|
Namiestnik Of Poland
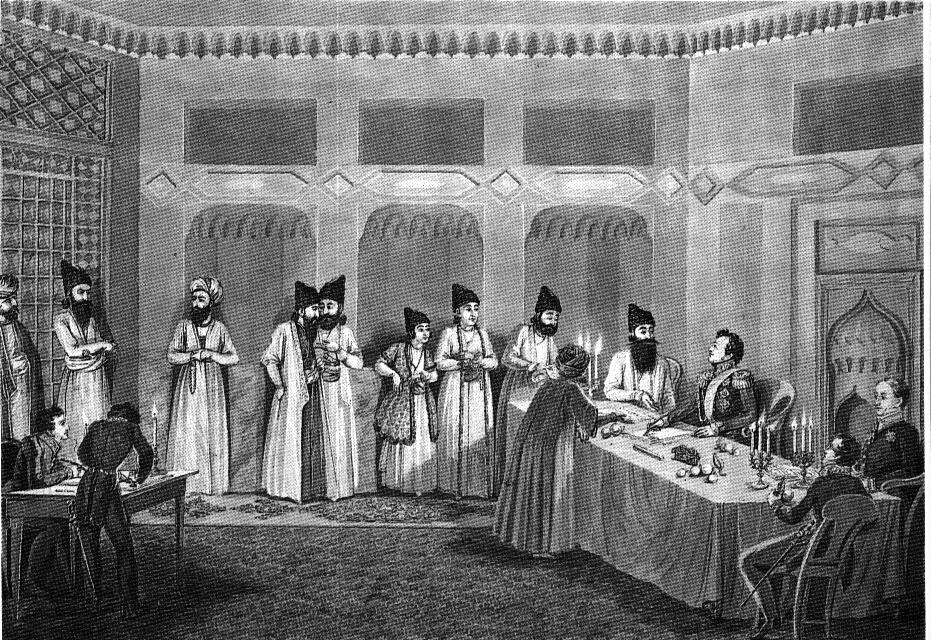
The Namiestnik (or Namestnik, Viceroy) of the Kingdom of Poland (, ) was the deputy of the Emperor of Russia who, under the Congress Kingdom of Poland (1815–1915), was styled "King of Poland". Between 1874 and 1914, the title ''Namiestnik'' was replaced by that of Governor-General of Warsaw (). History The office of ''Namiestnik'' was introduced in Poland by the Constitution of Congress Poland (1815), in its Article 3 (On the Namiestnik and Council of State). The namiestnik was chosen by the Tsar from among the noble citizens of the Russian Empire or the Kingdom of Poland, excluding naturalized citizens. The namiestnik supervised the entire public administration and, in the monarch's absence, chaired the Council of State of Congress Poland, as well as the Administrative Council of Congress Poland. He could veto the councils' decisions; other than that, his decisions had to be countersigned by the appropriate government minister. The namiestnik exercised broad powers and could no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Poland
The coat of arms of Poland is the Coat of arms, heraldic symbol representing Poland. The current version was adopted in 1990. It is a white, crowned Eagle (heraldry), eagle with a golden beak and talons, on a red background. In Poland, the coat of arms as a whole is referred to as ''godło'' both in official documents and colloquial speech, despite the fact that other coats of arms are usually called a ''herb'' (e.g. the Nałęcz coat of arms, Nałęcz ''herb'' or the coat of arms of Finland). This stems from the fact that in Polish heraldry, the word ''godło'' (plural: ''godła'') means only a heraldic charge (in this particular case a white crowned eagle) and not an entire coat of arms, but it is also an archaic word for a national symbol of any sort. In later legislation only the ''herb'' retained this designation; it is unknown why. Legal basis The coat of arms of the Republic of Poland is described in two legal documents: the Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 1997 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full Priest#Christianity, priesthood given by Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Lambert
Count Karl Karlovich Lambert (; ) (1815 – 20 July 1865) was a Russian General of Cavalry and Namestnik of the Kingdom of Poland from August to October 1861. From 1840 to 1844, he fought against Chechnya, Chechen highlanders during the Caucasian War. In 1848, he became chief of staff of II Russian Corps suppressing the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. On 14 October 1861, he instituted martial law in the territory of Congress Poland. References Ламберт граф Карл Карлович 1815 births 1865 deaths People of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 Imperial Russian Army generals Members of the State Council (Russian Empire) Namestniks of the Kingdom of Poland People of the Revolutions of 1848 Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Russia) {{Russia-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Sukhozanet
Nikolai Onufrievich Sukhozanet () (1794 – 22 July 1871) was an Imperial Russian Army general and statesman. Nikolai Sukhozanet was born in a noble family of Vitebsk Governorate. During the Napoleon's invasion of Russia he fought in numerous battles and finished the campaign in Paris in the rank of lieutenant of artillery. His awards included Order of St. Vladimir of 4th degree and Order of St. Anna of 2nd degree. After the war he occupied different positions in the 1st Army and in 1824 was promoted to Major General. When the November Uprising began he led the Staff of artillery in the acting army. He distinguished himself in the Battle of Ostrołęka and received the Order of St. George of 3rd degree. From 1836 to 1849 he commanded the 4th artillery division. From 1849 until the Battle of Chernaya River of Crimean War he commanded the artillery of the acting army, after that Sukhozanet got the 3rd Corps and the Southern Army the next year. On 17 April 1856 he became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Dmitrievich Gorchakov
Prince Mikhail Dmitrievich Gorchakov (, ; – , Warsaw) was a Russian General of the Artillery from the Gorchakov family, who commanded the Russian forces in the latter stages of the Crimean War and later served as a Namestnik of Kingdom of Poland from 1856 until his death. His military career included remarkable successes, such as the Battle of the Great Redan, as well as significant setbacks, such as the Battle of the Chernaya. Life and career Mikhail and his brother Pyotr Gorchakov were the children of a notable writer Prince Dmitri Petrovich Gorchakov and his wife Natalie Boborykina. Mikhail entered the Russian army in 1807 as a cadet of the Leub Guard Artillery battalion. In 1809 in the rank of lieutenant he took part in the campaigns against Persia. During the Napoleonic Wars he distinguished himself at Borodino (received the Order of St. Vladimir of 4th degree) and at Bautzen (received the Order of St. Anna of 2nd degree, the Prussian Order Pour le Mérite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Paskevich
Count Ivan Fyodorovich Paskevich-Erevansky, Serene Prince of Warsaw ( – ) was a Russian military leader who was the ''namiestnik'' of Poland. Paskevich is known for leading Russian forces in Poland during the November Uprising and for a series of leadership roles throughout the early and mid-19th century, such as the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828, and the beginning phase of the Crimean War. In Russian history, he is remembered as a prominent military commander, rated on a par with Ivan Dibich-Zabalkansky, commander of the Russian armies during the same time. Paskevich started as an officer during the Napoleonic Wars serving in the battles of Austerlitz and Borodino. After the war, he was a leader in the Russo-Persian War. He was made count of Yerevan in 1828. Afterwards, he became the ''namiestnik'' of Poland in 1831 after he crushed the Polish rebels in the November Uprising. He then helped crush the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. His last engagement was the Crimean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Council
Administrative Council () was a part of Council of State (Kingdom of Poland), Council of State of the Congress Poland. Introduced by the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland in 1815, it was composed of 5 ministers, special nominees of the Tsar, King and the Namestnik of the Kingdom of Poland. The Council executed King's will, ruled in the cases outside the ministers competence and prepared projects for the Council of State. The Council decided to revolt during the November Uprising in 1830 against Tsar Nicholas I, and transformed itself into governing Executive Commission. The Council was reformed after the death of namestnik Józef Zajączek in 1826, after the fall of November Uprising in 1831, after the liquidation of Council of State in 1841, after the reforms of Aleksander Wielopolski in 1863 and after the fall of January Uprising. It was liquidated on 15 June 1867. The Council was reformed: * after the death of namestnik Józef Zajączek in 1826 * after the fall of the Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declaration (law)
In law, a declaration is an authoritative establishment of fact. Declarations take various forms in different legal systems. Canon law In the canon law of the Catholic Church, a declaration of nullity, (commonly called an annulment and less commonly a decree of nullity) EWTN.com, accessed 9/11/2015 is authoritative judgment on the part of an ecclesiastical tribunal juridically establishing the fact that a marriage was invalidly contracted or, less frequently, a judgment juridically establishing the fact that an ordination was invalidly conferred. It does not dissolve a valid bond of marriage, but it is merely a factual declaration of the nullity of the bond. Common law In < ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Sentence
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is called a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term ''capital'' (, derived via the Latin ' from ', "head") refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing. Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against a person, such as murder, assassination, mass murder, child murder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Military District (Russian Empire)
The Warsaw Military District () was a Russian military district of the Imperial Russian Army. It covered the territory of Congress Poland Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established w ... (without the part of Suwałki Governorate, Suwałki in Vilno Military District (Russian Empire), Vilno Military District). The Warsaw Military District was created in 1862. When World War I broke out, most of the units of the district (three out of its five infantry corps) were used to form the 2nd Army (Russian Empire), 2nd Army. Since the territory of the district was overrun by German and Austro-Hungarian armies in the course of 1915, it was dissolved, and its staff used in creating the new Minsk Military District. Composition The Warsaw Military District was an umbrella organisation for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
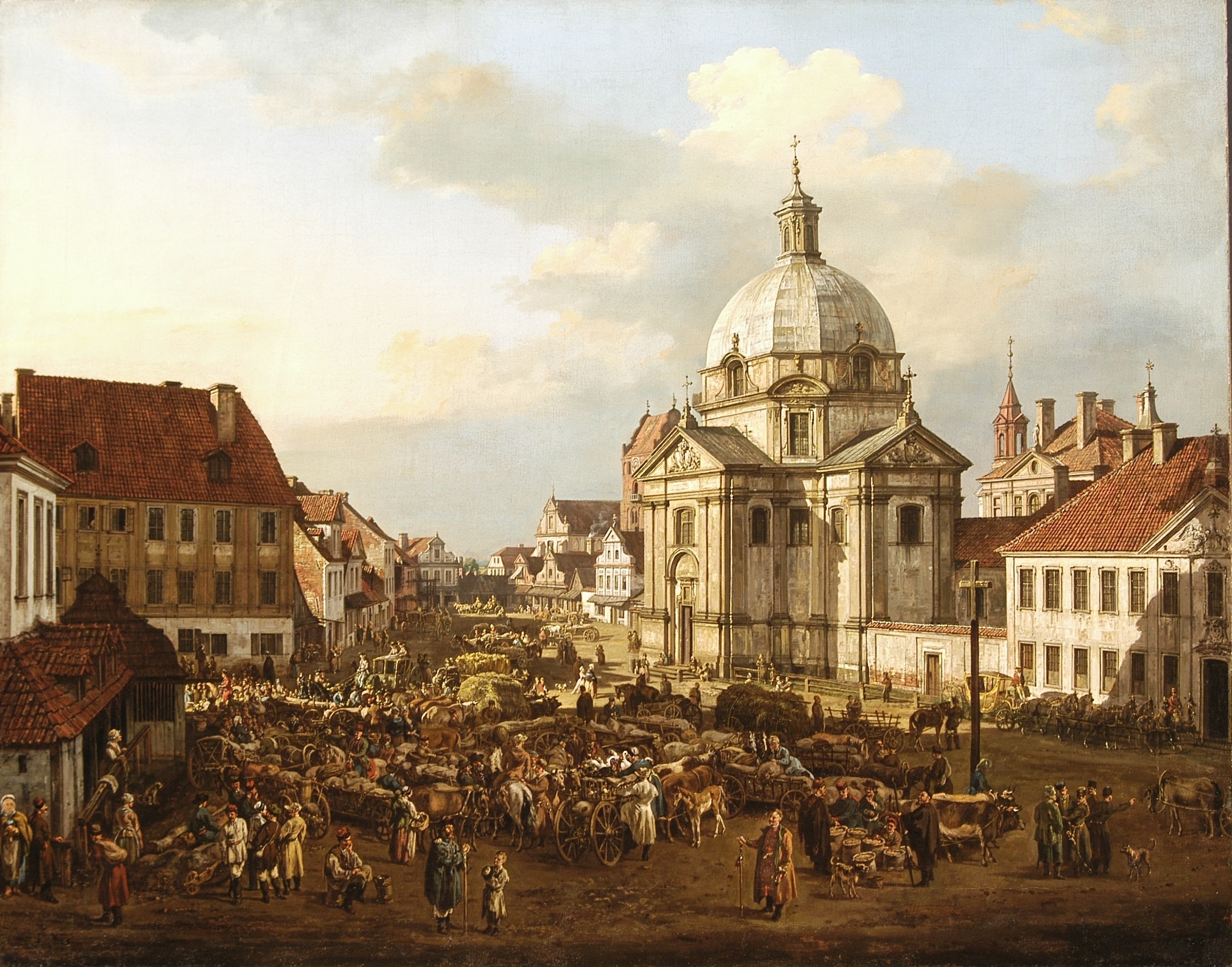
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-General
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general continue to be appointed as viceroy to represent the monarch of a personal union in any sovereign state over which the monarch does not normally reign in person (non-UK Commonwealth realm). In the British Empire, governors-general were appointed on the advice of the government of the United Kingdom and were often British aristocracy, but in the mid-twentieth century they began to be appointed on the advice of the independent government of each realm and be citizens of each independent state. Governors-general have also previously been appointed in respect of major colonial states or other territories held by either a monarchy or republic, such as Japan, Korea, Taiwan and France in Indochina. Current uses In modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |