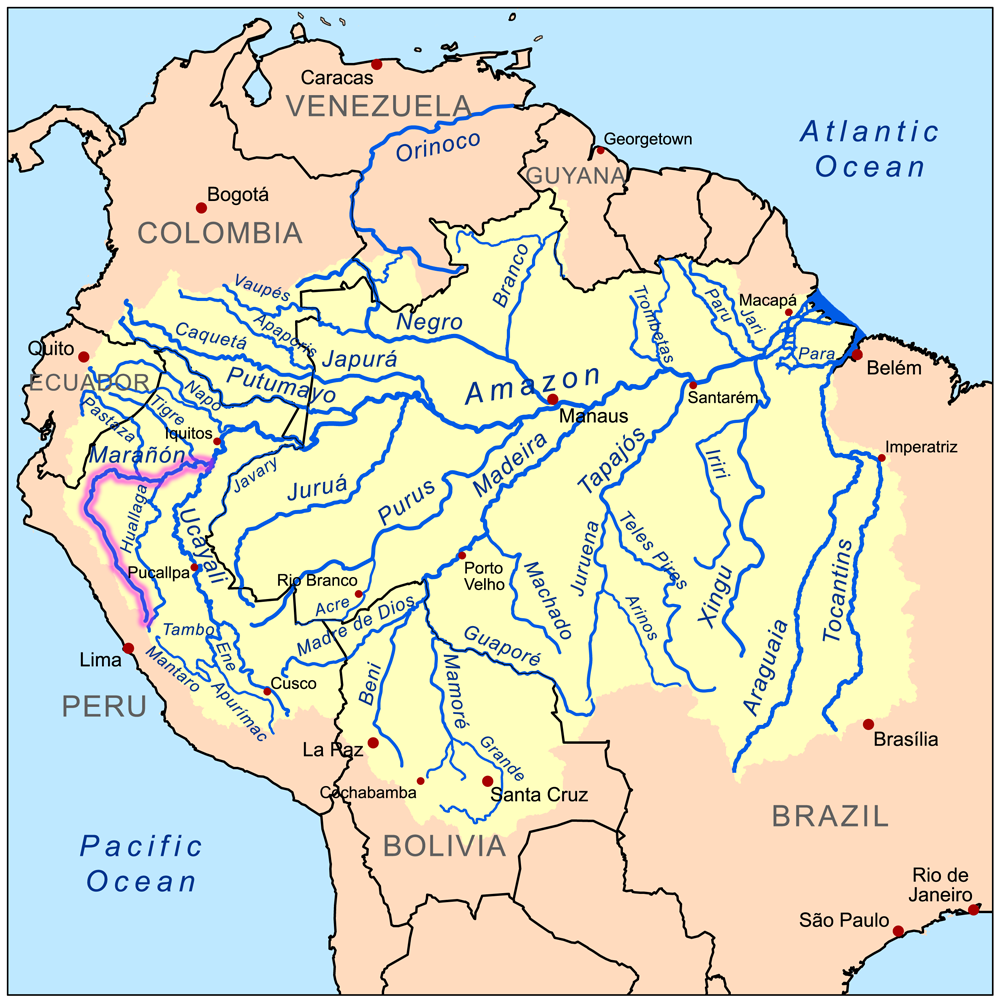
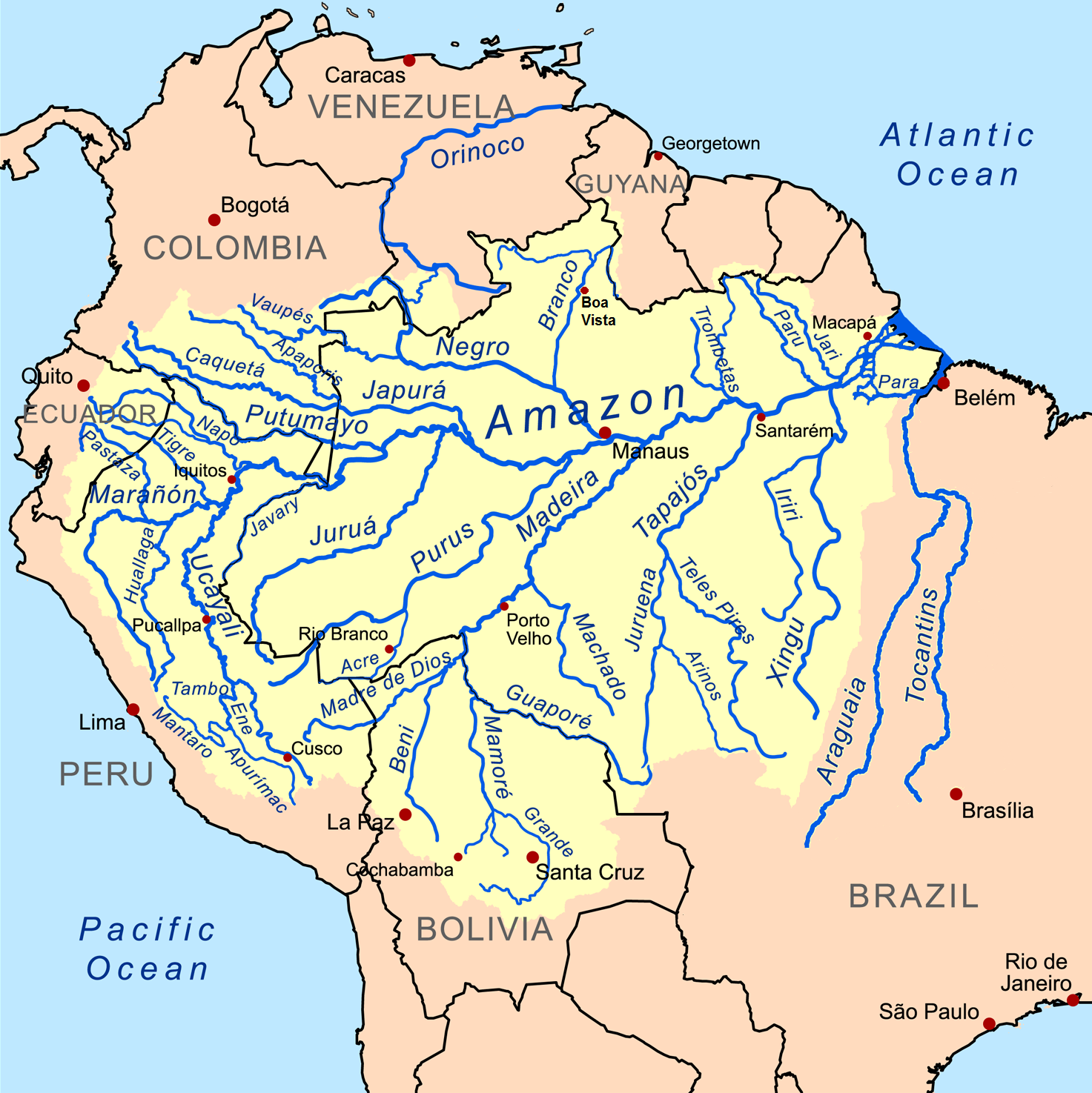
Nauta
Nauta is a town in the northeastern part of Loreto Province in the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest, Amazon, roughly south of Iquitos, the provincial capital. Nauta is located on the north bank of the Marañón River, a major tributary of the Upper Amazon, a few miles from the confluence of the Río Ucayali. Established by Manuel Pacaya–Samiria, a leader of the Kokama people, following the 1830 uprising at the Jesuit mission of Lagunas, Nauta soon became the primary commercial hub of the Peruvian ''selva baja'' (known also as Omagua, or the Amazon Basin, Amazonian lowlands). In 1853, a Brazilian-owned paddle steamer made it all the way to Nauta. Nauta is the primary destination of the only major road leading out of Iquitos, and is a staging area for several ecotourism lodges and ships on the Marañòn River. Boats take passengers from Nauta to the Pacaya-Samiria National Reserve. History Towards the end of the second decade of the 19th century, Chief Manuel Pacaya, leader of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauta District
Nauta District is one of five districts of the province Loreto in Peru. Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática The Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática (INEI) ("National Institute of Statistics and Informatics") is a semi-autonomous Peruvian government agency which coordinates, compiles, and evaluates statistical information for the country. .... Banco de Información Distrital''. Retrieved April 11, 2008. Climate References Districts of the Loreto province Districts of the Department of Loreto {{Loreto-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacaya–Samiria
Pacaya–Samiria National Reserve, is a protected area located in the region of Loreto, Peru and spans an area of . It protects an area of low hills and seasonally flooded forest in the Amazon rainforest. Pacaya-Samiria National Reserve and the near Tamshiyacu-Tahuayo Reserve both forms a biodiversity hotspot in the Amazon jungle. Biodiversity Flora Some of the native plant species present in the reserve are: ''Spondias mombin, Quararibea cordata, Mauritia flexuosa, Parinari excelsa, Cedrela odorata, Ocotea'' spp., '' Myrciaria dubia, Socratea exorrhiza, Calathea allouia, Solanum sessiliflorum, Hevea guianensis, Pouteria caimito, Clidemia hirta, Ficus maxima, Heliconia psittacorum, Inga'' spp., '' Psychotria poeppigiana, Alibertia edulis, Victoria amazonica, Ceiba pentandra, Phytelephas macrocarpa, Clusia'' spp., ''Swietenia macrophylla, Asclepias curassavica, Pachira aquatica, Cragious Psychotria,'' etc. Fauna Mammal species found in the reserve include: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loreto Region
Loreto () is Peru's northernmost department and region. Covering almost one-third of Peru's territory, Loreto is by far the nation's largest department, slightly smaller than Japan; it is also one of the most sparsely populated regions due to its remote location in the Amazon Rainforest. Its capital is Iquitos. Geography * Northwest: Ecuador: Sucumbíos Province, Orellana Province, Pastaza Province and Morona-Santiago Province * North: Colombia: Putumayo Department * Northeast: Colombia: Amazonas Department * East: Brazil: Amazonas State and Acre State * South: Ucayali and Huánuco regions * West: San Martín and Amazonas regions Loreto's large territory comprises parts of the high and low jungle, and is largely covered with thick vegetation. This territory has wide river flood plains, which are covered with rainwater and are usually swamped in summer. In these flood areas there are elevated sectors called ''restingas'', which always remain above water, even in time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marañón River
The Marañón River (, , ) is the principal or mainstem source of the Amazon River, arising about 160 km (100 miles) to the northeast of Lima, Peru, and flowing northwest across plateaus 3,650 m (12,000 feet) high, it runs through a deeply eroded Andean valley, along the eastern base of the Cordillera of the Andes, as far as 5° 36′ southern latitude; from where it makes a great bend to the northeast, and cuts through the jungle Ande in its midcourse, until at the Pongo de Manseriche it flows into the flat Amazon basin. Although historically, the term "Marañón River" often was applied to the river all the way to the Atlantic Ocean, nowadays the Marañón River is generally thought to end at the confluence with the Ucayali River, after which most cartographers label the ensuing waterway the Amazon River. As the Marañón passes through high jungle in its midcourse, it is marked by a series of unnavigable rapids and falls. The Marañón was the subject of a landmark legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province, Peru, Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the List of cities in Peru, ninth-most populous city in Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world that cannot be reached by road that is not on an island; it is only accessible by river and air. It is known as the "capital of the Peruvian Amazon". The city is located in the Great Plains of the Amazon Basin, fed by the Amazon River, Amazon, Nanay River, Nanay, and Itaya River, Itaya rivers. Overall, it constitutes the Iquitos metropolitan area, a conurbation of 471,993 inhabitants consisting of four districts: Iquitos District, Iquitos, Punchana District, Punchana, Belén District, Maynas, Belén, and San Juan Bautista District, Maynas, San Juan Bautista. The area has long been inhabited by indigenous peoples. According to Spanish historical documents, Iquitos was established around 1757 as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ucayali
The Ucayali River (, ) is the main headstream of the Amazon River. It rises about north of Lake Titicaca, in the Arequipa region of Peru and becomes the Amazon at the confluence of the Marañón close to Nauta city. The city of Pucallpa is located on the banks of the Ucayali. Description The Ucayali, together with the Apurímac River, the Ene River and the Tambo River, is today considered the main headwater of the ''Amazon River'', totaling a length of from the source of the ''Apurímac'' at Nevado Mismi to the confluence of the Ucayali and Marañón Rivers: *Apurímac River (total length): *Ene River (total length): *Tambo River (total length): * Ucayali River (confluence with Tambo River to confluence with the Marañón): Exploration The Ucayali was first called ''San Miguel'', then ''Ucayali'', ''Ucayare'', ''Poro'', ''Apu-Poro'', ''Cocama'' and ''Rio de Cuzco''. Peru has organised many costly and ably-conducted expeditions to explore it. One of them (1867) claimed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Peru
The provinces of Peru () are the second-level administrative subdivisions of the country. They are divided into districts (). There are 196 provinces in Peru, grouped into 25 regions, except for Lima Province which does not belong to any region. This makes an average of seven provinces per region. The region with the fewest provinces is Callao (one) and the region with the most is Ancash (twenty). While provinces in the sparsely populated Amazon rainforest of eastern Peru tend to be larger, there is a large concentration of them in the north-central area of the country. The province with the fewest districts is Purús Province, with just one district. The province with the most districts is Lima Province, with 43 districts. The most common number of districts per province is eight; a total of 29 provinces share this number of districts. Provinces table The table below shows all provinces with their capitals and the region in which they are located. The UBIGEO code unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Peru
The districts of Peru () are the third-level country subdivisions of Peru. They are subdivisions of the provinces of Peru, provinces, which in turn are subdivisions of the larger regions of Peru, regions or departments. There are 1,838 districts in total. Overview A 1982 law requires a minimum of residents in an area for a new district to be legally established: 3,500 if it is located in the rainforest, 4,000 in the Andes highlands and 10,000 in the Chala, coastal area. In the dry Andean area, many districts have less than 3,500 inhabitants due to low population density in the area. In some cases, their populations have decreased in comparison to the days when they were founded. Districts that are located at very high altitudes tend to be scarcely populated. These districts usually are large in area, have few available land for use. Many basic government services do not reach all residents of these districts due to their difficult geography. Many lack financial means to govern th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrau Turtle
The Arrau turtle (''Podocnemis expansa''), also known as the South American river turtle, giant South American turtle, giant Amazon River turtle, Arrau sideneck turtle, Amazon River turtle or simply the Arrau, is the largest of the side-neck turtles (Pleurodira) and the largest freshwater turtle in Latin America. The species primarily feeds on plant material and typically nests in large groups on beaches. Due to hunting of adults, collecting of their eggs, pollution, habitat loss, and dams, the Arrau turtle is seriously threatened. Range and habitat Arrau turtles are found in the Amazon Basin, Amazon, Orinoco and Essequibo River, Essequibo basins in Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela and Guyana. On occasion, typically after floods, individuals turn up in Trinidad. They are found in deep rivers, ponds, freshwater lagoons and flooded forest in Whitewater river (river type), white-, Blackwater river, black- and Clearwater river (river type), clear-water. Appearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the sides, with their eyes, ears, and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |