|
NLS (computer System)
NLS (oN-Line System) was a revolutionary computer collaboration system developed in the 1960s. It was designed by Douglas Engelbart and implemented by researchers at the Augmentation Research Center (ARC) at the SRI International, Stanford Research Institute (SRI). It was the first computer system to employ the practical use of hypertext links, a computer mouse, raster scan, raster-scan computer monitor, video monitors, information organized by relevance, GUI, screen windowing, presentation programs, and other modern computing concepts. It was funded by ARPA (the predecessor to DARPA, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency), NASA, and the United States Air Force, US Air Force. The NLS was demonstrated in "The Mother of All Demos". Development Douglas Engelbart developed his concepts while supported by the US Air Force from 1959 to 1960 and published a framework in 1962. The strange acronym, NLS (rather than OLS), was an artifact of the evolution of the system. Engelbart's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Interactive Visualization
Visualization (or visualisation ), also known as graphics visualization, is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or animations to communicate a message. Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to communicate both abstract and concrete ideas since the dawn of humanity. from history include cave paintings, Egyptian hieroglyphs, Greek geometry, and Leonardo da Vinci's revolutionary methods of technical drawing for engineering purposes that actively involve scientific requirements. Visualization today has ever-expanding applications in science, education, engineering (e.g., product visualization), interactive multimedia, medicine, etc. Typical of a visualization application is the field of computer graphics. The invention of computer graphics (and 3D computer graphics) may be the most important development in visualization since the invention of central perspective in the Renaissance period. The development of animation also helped advance visualiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Bus (computing)
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers Data (computing), data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both Computer hardware, hardware (e.g., wires, optical fiber) and software, including communication protocols. At its core, a bus is a shared physical pathway, typically composed of wires, traces on a circuit board, or busbars, that allows multiple devices to communicate. To prevent conflicts and ensure orderly data exchange, buses rely on a communication protocol to manage which device can transmit data at a given time. Buses are categorized based on their role, such as system buses (also known as internal buses, internal data buses, or memory buses) connecting the Central processing unit, CPU and Computer memory, memory. Expansion buses, also called peripheral buses, extend the system to connect additional devices, including peripherals. Examples of widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Chord Keyset
A keyset or chorded keyboard (also called a chorded keyset, ''chord keyboard'' or ''chording keyboard'') is a computer input device that allows the user to enter characters or commands formed by pressing several keys together, like playing a " chord" on a piano. The large number of combinations available from a small number of keys allows text or commands to be entered with one hand, leaving the other hand free. A secondary advantage is that it can be built into a device (such as a pocket-sized computer or a bicycle handlebar) that is too small to contain a normal-sized keyboard. A chorded keyboard minus the board, typically designed to be used while held in the hand, is called a keyer. Douglas Engelbart introduced the chorded keyset as a computer interface in 1968 at what is often called "The Mother of All Demos". Principles of operation Each key is mapped to a number and then can be mapped to a corresponding letter or command. By pressing two or more keys together the user ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
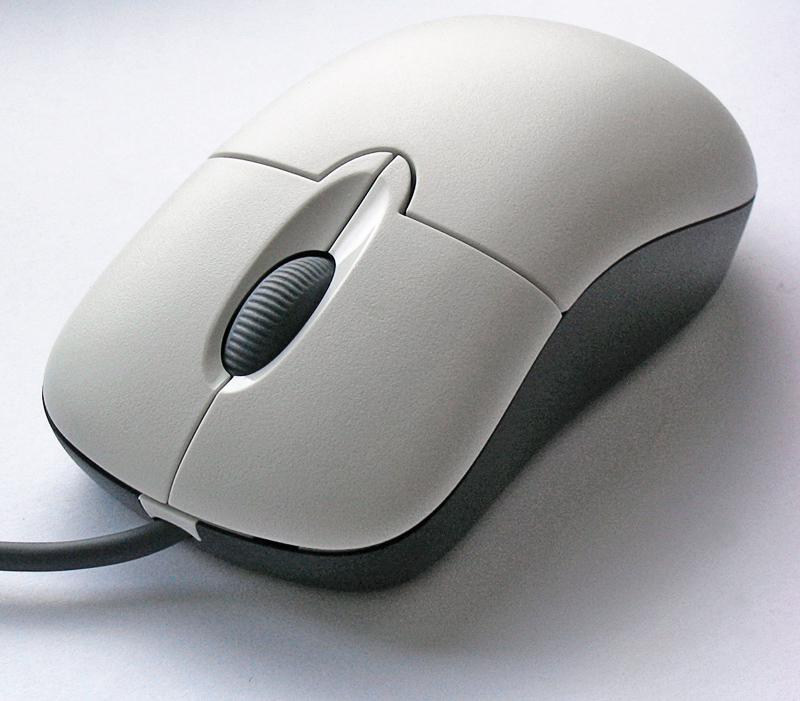 |
Computer Mouse
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the Cursor (user interface)#Pointer, pointer (called a cursor) on a computer monitor, display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was done by Doug Engelbart in 1968 as part of the Mother of All Demos. Mice originally used two separate wheels to directly track movement across a surface: one in the x-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to use a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, in turn connected to internal rollers. Most modern mice use optical mouse, optical movement detection with no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Computer Monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a electronic visual display, visual display, support electronics, power supply, Housing (engineering), housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls. The display in modern monitors is typically an Liquid-crystal display, LCD with LED-backlit LCD, LED backlight, having by the 2010s replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp, CCFL Backlight, backlit LCDs. Before the mid-2000s, most monitors used a cathode-ray tube, cathode-ray tube (CRT) as the image output technology. A monitor is typically connected to its host computer via DisplayPort, HDMI, USB-C, Digital Visual Interface, DVI, or VGA connector, VGA. Monitors sometimes use other proprietary connectors and signals to connect to a computer, which is less common. Originally computer monitors were used for data processing while television sets were used for video. From the 1980s onward, computers ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Raster-scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image systems. The word ''raster'' comes from the Latin word ''rastrum'' (a rake), which is derived from '' radere'' (to scrape); see also rastrum, an instrument for drawing musical staff lines. The pattern left by the lines of a rake, when drawn straight, resembles the parallel lines of a raster: this line-by-line scanning is what creates a raster. It is a systematic process of covering the area progressively, one line at a time. Although often a great deal faster, it is similar in the most general sense to how one's gaze travels when one reads lines of text. In most modern graphics cards the data to be drawn is stored internally in an area of semiconductor memory called the framebuffer. This memory area holds the values for each pixel on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Berkeley Timesharing System
The Berkeley Timesharing System was a pioneering time-sharing operating system implemented between 1964 and 1967 at the University of California, Berkeley. It was designed as part of Project Genie and marketed by Scientific Data Systems for the SDS 940 computer system. It was the first commercial time-sharing which allowed general-purpose user programming, including machine language. History In the mid-1960s, most computers used batch processing: one user at a time with no interactivity. A few pioneering systems such as the Atlas Supervisor at the University of Manchester, Compatible Time-Sharing System at MIT, and the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System at Dartmouth College required large expensive machines. Implementation started in 1964 with the arrival of the SDS 930 which was modified slightly, and an operating system was written from scratch. Students who worked on the Berkeley Timesharing System included undergraduates Chuck Thacker and L. Peter Deutsch and doctoral student B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
SDS 940
The SDS 940 was Scientific Data Systems' (SDS) first machine designed to directly support time-sharing. The 940 was based on the SDS 930's 24-bit CPU, with additional circuitry to provide protected memory and virtual memory. It was announced in February 1966 and shipped in April, becoming a major part of Tymshare's expansion during the 1960s. The influential Stanford Research Institute "oN-Line System" (NLS) was demonstrated on the system. This machine was later used to run Community Memory, the first bulletin board system. After SDS was acquired by Xerox in 1969 and became Xerox Data Systems, the SDS 940 was renamed as the XDS 940. History The design was originally created by the University of California, Berkeley as part of their Project Genie that ran between 1964 and 1969. Genie added memory management and controller logic to an existing SDS 930 computer to give it page-mapped virtual memory, which would be heavily copied by other designs. The 940 was simply a commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Stanford Research Institute
SRI International (SRI) is a nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California, United States. It was established in 1946 by trustees of Stanford University to serve as a center of innovation to support economic development in the region. The organization was founded as the Stanford Research Institute. SRI formally separated from Stanford University in 1970 and became known as SRI International in 1977. SRI performs client-sponsored research and development for government agencies, commercial businesses, and private foundations. It also licenses its technologies, forms strategic partnerships, sells products, and creates Research spin-off, spin-off companies. SRI's headquarters are located near the Stanford University campus. SRI's annual revenue in 2014 was approximately $540 million, which tripled from 1998 under the leadership of Curtis Carlson. In 1998, the organization was on the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Jeff Rulifson
Johns Frederick (Jeff) Rulifson (born August 20, 1941) is an American computer scientist. Early life and education Johns Frederick Rulifson was born August 20, 1941, in Bellefontaine, Ohio. His father was Erwin Charles Rulifson and mother was Virginia Helen Johns. Rulifson married Janet Irving on June 8, 1963, and had two children. He received a B.S. in mathematics from the University of Washington in 1966. Rulifson earned a Ph.D. in computer science from Stanford University in 1973. Career Rulifson joined the Augmentation Research Center, at the Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International) in 1966, working on a form of software called “timesharing”. He led the software team that implemented the oN-Line System (NLS), a system that foreshadowed many future developments in modern computing and networking. Specifically, Rulifson developed the command language for the NLS, among other features. His first job was to create the first display-based on the CDC 3100, and the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
CDC 3000
The CDC 3000 series ("thirty-six hundred" or "thirty-one hundred") are a family of mainframe computers from Control Data Corporation (CDC). The first member, the CDC 3600, was a 48-bit system introduced in 1963. The same basic design led to the cut-down CDC 3400 of 1964, and then the 24-bit CDC 3300, 3200 and 3100 introduced between 1964 and 1965. The 3000 series replaced the earlier CDC 1604 and CDC 924 systems. The line was a great success and became CDC's cash cow through the 1960s. The series significantly outsold the much faster and more expensive machines in the CDC 6000 series, but the performance of the 3000's relative to other vendors quickly eroded. The line was phased out of production in the early 1970s in favour of new members of the 6000 series, and then the CDC Cyber series, initially based on the 6600 design but spanning a wide range of performance. Specifications Upper 3000 series The upper 3000 series uses a 48-bit word size. The first 3000 machine to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |