|
Napier Nomad
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel economy. Two versions were tested, the complex Nomad I which used two propellers, each driven by the mechanically independent stages, and the Nomad II, using the turbo-compound principle, coupled the two parts to drive a single propeller. The Nomad II had the lowest specific fuel consumption figures seen up to that time. Despite this the Nomad project was cancelled in 1955 having spent £5.1 million on development, as most interest had passed to turboprop designs. Design and development In 1945 the Air Ministry asked for proposals for a new class engine with good fuel economy. Curtiss-Wright was designing an engine of this sort of power known as the turbo-compound engine, but Sir Harry Ricardo, one of Britain's great engine designers, suggested that the most economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo-compound
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well. As this recovery process does not increase fuel consumption, it has the effect of reducing the specific fuel consumption, the ratio of fuel use to power. Turbo-compounding was used for commercial airliners and similar long-range, long-endurance roles before the introduction of turbojet engines. Examples using the Duplex-Cyclone include the Douglas DC-7B and Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation, while other designs did not see production use. Concept Most piston engines have a hot ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range (takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. In the second half of the 20th century, heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers, which were often smaller in size, but had much longer ranges and were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. Because of advances in aircraft design and engineering — especially in powerplants and aerodynamics — the size of payloads carried by heavy bombers has increased at rates greater than increases in the size of their airframes. The largest bombers of World War I, the four engine aircraft built by the Sikorsky company in the Soviet Union, could carry a payload of up to of bombs. By the middle of World War II even a single-engine fighter-bomber could carry a bomb load, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Naiad
The Napier Naiad is a British turboprop gas-turbine engine designed and built by D. Napier & Son in the late 1940s. It was the company's first gas turbine engine. A twin version known as the Coupled Naiad was developed but both engine projects were cancelled before finding a market. The Naiad was also used, in adapted form, in the Napier Nomad turbo-compound engine design. Applications *Avro Lincoln - Test bed only Engines on display A Napier Naiad is on display at the Science Museum, London London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow .... Retrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twincharger
A twincharger refers to a compound forced induction system used on some internal combustion engines. It is a combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and a mechanically driven supercharger, each mitigating the weaknesses of the other. Twincharging does not refer to a twin-turbo arrangement, but to a setup where two different types of compressors are used (instead of only turbochargers). Overview and advantages A mechanically driven supercharger offers exceptional response and low-rpm performance, as it does not rely on pressurization of the exhaust manifold (assuming that it is a positive-displacement design, such as a Roots-type or twin-screw, as opposed to a centrifugal supercharger, which does not provide substantial boost in the lower rpm range), but is less efficient than a turbocharger due to increased parasitic load. A turbocharger sized to move a large volume of air tends to respond slowly to throttle input, while a smaller, more responsive turbocharger may fail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first flew on December 20, 1957. Pan American World Airways began regular 707 service on October 26, 1958. With versions produced until 1979, the 707 was a swept wing, quadjet with podded engines. Its larger fuselage cross-section allowed six-abreast economy seating, retained in the later 720, 727, 737, and 757 models. Although it was not the first commercial jetliner in service, the 707 was the first to be widespread and is often credited with beginning the Jet Age. It dominated passenger air transport in the 1960s, and remained common through the 1970s, on domestic, transcontinental, and transatlantic flights, as well as cargo and military applications. It established Boeing as a dominant airliner manufacturer with its 7x7 series. The initial, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (engine)
In a reciprocating engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels. The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings, which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil. Steam engines The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. Internal combustion engines The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled to the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. In an ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, whereby each cylinder has two pistons sharing a central combustion chamber. The most common configuration of flat engines is the boxer engine configuration, in which the pistons of each opposed pair of cylinders move inwards and outwards at the same time. The other configuration is effectively a V engine with a 180-degree angle between the cylinder banks; in this configuration each pair of cylinders shares a single crankpin, so that as one piston moves inward, the other moves outward. The first flat engine was built in 1897 by Karl Benz. Flat engines have been used in aviation, motorcycle and automobile applications. They are now less common in cars than straight engines (for engines with less than six cylinders) and V engines (for engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
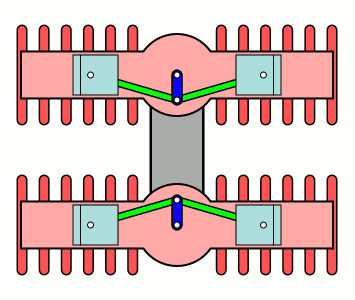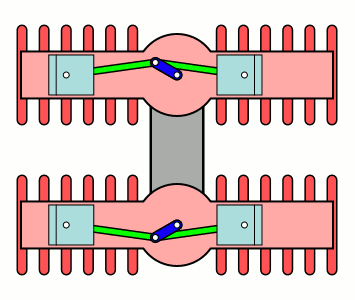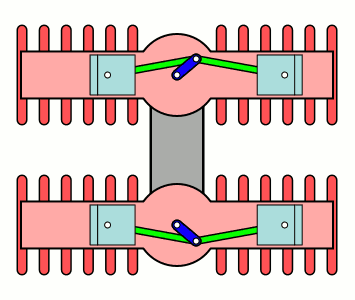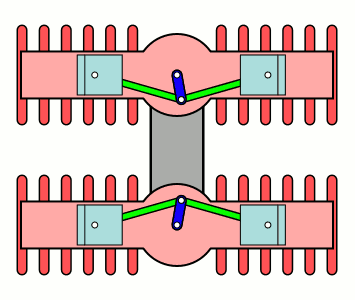
H Engine
An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate flat engines (complete with separate crankshafts), most often geared to a common output shaft. The name "H engine" is due to the engine blocks resembling a letter "H" when viewed from the front. The most successful "H" engine in this form was the Napier Dagger and its derivatives. The name was also applied to engines of the same basic layout, but rotated through 90 degrees—most famously the Napier Sabre series. A variation on the "H" theme were the Fairey Prince (H-16) & Fairey P.24 Monarch, where the two engines retained separate drives, driving Contra-rotating propellers through separate concentric shafts. Although successful, they only existed in prototype form. The H engine is a relatively rare layout, with its main use being in aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s. The 1966 Lotus 43 Formula One car used a BRM 16-cylinder H engine, and an 8-cylinder H engine was used for powerboat racing in the 1970s. Desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Sabre
The Napier Sabre is a British H-24-cylinder, liquid-cooled, sleeve valve, piston aero engine, designed by Major Frank Halford and built by D. Napier & Son during World War II. The engine evolved to become one of the most powerful inline piston aircraft engines in the world, developing from in its earlier versions to in late-model prototypes. The first operational aircraft to be powered by the Sabre were the Hawker Typhoon and Hawker Tempest; the first aircraft powered by the Sabre was the Napier-Heston Racer, which was designed to capture the world speed record. Other aircraft using the Sabre were early prototype and production variants of the Blackburn Firebrand, the Martin-Baker MB 3 prototype and a Hawker Fury prototype. The rapid introduction of jet engines after the war led to the quick demise of the Sabre, as there was less need for high power military piston aero engines and because Napier turned its attention to developing turboprop engines such as the Naiad and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)