|
N-Arachidonylglycine
''N''-Arachidonylglycine (NAGly) is a carboxylic metabolite of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA). Since it was first synthesized in 1996, NAGly has been a primary focus of the relatively contemporary field of lipidomics due to its wide range of signaling targets in the brain, the immune system and throughout various other bodily systems. In combination with 2‐arachidonoyl glycerol (2‐AG), NAGly has enabled the identification of a family of lipids often referred to as endocannabinoids. Recently, NAGly has been found to bind to G-protein coupled receptor 18 (GPR18), the putative abnormal cannabidiol receptor. NaGly is an endogenous inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and thereby increases the ethanolamide endocannabinoids AEA, oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) levels. NaGly is found throughout the body and research on its explicit functions is ongoing. Biosynthesis and degradation The biosynthesis and degradation of NaGly is not compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR18
''N''-Arachidonyl glycine receptor (NAGly receptor), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 18 (GPR18), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR18'' gene. Along with the other previously orphan receptors GPR55 and GPR119, GPR18 has been found to be a receptor for endogenous lipid neurotransmitters, several of which also bind to cannabinoid receptors. It has been found to be involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure. Research supports the hypothesis that GPR18 is the abnormal cannabidiol receptor and N-arachidonoyl glycine, the endogenous lipid metabolite of anandamide, initiates directed microglial migration in the CNS through activation of GPR18, though recent evidence demonstrates that NAGly was not shown to be a GPR18 agonist in rat sympathetic neurons. Resolvin D2 (RvD2), a member of the specialized proresolving mediators (SPM) class of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites, is an activating ligand for GPR18; RvD2 and its activation of GPR18 contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the central nervous system (including the brain) and peripheral nervous system. The endocannabinoid system is still not fully understood, but may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre- and postnatal development, various activity of immune system, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory, and in mediating the pharmacological effects of cannabis. The ECS plays an important role in multiple aspects of neural functions, including the control of movement and motor coordination, learning and memory, emotion and motivation, addictive-like behavior and pain modulation, among others. Two primary cannabinoid receptors have been identified: CB1, first cloned (or isolated) in 1990; and CB2, cloned in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farnesyl Pyrophosphate
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is the precursor to all sesquiterpenes, which comprises thousands of compounds. These include all sesquiterpenes as well as sterols and carotenoids. It is also used in the synthesis of CoQ (part of the electron transport chain), as well as dehydrodolichol diphosphate (a precursor of dolichol, which transports proteins to the ER lumen for ''N''-glycosylation). Biosynthesis Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (a prenyl transferase) catalyzes sequential condensation reactions of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate with 2 units of 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate: : Pharmacology The above reactions are inhibited by bisphosphonates (used for osteoporosis). Farnesyl pyrophosphate is a selective agonist of TRPV3. Related compounds * Farnesene * Farnesol * Geranyl pyrophosphate *Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
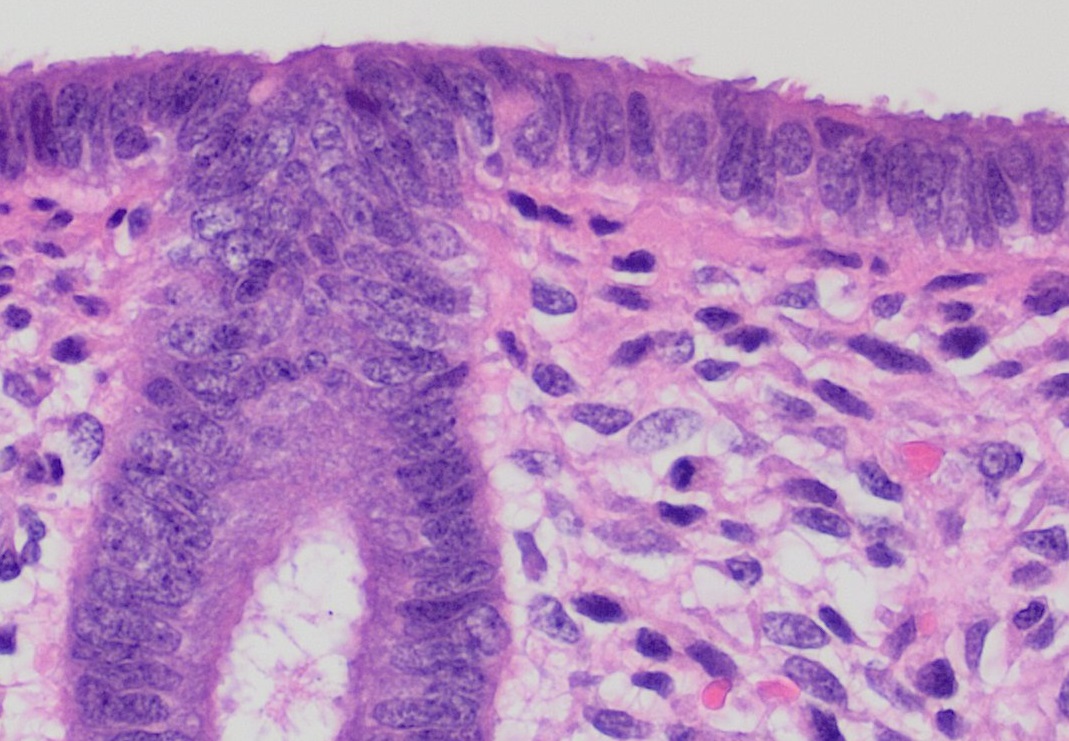
Endometrial
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including other apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil. Medical uses THC, referred to as dronabinol in the pharmaceutical context, is approved in the United States as a capsule or solution to relieve chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia. THC is an active ingredient in nabiximols, a specific extract of ''Cannabis'' that was approved as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom in 2010 as a mouth spray for people with multiple sclerosis to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms. Nabiximols (as Sativex) is available as a prescription drug in Canada. In 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR55
G protein-coupled receptor 55 also known as GPR55 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR55'' gene. GPR55, along with GPR119 and GPR18, have been implicated as novel cannabinoid receptors. History GPR55 was identified and cloned for the first time in 1999. Later it was identified by an in silico screen as a putative cannabinoid receptor because of a similar amino acid sequence in the binding region. Research groups from Glaxo Smith Kline and Astra Zeneca characterized the receptor extensively because it was hoped to be responsible for the blood pressure lowering properties of cannabinoids. GPR55 is indeed activated by endogenous and exogenous cannabinoids such as plant and synthetic cannabinoids but GPR-55 knockout mice generated by a research group from Glaxo Smith Kline showed no altered blood pressure regulation after administration of the cannabidiol-derivative abnormal cannabidiol. Signal cascade GPR55 is coupled to the G-protein G1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEK Cell
Human embryonic kidney 293 cells, also often referred to as HEK 293, HEK-293, 293 cells, are an immortalised cell line derived from HEK cells isolated from a female fetus in the 1970s. The HEK 293 cell line has been widely used in research for decades due to its reliable and fast growth and propensity for transfection. The cell line is used by the biotechnology industry to produce therapeutic proteins and viruses for gene therapy as well as safety testing for a vast array of chemicals. History HEK 293 cells were generated in 1973 by transfection of cultures of normal human embryonic kidney cells with sheared adenovirus 5 DNA in Alex van der Eb's laboratory in Leiden, the Netherlands. The cells were obtained from a single, aborted or miscarried fetus, the precise origin of which is unclear. The cells were cultured by van der Eb; the transfection with adenoviral DNA was performed by Frank Graham, a post-doc in van der Eb's lab. They were published in 1977 after Graham left Leid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the CNS. Microglia originate in the yolk sac under tightly regulated molecular conditions. These cells (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenancethey are constantly scavenging the CNS for senile plaques, plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular pota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperalgesia
Hyperalgesia ( or ; ''hyper'' from Greek ὑπέρ (''huper'') 'over' + ''-algesia'' from Greek ἄλγος (algos) 'pain') is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection. Types Hyperalgesia can be experienced in focal, discrete areas, or as a more diffuse, body-wide form. Conditioning studies have established that it is possible to experience a learned hyperalgesia of the latter, diffuse form. The focal form is typically associated with injury, and is divided into two subtypes: * ''Primary hyperalgesia'' describes pain sensitivity that occurs directly in the damaged tissues. * ''Secondary hyperalgesia'' describes pain sensitivity that occurs in surrounding undamaged ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secretion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |