|
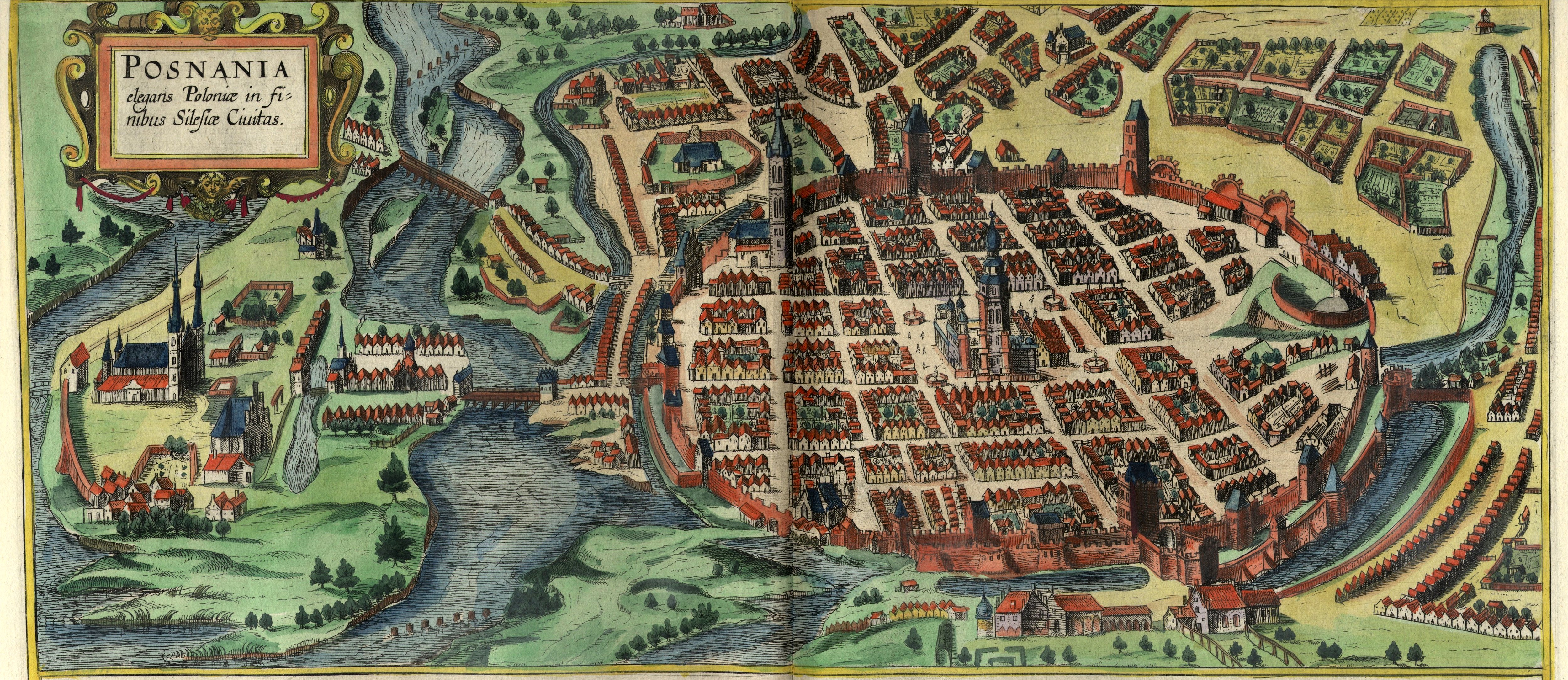
Narmeln
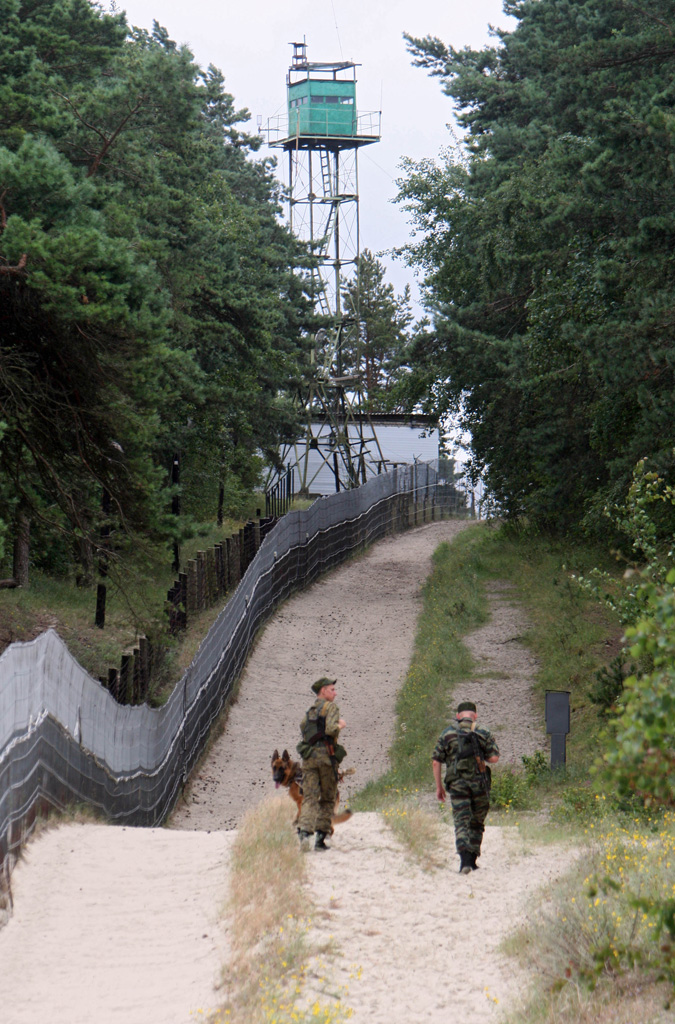
Narmeln (, ), alternatively known as Polski,Georg Mielcarczyk, ''Narmeln-Neukrug-Vöglers. Ein Kirchspiel auf der Frischen Nehrung'', Bremerhaven, 1971. is an abandoned village in Baltiysky District of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Vistula Spit, on the border with Poland, the westernmost point of Russia. Narmeln is distinct as it is one of the few places in Kaliningrad Oblast whose German name was not officially changed when the territory was annexed to the Soviet Union following World War II, and is also the only part of historic Gdańsk Pomerania to be annexed by the Soviet Union by the Potsdam Agreement. Narmeln was depopulated after the war, and the Soviet side of the Vistula Spit was made into an exclusion zone, which remains in effect today. Geographical location Narmeln is located about south-west of Baltiysk. The westernmost point of Russia is located on the Poland–Russia border nearby. () History Coaching inn and border station In 1466, foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Village
An abandoned village is a village that has, for some reason, been deserted. In many countries, and throughout history, thousands of villages have been deserted for a variety of causes. Abandonment of villages is often related to epidemic, famine, war, climate change, economic depressions, environmental destruction, or deliberate clearances. Armenia and Azerbaijan Hundreds of villages in Nagorno-Karabakh were deserted following the First Nagorno-Karabakh War. Between 1988 and 1993, 400,000 ethnic Azeris, and Kurds fled the area and nearly 200 villages in Armenia itself populated by Azeris and Kurds were abandoned by 1991. Likewise, nearly 300,000 Armenians fled from Azerbaijan between 1988 and 1993, including 50 villages populated by Armenians in Northern Nagorno Karabakh that were abandoned. Some of the Armenian settlements and List of Armenian churches in Azerbaijan, churches outside Armenia and the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic have either been destroyed or damaged including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk Pomerania
Gdańsk Pomerania (; ; ) is the main geographical region within Pomerelia (also known as Vistula Pomerania, Eastern Pomerania, and previously Polish Pomerania) in northern Poland, covering the bulk of Pomeranian Voivodeship. In contrast to ''Pomerelia'' and its synonyms, the term does not cover the historical areas of Chełmno Land and Michałów Land, sometimes with the addition of Lubawa Land. The area has traditionally been divided into the Kashubia, Kociewie and Tuchola Forest regions. The Lębork and Bytów Land is considered by the Polish historiography a part of Kashubia (and thus Gdańsk Pomerania), while German historiography tends to treat it as a part of Farther Pomerania. Gdańsk Pomerania has been inhabited by ethnic Kashubians, Kociewians and Borowians, respectively. A small portion of Gdańsk Pomerania in the eastern part of the Vistula Spit around the abandoned village of Polski is now part of the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Name In Polish language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Poland to the south and Lithuania to the north and east. The largest city and administrative centre is the city of Kaliningrad. The port city of Baltiysk is Russia's only port on the Baltic Sea that remains ice-free in winter. Kaliningrad Oblast had a population of roughly one million in the 2021 Russian census. It has an area of . Various peoples, including Lithuanians, Germans, and Polish people, Poles, lived on the land which is now Kaliningrad. The territory was formerly the northern part of East Prussia. With the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II, the territory was annexed to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR by the Soviet Union. Following the Aftermath of World War II, post-war migration and Flight and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia (; or , ) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) became a province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, which was annexed following the Second Peace of Thorn (1466) from territory in Pomerelia and western Prussia which had been part of the State of the Teutonic Order. Royal Prussia retained its autonomy, governing itself and maintaining its own laws, customs, rights and German language for the Germans (mainly in urban areas) and Polish language for the Polish (mainly in rural areas). The inhabitants, from various ethnic groups, had a strong local identity and called themselves 'Prussians'. In 1569, Royal Prussia was fully integrated into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and its autonomy was largely abolished. As a result, the Royal Prussian parliament was incorporated into the Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1772 and 1793, after the first and se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free City Of Danzig (Napoleonic)
The Free City of Danzig ( French: ''Ville libre de Dantzig''; ; ), sometimes referred to as the Republic of Danzig (French: ''République de Dantzig''; German: ''Republik Danzig''), was a semi-independent city-state established by Napoleon on 21 July 1807, during the time of the Napoleonic Wars following the capture of the city in the siege of Danzig in May. After the Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815, Danzig was re-incorporated into the Kingdom of Prussia. History Prussia had acquired the City of Danzig in the course of the Second Partition of Poland in 1793. After the defeat of King Frederick William III of Prussia at the 1806 Battle of Jena–Auerstedt, according to the Franco-Prussian Treaty of Tilsit of 9 July 1807, the territory of the free state was carved out from lands that made up part of the West Prussia province. It consisted of the city of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland) along with its rural surroundings on the mouth of Vistula, through Oliva, together with the Hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltiysky District, Kaliningrad Oblast
Baltiysky District () is an administrative district (raion), one of the fifteen in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia.Law #463 As a municipal division, it is incorporated as Baltiysky Municipal District.Law #274 Its administrative center is the town of Baltiysk, which accounts for 90.7% of the district's total population of Resolution #639 It is the westernmost district in Russia, with the abandoned village of Narmeln being the westernmost point. Baltiysky District is located on the Sambia Peninsula Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea. The peninsula is bounded by the Curonian Lagoon to ... in the west of the oblast along the Baltic Sea coast, and partially forms the Vistula Lagoon. The area of the district is , with roughly half consisting of the Russian side of the Vistula Spit, which is an unpopulated exclusion zone except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistula Spit
The Vistula Spit (; ; ; ) is an aeolian sand spit, or peninsular stretch of land, separating Vistula Lagoon from Gdańsk Bay, in the Baltic Sea, with its tip separated from the mainland by the Strait of Baltiysk. The border between Poland (Pomeranian Voivodeship) and Kaliningrad Oblast, an exclave of Russia, bisects it, politically dividing the spit into two pieces between the two countries. The westernmost geographical point of Russia is located on the Vistula Spit. The Polish part contains a number of tourist resorts, incorporated administratively as the town of Krynica Morska. Geography Situated in the Gdańsk Bay this narrow headland (spit) is on average only few hundred meters wide (widest point is ) and with the total length of twice as long as the better known and more populous Hel Peninsula in the western part of the Gdańsk Bay. The Vistula Spit stretches in a north-easterly direction and separates the Vistula Lagoon from the southern Baltic Sea. It is separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Points Of Russia
This is a list of the extreme points and extreme elevations in Russia. The northernmost and easternmost points of Russia coincide with those of Eurasia (both for the mainland and including the islands). The extreme points of the Soviet Union were identical, except that the southernmost point of the Soviet Union was Kushka in Turkmenistan, and the extreme elevation was the Communism Peak in Tajikistan, at . The other extreme points of Russia are the same as those of the Soviet Union. From 1799 until 1867 the easternmost point of the Russian Empire was located in North America, on the border between Russian Alaska and British North America, which superimposed on the then International Date Line. The westernmost point of the Empire was located at Ruda Komorska in Congress Poland from 1815 until its occupation by German and Austro-Hungarian troops in 1915. Kushka in present-day Turkmenistan had been the southernmost point of the Empire since 1885. Again, until the Alaska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Extreme Points Of Russia
This is a list of the extreme points and extreme elevations in Russia. The northernmost and easternmost points of Russia coincide with Extreme points of Eurasia, those of Eurasia (both for the mainland and including the islands). The extreme points of the Soviet Union were identical, except that the southernmost point of the Soviet Union was Serhetabat, Kushka in Turkmenistan, and the extreme elevation was the Ismoil Somoni Peak, Communism Peak in Tajikistan, at . The other extreme points of Russia are the same as those of the Soviet Union. From 1799 until 1867 the easternmost point of the Russian Empire was located in North America, on the border between Russian Alaska and British North America, which superimposed on the then International Date Line. The westernmost point of the Empire was located at Ruda Komorska in Congress Poland from 1815 until its Eastern Front (World War I), occupation by German and Austro-Hungarian troops in 1915. Serhetabat, Kushka in present-day Turk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomeranian Voivodeship (1466–1772)
The Pomeranian Voivodeship () was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1454/1466 until the First partition of Poland in 1772. From 1613 the capital was at Skarszewy. The name ''Pomerania'' derives from the Slavic ''po more'', meaning "by the sea" or "on the sea". (Pommersches Landesmuseum, German) History The comprised the westernmost part of the province of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Province, Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
Greater Poland Province () was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795. The name of the province comes from the historic land of Greater Poland. The Greater Poland Province consisted initially of twelve voivodeships (after 1768 thirteen voivodeships) and one duchy: # Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship # Chełmno Voivodeship # Gniezno Voivodeship, est. in 1768 # Inowrocław Voivodeship # Kalisz Voivodeship # Łęczyca Voivodeship # Malbork Voivodeship # Masovian Voivodeship # Płock Voivodeship # Pomeranian Voivodeship # Poznań Voivodeship # Rawa Voivodeship # Sieradz Voivodeship # Prince-Bishopric of Warmia The location of the Crown Tribunal for the Greater Poland Province (the highest appeal court of the province) was Piotrków Trybunalski, and after the Convocation Sejm (1764) also Poznań and Bydgoszcz. Cities The five most influential cities, i.e. Warsaw, Poznań, Gdańsk, Toruń and Elbląg Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaching Inn
The coaching inn (also coaching house or staging inn) was a vital part of Europe's inland transport infrastructure until the development of the railway, providing a resting point ( layover) for people and horses. The inn served the needs of travellers, for food, drink, and rest. The attached stables, staffed by hostlers, cared for the horses, including changing a tired team for a fresh one. Coaching inns were used by private travellers in their coaches, the public riding stagecoaches between one town and another, and (in England at least) the mail coach. Just as with roadhouses in other countries, although many survive, and some still offer overnight accommodation, in general coaching inns have lost their original function and now operate as ordinary pubs. Coaching inns stabled teams of horses for stagecoaches and mail coaches and replaced tired teams with fresh teams. In America, stage stations performed these functions. Traditionally English coaching inns were apart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |