|
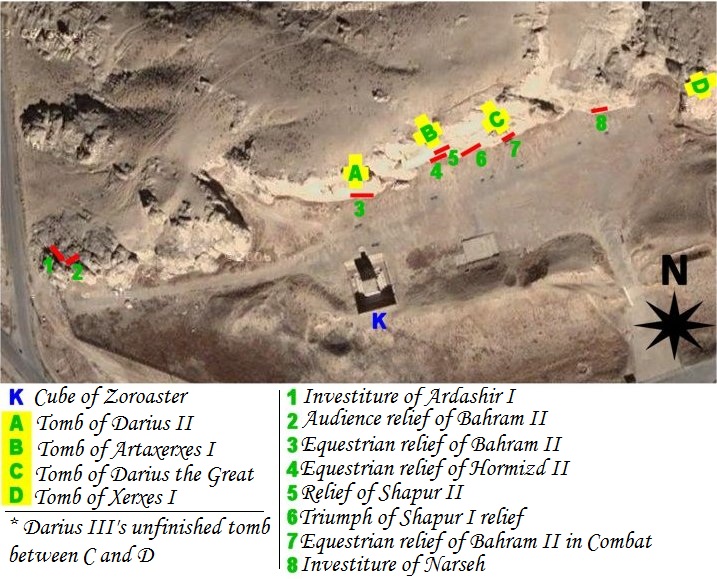
Naqsh-e Rustam
Naqsh-e Rostam (; , ) is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 13 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes I, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranian peoples, Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenids to Sassanian Empire, Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest. Naqsh-e Rostam is the necropolis of the Achaemenid dynasty ( 550–330 BC), with four large tombs cut high into the cliff face. These have mainly architectural decoration, but the facades include large p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvdasht
Marvdasht () is a city in the Central District (Marvdasht County), Central District of Marvdasht County, Fars province, Fars province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Etymology Some historians hold that Marvdasht was originally the name of one of the neighborhoods of the ancient city of Estakhr, until gradually the whole area was called Marvdasht. Others have argued that ''marv'' was the name of a plant which grew in the area and the suffix ''dasht'' (meaning plain in the Persian language) was added to form a descriptive placename. History Marvdasht is as ancient as the history of Iran and the Persian Empire. Its former capital Persepolis is in the vicinity of the city, and few kilometers farther Naqsh-e-Rostam, Naqsh-e Rajab and the ruins of the ancient city of Estakhr are reminiscent of the region's importance in historic times. Archaeological excavations have shown that civilized people had already been living in the Marvdasht Plains fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The Proto-Iranian language, Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe; from the Danube, Danubian Plains in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems from the Sumerian language, Sumerian transliteration ''elam(a)'', along with the later Akkadian language, Akkadian ''elamtu'', and the Elamite ''haltamti.'' Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East. In classical literature, Elam was also known as Susiana ( ; ''Sousiānḗ''), a name derived from its capital Susa. Elam was part of the early Cities of the Ancient Near East, urbanization of the Near East during the Chalcolithic period (Copper Age). The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Sumerian history, where slightly earlier records have been found. In the Old Elamite period (Bronze Age, Middle Bronze Age), Elam consisted of kingdoms on the Iranian plateau, centered in Ansha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes Tomb At Naqsh-e Rostam- Upper Register (4614878357)
Xerxes ( ) may refer to: People * Xerxes I of Persia, "Xerxes the Great", reigned 486–465 BC * Xerxes II of Persia, briefly reigned 424 BC * Xerxes of Sophene, ruler of Sophene and Commagene, 228–201 BC * Xerxes (Sasanian prince), 6th-century prince and general * Xerxes (name), a list of people with the name Fiction, stage and video *'' Il Xerse'' (''Xerxès'' in its 1660 French version), a 1654 opera by Francesco Cavalli * ''Xerse'' (Bononcini), a 1694 opera by Giovanni Bononcini *''Serse'' (''Xerxes''), a 1738 opera by George Frideric Handel *''Xerxes'', a 1919 novel by Louis Couperus * ''Xerxes'' (TV series), a 1988 Swedish TV series about young adults * ''Xerxes'' (graphic novel), a 2018 graphic novel by Frank Miller Other * Xerxes Peak, a mountain in the Canadian Rockies * XerxesDZB, a Dutch professional football team based in Rotterdam *Roksan Xerxes, a series of record turntables from Roksan Audio (UK) *XerXeS, a denial-of-service attack tool developed by The Jester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Naqsh-e Rostam
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
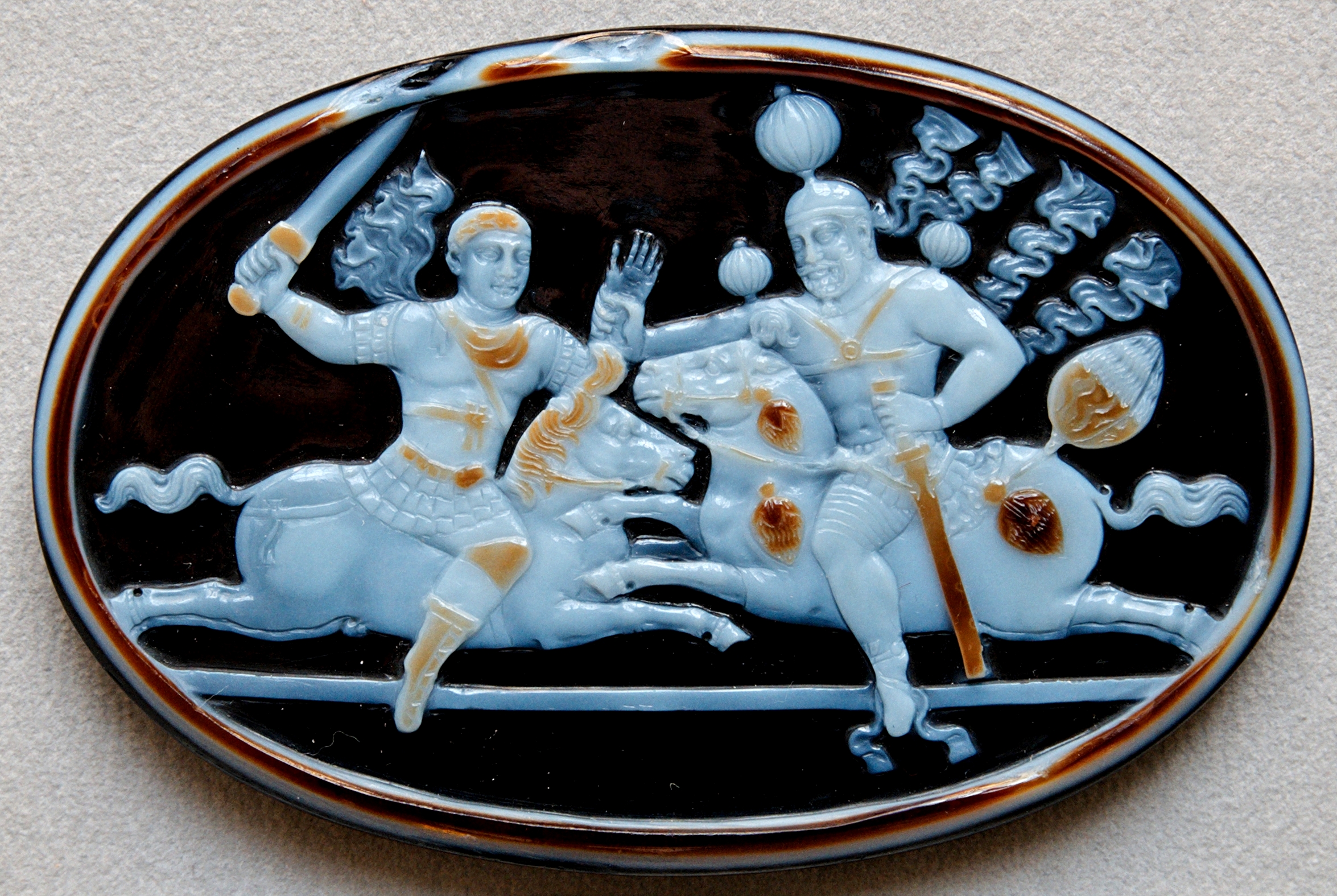
Battle Of Edessa
The Battle of Edessa took place between the armies of the Roman Empire under the command of Emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian and the Sasanian Empire under Shapur I, in Edessa, Mesopotamia, Edessa (now the Turkish city of Urfa) in 260. The Roman army was defeated and captured in its entirety by the Sasanian forces; for the first time, a Roman emperor was taken prisoner. Background and prelude Prior to the battle, Shapur I had penetrated several times deeply into Roman territory, conquering and plundering Antioch in Syria (Roman province), Syria in 253 or 256. After defeating the usurper Aemilianus and assuming imperial power for himself, Valerian arrived in the eastern provinces as soon as he could (254 or 255) and gradually restored order. Soon he had to confront a naval Gothic invasion in northern Asia Minor. The Goths ravaged Pontus and moved south into Cappadocia. An attempt by Valerian and his army in Antiocheia to intercept them failed because of the Plague of Cyprian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordian III
Gordian III (; 20 January 225 – February 244) was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor of the united Roman Empire. Gordian was the son of Maecia Faustina and her husband Junius Balbus, who died before 238. Their names are mentioned in the unreliable ''Historia Augusta''. Maecia was the daughter of Emperor Gordian I and sister of Emperor Gordian II. Very little is known of his early life before his acclamation. Rise to power In 235, following the murder of Emperor Alexander Severus in Moguntiacum (modern Mainz), the capital of the Roman province Germania Superior, Maximinus Thrax was acclaimed emperor. In the following years, there was a growing opposition against Maximinus in the Roman Senate and amongst the majority of the population of Rome. In 238, a rebellion broke out in the Africa Province, where Gordian's grandfather and uncle, Gordian I and II, were proclaimed joint emperors. This revolt was suppressed within a mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Arab
Philip I (; – September 249), commonly known as Philip the Arab, was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, who had been Praetorian prefect, rose to power. He quickly negotiated peace with the Sasanian Empire and returned to Rome to be confirmed by the Roman Senate, Senate. According to many historians, he was possibly the first Christian Roman Emperor. Although his reign lasted only five years, it marks an unusually stable period in a century that is otherwise known for having been turbulent. Near the end of his rule, Philip commemorated Ab urbe condita#Use, Rome's first millennium. In September 249 he was killed during or shortly after the Battle of Verona (249), Battle of Verona against the usurper Decius, Trajan Decius, who was subsequently recognized by the Senate as his successor. Born in modern-day Shahba#Roman history, Shahba, Syria, in what was then Arabia Petraea, Philip's ethnicity was most likely Arabs, Arab. While h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerian (emperor)
Valerian ( ; ; – 260 or 264) was Roman emperor from 253 to spring 260 AD. Valerian is known as the first Roman emperor to have been taken captive in battle, captured by the Sassanid Empire, Persian emperor Shapur I after the Battle of Edessa, causing shock and instability throughout the Roman Empire. The unprecedented event and his unknown fate generated a variety of different reactions and "new narratives about the Roman Empire in diverse contexts". Biography Origins and rise to power Unlike many of the would-be emperors and rebels who vied for imperial power during the Crisis of the Third Century, Valerian was of a noble and traditional Roman Senate, senatorial family. Details of his early life are sparse, except for his marriage to Egnatia Mariniana, with whom he had two sons: Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (his co-emperor and later successor) and Licinius Valerianus (brother of Gallienus), Licinius Valerianus. Valerian was Roman consul, consul for the first time eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; ) was the second Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nusaybin, Nisibis and Harran, Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III (), the following year he was able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab () to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty". Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:σάρξ, σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and wikt:φαγεῖν, φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' (wikt:λίθος, λίθος wikt:σαρκοφάγος, σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the corpse decomposition, decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 BC. The Hagia Triada sarcoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |